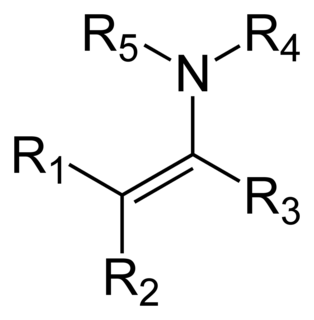
An enamine is an unsaturated compound derived by the condensation of an aldehyde or ketone with a secondary amine. Enamines are versatile intermediates.

A protecting group or protective group is introduced into a molecule by chemical modification of a functional group to obtain chemoselectivity in a subsequent chemical reaction. It plays an important role in multistep organic synthesis.
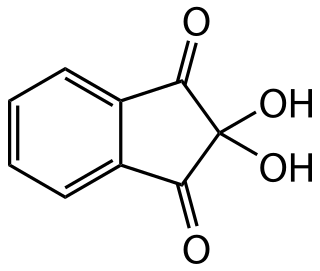
Ninhydrin (2,2-dihydroxyindane-1,3-dione) is a chemical used to detect ammonia or primary and secondary amines. When reacting with these free amines, a deep blue or purple color known as Ruhemann's purple is produced. Ninhydrin is most commonly used to detect fingerprints, as the terminal amines of lysine residues in peptides and proteins sloughed off in fingerprints react with ninhydrin. It is a white solid which is soluble in ethanol and acetone at room temperature. Ninhydrin can be considered as the hydrate of indane-1,2,3-trione.

In organic chemistry, peptide synthesis is the production of peptides, compounds where multiple amino acids are linked via amide bonds, also known as peptide bonds. Peptides are chemically synthesized by the condensation reaction of the carboxyl group of one amino acid to the amino group of another. Protecting group strategies are usually necessary to prevent undesirable side reactions with the various amino acid side chains. Chemical peptide synthesis most commonly starts at the carboxyl end of the peptide (C-terminus), and proceeds toward the amino-terminus (N-terminus). Protein biosynthesis in living organisms occurs in the opposite direction.
In chemistry, solid-phase synthesis is a method in which molecules are covalently bound on a solid support material and synthesised step-by-step in a single reaction vessel utilising selective protecting group chemistry. Benefits compared with normal synthesis in a liquid state include:

A trimethylsilyl group (abbreviated TMS) is a functional group in organic chemistry. This group consists of three methyl groups bonded to a silicon atom [−Si(CH3)3], which is in turn bonded to the rest of a molecule. This structural group is characterized by chemical inertness and a large molecular volume, which makes it useful in a number of applications.

Benzyl chloroformate is the benzyl ester of chloroformic acid. Also known as benzyl chlorocarbonate it is an oily colorless liquid although impure samples appear yellow. It is also known for its pungent odor. In contact with water it degrades.
In organic chemistry a methylthiomethyl (MTM) ether is a protective group for hydroxyl groups. Hydroxyl groups are present in many chemical compounds and they must be protected during oxidation, acylation, halogenation, dehydration and other reactions to which they are susceptible.
Silyl ethers are a group of chemical compounds which contain a silicon atom covalently bonded to an alkoxy group. The general structure is R1R2R3Si−O−R4 where R4 is an alkyl group or an aryl group. Silyl ethers are usually used as protecting groups for alcohols in organic synthesis. Since R1R2R3 can be combinations of differing groups which can be varied in order to provide a number of silyl ethers, this group of chemical compounds provides a wide spectrum of selectivity for protecting group chemistry. Common silyl ethers are: trimethylsilyl (TMS), tert-butyldiphenylsilyl (TBDPS), tert-butyldimethylsilyl (TBS/TBDMS) and triisopropylsilyl (TIPS). They are particularly useful because they can be installed and removed very selectively under mild conditions.
Dioxolane is a heterocyclic acetal with the chemical formula (CH2)2O2CH2. It is related to tetrahydrofuran by interchange of one oxygen for a CH2 group. The corresponding saturated 6-membered C4O2 rings are called dioxanes. The isomeric 1,2-dioxolane (wherein the two oxygen centers are adjacent) is a peroxide. 1,3-Dioxolane is used as a solvent and as a comonomer in polyacetals.

