
Anik Mountain is the highest peak of Primorsky Krai, Russia. It is located in the north of Primorsky Krai on the border with Khabarovsk Krai. Anik Mountain is third highest peak of the Sikhote-Alin mountain system.

Krasnoarmeysky District is an administrative and municipal district (raion), one of the twenty-two in Primorsky Krai, Russia. It is located in the center of the krai and borders with Pozharsky District in the northwest and north, Terneysky District in the east, the territory of Dalnegorsk Town Under Krai Jurisdiction in the south, and with Dalnerechensky District in the southwest and west. The area of the district is 20,603.4 square kilometers (7,955.0 sq mi). Its administrative center is the rural locality of Novopokrovka. Population: 18,537 (2010 Census); 20,820 (2002 Census); 27,555 (1989 Census). The population of Novopokrovka accounts for 19.7% of the district's total population.

An iron meteorite fell on the Sikhote-Alin Mountains, in southeastern Russia, in 1947. Though large iron meteorite falls had been witnessed previously and fragments recovered, never before in recorded history had a fall of this magnitude been observed. An estimated 70 tonnes of material survived the fiery passage through the atmosphere and reached the Earth.

Anyuy River, also known as Onyuy River (Онюй) or Dondon River (Дондон) is a river in the Khabarovsk Krai in Russia. It is a right tributary of the Amur River. It originates on slope of Tordoki Yani in the Sikhote-Alin mountain range, and falls into the Amur between Khabarovsk and Komsomolsk-on-Amur.

Mount Livadiyskaya, unofficially known as Mount Pedan (Педа́н) or Mount Pidan (Пида́н) is one of the highest peaks in Shkotovsky District of Primorsky Krai, Russia.
Akhtenskite is a manganese oxide mineral with the chemical formula of MnO2 (or: ε-Mn4+O2) that was named after the Akhtensk deposit in Russia, where it was first discovered and noted in 1979. It can be found in the Akhtensk brown ironstone deposit, in the southern Ural Mountains, on Mt. Zarod, on the Sikhote-Alin Mountains, and in the Primorskiy Krai, all in Russia.

Sikhote-Alin Nature Reserve is a biosphere reserve in Primorsky Krai. It is an important reserve for the endangered Siberian tiger.

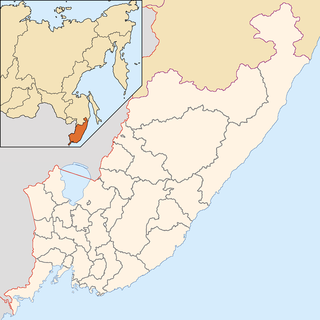
The Arsenyevka River is a left tributary of the Ussuri River in Anuchinsky and Yakovlevsky Districts of Primorsky Krai, Russia.

Khor River is a river in Khabarovsk Krai. It is a right tributary of the Ussuri River.
Ko is a peak in the southern part of Khabarovsk Krai near the border of Primorsky Krai.
The temperate rainforests of the Russian Far East are found within the Russian states of Primorsky Krai and Khabarovski Krai and contains the Sikhote-Alin mountain range. Found within the Russian Federation, this area is one of the most productive and diverse forests in the world and also contains one of the highest endangered species densities on Earth. While most temperate rainforests around the world have retained only a fraction of their historical range, these forests maintain the majority of their former range and almost all of their historical biodiversity. The region is also notable for having what has become the last remaining large tract of viable habitat for the critically endangered Amur tiger and Amur leopard.
Manoma is a river in Russia, Khabarovsk Krai. It is the main tributary of Anyuy River. It flows between Khabarovsk and Komsomolsk-on-Amur. Length - 198 kilometres (123 mi). It originates on the slopes of Sikhote-Alin mountain range. In its upper reaches it is a typical mountain river, downstream it flows through flat fields.

Anyuysky National Park, covers the basin of the Anyuy River, on the west slope of the Central Sikhote-Alin Mountain range in the Russian Far East. The Anyuy flows west into the Amur River, the main river of the region, as it flows northeast into the Sea of Okhotsk. The park is important because it creates an ecological corridor from the low floodplain of the Amur, to the high forested mountains of the Sikhote-Alin. The park is in the Nanaysky District in Khabarovsk Krai, about 50 miles downstream of the city of Khabarovsk. The area is remote, with few towns and sparse population. The area has historically depended on salmon fishing, logging, and hunting. The local indigenous people are the Nanai people, representing about a quarter of the nearby settlements.

Udegeyskaya Legenda National Park covers the richest coniferous-deciduous forest on the western slope of the Central Sikhote-Alin mountains of the Russian Far East. The Sikhote-Alin is a range that runs north-south through Primorsky Krai. The park is designed to protect west-slope river valley habitat, and to support the remnant of the indigenous Udege people. The area is known for abundant fishing and boating on the streams and rivers. It is also a refuge for the endangered Amur tiger. The park is roughly midway between the city of Vladivostok, and Khabarovsk. The relatively warm waters of the Sea of Japan are to the east, the Korean peninsula to the south, and China to the West.

Bikin National Park was created on November 3, 2015 to protect the largest remaining old-growth mixed forest in the Northern Hemisphere, as well as the territory of 10% of all Amur tigers in the wild. The park was also created for the purpose of protecting the forest culture of the 600 indigenous inhabitants of the Bikin River Basin living in the territory - Udeghes and Nanai people. Because of its size for pristine forest, and its characterization as a "temperate rain forest", it has an important status as a center for biodiversity of both plants and animals.The park sits in the administrative region of Pozharsky District, in Primorsky Krai in the Russian Far East on the west slope of the Sikhote-Alin mountains. The Bikin River Valley is also a World Heritage site.

Botcha Nature Reserve is a Russian 'zapovednik'. It is the northernmost reserve inhabited by the endangered Amur Tiger. The reserve is located in the north-eastern part of the Sikhote-Alin mountain range; it includes the Botchi River basin on its eastern slopes. The reserve is about 120 km south of the port city of Sovetskaya Gavan in the Sovetsko-Gavansky District of Khabarovsk Krai. The reserve was created in 1994, and covers an area of 267,380 ha (1,032.4 sq mi).

Ussurisky Nature Reserve is a Russian 'zapovednik' that protects one of the remaining virgin mixed deciduous-conifer forests in the Primorsky (Maritime) region of the Russian Far East. The mountainous terrain is located on a southern spur of the Sikhote-Alin Mountains, in the upper reaches of the Komarovka River, about 50 km northeast of the city of Vladivostok. The reserve is named after Vladimir L. Komarov, an important early botanist and early explorer of the Primorsky region. The Ussursisky Reserve is situated in the Shkotovsky District of Primorsky Krai.

The Ussuri broadleaf and mixed forests ecoregion covers a mountainous areas above the lower Amur River and Ussuri River in Primorsky Krai and Khabarovsk Krai in the Russian Far East. The ecoregion is in the Palearctic ecozone, with a Humid Continental climate. It covers 187,357 km2 (72,339 sq mi).
















