
Cádiz is a province of southern Spain, in the southwestern part of the autonomous community of Andalusia. It is the southernmost part of mainland Spain, as well as the southernmost part of continental Europe.

Tarifa is a small town in the province of Cádiz, Andalusia, on the southernmost coast of mainland Spain. It is primarily known as one of the world's most popular destinations for wind sports. The town is located on the Costa de la Luz and across the Strait of Gibraltar facing Morocco.
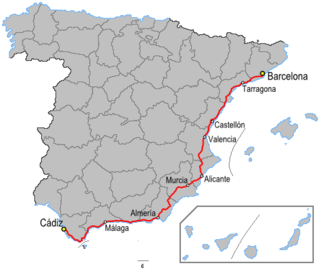
The N-340 is a major highway in Spain. It is over 1,000 km long starting south of Barcelona and running predominantly along the coast to Chiclana de la Frontera and the N-IV to Cádiz. In many places the road has now been by-passed by the Autovía A-7 and Autopista AP-7.

Canale-di-Verde is a commune in the Haute-Corse department of France on the island of Corsica.

The Tower of Punta d'Arcu is a ruined Genoese tower located in the commune of Borgo, Haute-Corse on the east coast of Corsica. Only part of the base survives.

The Tower of Sant'Amanza is a ruined Genoese tower located in the commune of Bonifacio on the south east coast of the Corsica. The tower sits at a height of 125 metres (410 ft) on the Punta di u Capicciolu headland. Only the round base survives.

The Tower of Spanu is a ruined Genoese tower located in the commune of Lumio on the west coast of the Corsica. It sits on the Punta Spano headland at a height of 25 metres (82 ft) above the sea. Only the lower portion of the tower survives.

The Castle of Jimena de la Frontera is a castle located in Jimena de la Frontera, Spain. It was declared Bien de Interés Cultural in 1931.

Torre del Almirante is a tower located in Algeciras, Spain. It was declared Bien de Interés Cultural in 1985.

Cala Arenas is a beach situated near the city of Algeciras in Spain, within the El Estrecho Natural Park. It is located at the southern end of the Bay of Gibraltar and faces the Strait of Gibraltar. It measures about 400 metres (1,300 ft) long by about 30 metres (98 ft) deep. The beach is somewhat difficult to access, but can be reached via coastal paths from Punta Carnero and Punta del Fraile. It consists of a series of three small coves of similar appearance, with beaches of rocks and small stones. Both the terrestrial and marine environment of the area lies within the natural park. Its surroundings are largely undisturbed by human activity; the nearest settlement is the coastal community of Getares, a small outlying development of the city of Algeciras located about 1 km to the north. The beach is framed by cliffs and the Isla de las Palomas lies a short distance offshore.

Fuerte de Isla Verde was a military installation formerly located in Algeciras, Spain. It occupied the Isla Verde, which gave its name to the city as a whole. The elongated island, which stood a short distance offshore of the city's old town, was already the site of an artillery battery in 1720. In 1734 the fort was constructed on the island to the plans of the military engineer Juan de Subreville. Further remodeling took place in 1745 under Lorenzo de Solís. The installation, which followed the roughly triangular shape of the island, was initially equipped with three batteries. These were:

The Kursaal of Algeciras is a building in the Paseo del Rio de la Miel of Algeciras, Spain. It is the work of artist Guillermo Pérez Villalta and architect Enrique Salvo. Also known as the Kursaal Congress Centre or Rio de la Miel, it was opened in 2007 after a decade of work. The building was designed in the late nineties as the seat of the Chamber of Commerce of Gibraltar but the work was halted until being rescued by the city council.

The Torre de los Adalides was a rectangular medieval look-out tower of Islamic design located in the vicinity of Algeciras, Spain. It was situated roughly 1 kilometre (0.62 mi) from the coast on a hill some 100 metres (330 ft) above sea level in the area which is now covered by the city's northern suburbs. The tower was demolished by the Spaniards during the Spanish–American War as they thought the Americans might use it as a base of their own. The ruins of the tower are within military limits and cannot be approached without a formal permit.
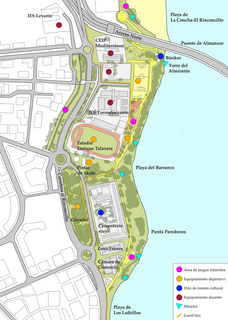
Paseo Cornisa is a park in Algeciras, Spain. It was inaugurated in May 2007. It stretches for just over a kilometre between Punta del Cementerio and Punta del Almirante in the north of the city near the old cemetery and parallel to the Playa del Barranco and Playa de El Rinconcillo. The park has an area of over 20,000 square metres (220,000 sq ft). Within the park is the Torre del Almirante or Admiral's Tower which dates from the 14th century.

Playa de El Chinarral is a beach in the municipality of Algeciras, southeastern Spain. It overlooks the Bay of Algeciras and the tip of the rock of Gibraltar. It is approximately 250 metres in length and 40 metres wide on average. It is located between Punta de San Garcia and El Rodeo, south of the city.
Hotel AC Algeciras is a hotel on Carretera del Rinconcillo in southern Algeciras, in the Province of Cádiz in southeastern Spain. It is located in close proximity to the Playa de Los Ladrillos. It is located in a modern, angular-looking, dark grey building, and is one of the newest and modern hotels in the city, built in 2005–06, operated by AC Hotels and Marriott Hotels. Frommer's said of it "The most contemporary hotel in town, this AC stands in front of the Puerto Marítimo, only 1km from the city center. The rooms are modern minimalist yet very comfortable, and the hotel is well maintained."

Fuerte de San García was a fort in Algeciras, Spain, It was built in the 1730s and destroyed in 1811 to deny it to the French. Today all that remains are the foundation and base ruins, in the Parque del Centenario, but it is a registered Bien de Interés Cultural landmark

Torre del Rocadillo is a historic ruined tower, located about a mile to the west of Puente Mayorga in the municipality of San Roque in the Province of Cádiz, Andalusia, Spain. It was constructed in the 16th century.

The ruins of Fuerte de San Diego are the remains of a castle located in Algeciras, Spain. The castle was built in 1730 following the Capture of Gibraltar in 1704.

Fuerte de Punta Carnero was a fort near Algeciras in Spain. It was built before 1735 and was destroyed in 1810 to deny it to the French. Today all that remains are ruined foundations which are a registered Bien de Interés Cultural landmark.


