Di-tert-butyl dicarbonate is a reagent widely used in organic synthesis. Since this compound can be regarded formally as the acid anhydride derived from a tert-butoxycarbonyl (Boc) group, it is commonly referred to as "Boc anhydride." This pyrocarbonate reacts with amines to give N-tert-butoxycarbonyl or so-called Boc derivatives. These carbamate derivatives do not behave as amines, which allows certain subsequent transformations to occur that would be incompatible with the amine functional group. The Boc group can later be removed from the amine using moderately strong acids. Thus, Boc serves as a protective group, for instance in solid phase peptide synthesis. Boc-protected amines are unreactive to most bases and nucleophiles, allowing for the use of the fluorenylmethyloxycarbonyl group (Fmoc) as an orthogonal protecting group.

The Holton Taxol total synthesis, published by Robert A. Holton and his group at Florida State University in 1994 was the first total synthesis of Taxol.

The tert-butyloxycarbonyl protecting group or tert-butoxycarbonyl protecting group is a protecting group used in organic synthesis.
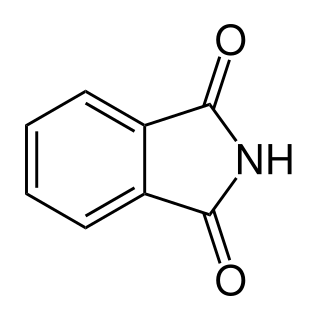
Phthalimide is the organic compound with the formula C6H4(CO)2NH. It is the imide derivative of phthalic anhydride. It is a sublimable white solid that is slightly soluble in water but more so upon addition of base. It is used as a precursor to other organic compounds as a masked source of ammonia.
Oligonucleotide synthesis is the chemical synthesis of relatively short fragments of nucleic acids with defined chemical structure (sequence). The technique is extremely useful in current laboratory practice because it provides a rapid and inexpensive access to custom-made oligonucleotides of the desired sequence. Whereas enzymes synthesize DNA and RNA only in a 5' to 3' direction, chemical oligonucleotide synthesis does not have this limitation, although it is most often carried out in the opposite, 3' to 5' direction. Currently, the process is implemented as solid-phase synthesis using phosphoramidite method and phosphoramidite building blocks derived from protected 2'-deoxynucleosides, ribonucleosides, or chemically modified nucleosides, e.g. LNA or BNA.

The Kuwajima Taxol total synthesis by the group of Isao Kuwajima of the Tokyo Institute of Technology is one of several efforts in taxol total synthesis published in the 1990s. The total synthesis of Taxol is considered a landmark in organic synthesis.
Glycopeptides are peptides that contain carbohydrate moieties (glycans) covalently attached to the side chains of the amino acid residues that constitute the peptide.
2,5-Diketopiperazine, also known as piperazine-2,5-dione and as the cyclodipeptide cyclo(Gly-Gly), is an organic compound and the smallest cyclic dipeptide that consists of a six-membered ring containing two amide linkages where the two nitrogen atoms and the two carbonyls are at opposite positions in the ring. It was first synthesized by Curtius and Gloebel in 1888 and was the first compound containing a peptide bond to be studied by X-ray crystallography in 1938. It occurs in cocoa and bread and has a metallic and bitter taste.
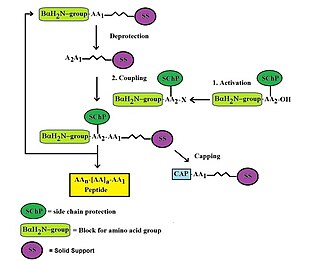
Custom peptide synthesis is the commercial production of peptides for use in biochemistry, biology, biotechnology, pharmacology and molecular medicine. Custom peptide synthesis provides synthetic peptides as valuable tools to biomedical laboratories. Synthetic oligopeptides are used extensively in research for structure-function analysis, for the development of binding assays, the study of receptor agonist/antagonists or as immunogens for the production of specific antibodies. Generally, peptides are synthesized by coupling the carboxyl group or C-terminus of one amino acid to the amino group or N-terminus of another using automated solid phase peptide synthesis chemistries. However, liquid phase synthesis may also be used for specific needs.
Amino acid N-carboxyanhydrides, also called Leuchs' anhydrides, are reactive derivatives of amino acids. They are classified as N-carboxyanhydrides or NCAs. Typically these compounds are derived from amino acids by treatment with triphosgene. They are white solids, prone to polymerization upon treatment with nucleophiles.














