
Treponema pallidum, formerly known as Spirochaeta pallida, is a spirochaete bacterium with various subspecies that cause the diseases syphilis, bejel, and yaws. It is transmitted only among humans. It is a helically coiled microorganism usually 6–15 μm long and 0.1–0.2 μm wide. T. pallidum's lack of either a tricarboxylic acid cycle or oxidative phosphorylation results in minimal metabolic activity. The treponemes have a cytoplasmic and an outer membrane. Using light microscopy, treponemes are visible only by using dark field illumination. Treponema pallidum consists of three subspecies, T. p. pallidum, T. p. endemicum, and T. p. pertenue, each of which has a distinct associated disease.

A spirochaete or spirochete is a member of the phylum Spirochaetota, which contains distinctive diderm (double-membrane) gram-negative bacteria, most of which have long, helically coiled cells. Spirochaetes are chemoheterotrophic in nature, with lengths between 3 and 500 μm and diameters around 0.09 to at least 3 μm.

Treponema is a genus of spiral-shaped bacteria. The major treponeme species of human pathogens is Treponema pallidum, whose subspecies are responsible for diseases such as syphilis, bejel, and yaws. Treponema carateum is the cause of pinta. Treponema paraluiscuniculi is associated with syphilis in rabbits. Treponema succinifaciens has been found in the gut microbiome of traditional rural human populations.
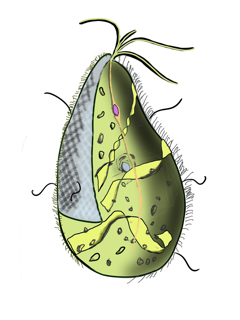
Mixotricha paradoxa is a species of protozoan that lives inside the gut of the Australian termite species Mastotermes darwiniensis.
Neocallimastigomycota is a phylum containing anaerobic fungi, which are symbionts found in the digestive tracts of larger herbivores. Anaerobic fungi were originally placed within phylum Chytridiomycota, within Order Neocallimastigales but later raised to phylum level, a decision upheld by later phylogenetic reconstructions. It encompasses only one family.
Fibrobacter succinogenes is a cellulolytic bacterium species in the genus Fibrobacter. It is present in the rumen of cattle. F. succinogenes is a gram negative, rod-shaped, obligate anaerobe that is a major contributor to cellulose digestion. Since its discovery in the 1950s, it has been studied for its role in herbivore digestion and cellulose fermentation, which can be utilized in biofuel production.
Treponema denticola is a Gram-negative, obligate anaerobic, motile and highly proteolytic spirochete bacterium. It is one of four species of oral spirochetes to be reliably cultured, the others being Treponema pectinovorum, Treponema socranskii and Treponema vincentii. T. denticola dwells in a complex and diverse microbial community within the oral cavity and is highly specialized to survive in this environment. T. denticola is associated with the incidence and severity of human periodontal disease. Treponema denticola is one of three bacteria that form the Red Complex, the other two being Porphyromonas gingivalis and Tannerella forsythia. Together they form the major virulent pathogens that cause chronic periodontitis. Having elevated T. denticola levels in the mouth is considered one of the main etiological agents of periodontitis. T. denticola is related to the syphilis-causing obligate human pathogen, Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum. It has also been isolated from women with bacterial vaginosis.
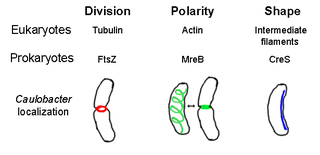
The prokaryotic cytoskeleton is the collective name for all structural filaments in prokaryotes. It was once thought that prokaryotic cells did not possess cytoskeletons, but advances in visualization technology and structure determination led to the discovery of filaments in these cells in the early 1990s. Not only have analogues for all major cytoskeletal proteins in eukaryotes been found in prokaryotes, cytoskeletal proteins with no known eukaryotic homologues have also been discovered. Cytoskeletal elements play essential roles in cell division, protection, shape determination, and polarity determination in various prokaryotes.
Brachyspira pilosicoli is a gram-negative, anaerobic, host-associated spirochete that colonizes the intestinal tract of animals and humans. It appears as a characteristic "false brush border" due to its end-on attachment to enterocytes of the colon where it interferes with intestinal absorption. B. pilosicoli is unique from other Brachyspira species because it colonizes a variety of domestic animals including pigs, chickens, dogs, wild birds, rodents, and humans. It is the causative agent of intestinal spirochetosis in pigs, chickens and humans. In particular, B. pilosicoli has been described as an important colonic pathogen of pigs and chickens, causing colitis and diarrhea resulting in depressed rates of growth and impaired production on farms where infections with B. pilosicoli may be endemic. Bacterial attachment disrupts the colonic enterocytes and associated villi, causing the symptoms characteristic of intestinal spirochetosis. Additionally, B. pilosicoli is associated with clinical disease in human infections where it has implications for public health.
