
The approximately 450 Oceanic languages are a branch of the Austronesian languages. The area occupied by speakers of these languages includes Polynesia, as well as much of Melanesia and Micronesia. Though covering a vast area, Oceanic languages are spoken by only two million people. The largest individual Oceanic languages are Eastern Fijian with over 600,000 speakers, and Samoan with an estimated 400,000 speakers. The Gilbertese (Kiribati), Tongan, Tahitian, Māori, Western Fijian and Tolai languages each have over 100,000 speakers. The common ancestor which is reconstructed for this group of languages is called Proto-Oceanic.
The nine South Vanuatu languages form a family of the Southern Oceanic languages, spoken in Tafea Province of Vanuatu.
The Huon Gulf languages are Western Oceanic languages spoken primarily in Morobe Province of Papua New Guinea. They may form a group of the North New Guinea languages, perhaps within the Ngero–Vitiaz branch of that family.
Proto-Polynesian is the hypothetical proto-language from which all the modern Polynesian languages descend. It is a daughter language of the Proto-Austronesian language. Historical linguists have reconstructed the language using the comparative method, in much the same manner as with Proto-Indo-European and Proto-Uralic. This same method has also been used to support the archaeological and ethnographic evidence which indicates that the ancestral homeland of the people who spoke Proto-Polynesian was in the vicinity of Tonga, Samoa, and nearby islands.

The Southern Oceanic languages are a linkage of Oceanic languages spoken in Vanuatu and New Caledonia. It was proposed by Lynch, Ross, and Crowley in 2002 and supported by later studies. They consider it to be a linkage rather than a language group with a clearly defined internal nested structure.

The South Bougainville or East Bougainville languages are a small language family spoken on the island of Bougainville in Papua New Guinea. They were classified as East Papuan languages by Stephen Wurm, but this does not now seem tenable, and was abandoned in Ethnologue (2009).
Andrew Kenneth Pawley, FRSNZ, FAHA, is Emeritus Professor at the School of Culture, History & Language of the College of Asia & the Pacific at the Australian National University.
Proto-Oceanic is a proto-language that historical linguists since Otto Dempwolff have reconstructed as the hypothetical common ancestor of the Oceanic subgroup of the Austronesian language family. Proto-Oceanic is a descendant of the Proto-Austronesian language (PAN), the common ancestor of the Austronesian languages.
Proto-Austronesian is a proto-language. It is the reconstructed ancestor of the Austronesian languages, one of the world's major language families. Proto-Austronesian is assumed to have begun to diversify c. 3,500–4,000 BCE on Taiwan.
The Reef Islands – Santa Cruz languages are a branch of the Oceanic languages comprising the languages of the Santa Cruz Islands and Reef Islands:
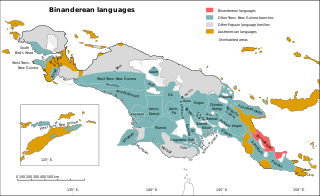
The Greater Binanderean or Guhu-Oro languages are a language family spoken along the northeast coast of the Papuan Peninsula – the "Bird's Tail" of New Guinea – and appear to be a recent expansion from the north. They were classified as a branch of the Trans–New Guinea languages by Stephen Wurm (1975) and Malcolm Ross (2005), but removed by Timothy Usher (2020). The Binandere family proper is transparently valid; Ross connected it to the Guhu-Semane isolate based on pronominal evidence, and this has been confirmed by Smallhorn (2011). Proto-Binanderean has been reconstructed in Smallhorn (2011).
The Gorontalo–Mongondow languages are a group of Austronesian languages spoken in northern Sulawesi, Indonesia.

The Tsouic languages are three Formosan languages, Tsou proper and the Southern languages Kanakanavu and Saaroa. The Southern Tsouic languages of Kanakanavu and Saaroa have the smallest phonemic inventories out of all the Formosan languages, with each language having only 13 consonants and 4 vowels. These two languages are highly endangered, as many Southern Tsouic speakers are shifting to Bunun and Mandarin Chinese.
Proto-Malayo-Polynesian (PMP) is the reconstructed ancestor of the Malayo-Polynesian languages, which is by far the largest branch of the Austronesian language family. Proto-Malayo-Polynesian is ancestral to all Austronesian languages spoken outside Taiwan, as well as the Yami language on Taiwan's Orchid Island. The first systematic reconstruction of Proto-Austronesian ("Uraustronesisch") by Otto Dempwolff was based on evidence from languages outside of Taiwan, and was therefore actually the first reconstruction of what is now known as Proto-Malayo-Polynesian.
Parartocarpus venenosa is a tree species in the family Moraceae.

Heliconia indica is a species of plant in the family Heliconiaceae. It is found in Maluku and the southwest Pacific.
Semecarpus forstenii is a species of tree in the family Anacardiaceae. It is found in Indonesia, Papua New Guinea, and the Solomon Islands. The tree's sap is poisonous.
Proto-Torres-Banks is the reconstructed ancestor of the seventeen languages of the Torres and Banks Islands of Vanuatu. Like all indigenous languages of Vanuatu, it belongs to the Oceanic branch of the Austronesian languages.
Proto-Temotu is the reconstructed ancestor of the Temotu languages of Temotu Province, Solomon Islands. It belongs to the Oceanic branch of the Austronesian languages.
Proto-Micronesian is the reconstructed ancestor of the Micronesian languages. It belongs to the Oceanic branch of the Austronesian languages.