There are several models of the Branching order of bacterial phyla, one of these was proposed in 1987 paper by Carl Woese.
Brachyspira innocens is a species of bacteria. It is thought to be a commensal bacterium.
Treponema primitia is a bacterium, the first termite gut spirochete to be isolated, together with Treponema azotonutricium.
Neocallimastix patriciarum is a species of fungus that lives in the rumen of sheep and other ruminant species. N. patriciarum is an obligate anaerobe and is an important component of the microbial population within the rumen. Only one of a few rumen fungi, this species is interesting and unique within the fungal world. Originally thought to be a flagellate protists, species within the phylum Neocallimastigomycota were first recognized as a fungi by Colin Orpin in 1975 when he demonstrated that they had cell walls of chitin
Spiral bacteria, bacteria of spiral (helical) shape, form the third major morphological category of prokaryotes along with the rod-shaped bacilli and round cocci. Spiral bacteria can be subclassified by the number of twists per cell, cell thickness, cell flexibility, and motility. The two types of spiral cells are spirillum and spirochete, with spirillum being rigid with external flagella, and spirochetes being with internal flagella.
Treponema socranskii was isolated from gum swabs of people with periodontitis and clinically-induced periodontitis. It is a motile, helically coiled, obligate anaerobe that grows best at 37 °C, and is a novel member of its genus because of its ability to ferment molecules that other Treponema species cannot. T. socranskii’s growth is positively correlated with gingival inflammation, which indicates that it is a leading cause of gingivitis and periodontitis.
Spirochaeta thermophila is a fairly recently discovered free-living, anaerobic, spirochaete that seems to be the most thermophilic of the Spirochaetales order. The type species was discovered in 1992 in Kuril islands, Russia and described in Aksenova, et al. It has been isolated in the sediments and water columns of brackish aquatic habitats of various ponds, lakes, rivers, and oceans. This organism is identified as a new species based on its unique ability to degrade cellulose, xylan, and other α- and β-linked sugars and use them as the sole carbon source by encoding many glycoside hydrolases. It is presumed to secrete cellulases to break down plant-matter around it but there has been little work on the characterization of the enzymes responsible for this.
Interspecies hydrogen transfer (IHT) is a form of interspecies electron transfer. It is a syntrophic process by which H2 is transferred from one organism to another, particularly in the rumen and other anaerobic environments.
Methanogens are a group of microorganisms that produce methane as a byproduct of their metabolism. They play an important role in the digestive system of ruminants. The digestive tract of ruminants contains four major parts: rumen, reticulum, omasum and abomasum. The food with saliva first passes to the rumen for breaking into smaller particles and then moves to the reticulum, where the food is broken into further smaller particles. Any indigestible particles are sent back to the rumen for rechewing. The majority of anaerobic microbes assisting the cellulose breakdown occupy the rumen and initiate the fermentation process. The animal absorbs the fatty acids, vitamins and nutrient content on passing the partially digested food from the rumen to the omasum. This decreases the pH level and initiates the release of enzymes for further breakdown of the food which later passes to the abomasum to absorb remaining nutrients before excretion. This process takes about 9–12 hours.

Anaeromyces robustus is a fungal microorganism that lives in the gut rumen of many ruminant herbivores such as cows and sheep. Previously thought to be protozoa from their flagellated zoospores, they are biomass degraders and help the animal by breaking down carbohydrates and plant materials from the food the animal ingests. This fungus, therefore, is anaerobic and lives without oxygen. Gut fungi are dramatically outnumbered by other organisms in the microbiome; however, they are important members of the gut microbiome in ruminants and hind-gut fermenters and play a key role in digestion.
Robert George Everitt Murray was an English-Canadian bacteriologist. He is known for his research on bacterial structure and pathology, as well as bacterial taxonomy.




