Cyclopentadiene is an organic compound with the formula C5H6. It is often abbreviated CpH because the cyclopentadienyl anion is abbreviated Cp−.
Cubane is a synthetic hydrocarbon compound with the formula C8H8, and that consists of eight carbon atoms arranged at the corners of a cube, with one hydrogen atom attached to each carbon atom. A solid crystalline substance, cubane is one of the Platonic hydrocarbons and a member of the prismanes. It was first synthesized in 1964 by Philip Eaton and Thomas Cole. Before this work, Eaton believed that cubane would be impossible to synthesize due to the "required 90 degree bond angles". The cubic shape requires the carbon atoms to adopt an unusually sharp 90° bonding angle, which would be highly strained as compared to the 109.45° angle of a tetrahedral carbon. Once formed, cubane is quite kinetically stable, due to a lack of readily available decomposition paths. It is the simplest hydrocarbon with octahedral symmetry.
In organic chemistry, arynes and benzynes are a class of highly reactive chemical species derived from an aromatic ring by removal of two substituents. Arynes are examples of didehydroarenes, although 1,3- and 1,4-didehydroarenes are also known. Arynes are examples of alkynes under high strain.
In organic chemistry, hydrocyanation is a process for conversion of alkenes to nitriles. The reaction involves the addition of hydrogen cyanide and requires a catalyst. This conversion is conducted on an industrial scale for the production of precursors to nylon.
An alkyne trimerisation is a [2+2+2] cycloaddition reaction in which three alkyne units react to form a benzene ring. The reaction requires a metal catalyst. The process is of historic interest as well as being applicable to organic synthesis. Being a cycloaddition reaction, it has high atom economy. Many variations have been developed, including cyclisation of mixtures of alkynes and alkenes as well as alkynes and nitriles.

1,3,5,7-Cyclooctatetraene (COT) is an unsaturated derivative of cyclooctane, with the formula C8H8. It is also known as [8]annulene. This polyunsaturated hydrocarbon is a colorless to light yellow flammable liquid at room temperature. Because of its stoichiometric relationship to benzene, COT has been the subject of much research and some controversy.
A dendralene is a discrete acyclic cross-conjugated polyene. The simplest dendralene is buta-1,3-diene (1) or [2]dendralene followed by [3]dendralene (2), [4]dendralene (3) and [5]dendralene (4) and so forth. [2]dendralene (butadiene) is the only one not cross-conjugated.

The Masamune-Bergman cyclization or Masamune-Bergman reaction or Masamune-Bergman cycloaromatization is an organic reaction and more specifically a rearrangement reaction taking place when an enediyne is heated in presence of a suitable hydrogen donor. It is the most famous and well-studied member of the general class of cycloaromatization reactions. It is named for Japanese-American chemist Satoru Masamune and American chemist Robert G. Bergman. The reaction product is a derivative of benzene.
Cycloocta-1,5-diene is a cyclic hydrocarbon with the chemical formula C8H12, specifically [−(CH2)2−CH=CH−]2.

Titanocene dichloride is the organotitanium compound with the formula (η5-C5H5)2TiCl2, commonly abbreviated as Cp2TiCl2. This metallocene is a common reagent in organometallic and organic synthesis. It exists as a bright red solid that slowly hydrolyzes in air. It shows antitumour activity and was the first non-platinum complex to undergo clinical trials as a chemotherapy drug.
In organic chemistry, carbon–hydrogen bond functionalization is a type of organic reaction in which a carbon–hydrogen bond is cleaved and replaced with a C−X bond. The term usually implies that a transition metal is involved in the C−H cleavage process. Reactions classified by the term typically involve the hydrocarbon first to react with a metal catalyst to create an organometallic complex in which the hydrocarbon is coordinated to the inner-sphere of a metal, either via an intermediate "alkane or arene complex" or as a transition state leading to a "M−C" intermediate. The intermediate of this first step can then undergo subsequent reactions to produce the functionalized product. Important to this definition is the requirement that during the C−H cleavage event, the hydrocarbyl species remains associated in the inner-sphere and under the influence of "M".
Acetone cyanohydrin (ACH) is an organic compound used in the production of methyl methacrylate, the monomer of the transparent plastic polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), also known as acrylic. It liberates hydrogen cyanide easily, so it is used as a source of such. For this reason, this cyanohydrin is also highly toxic.

Group 2 organometallic chemistry refers to the chemistry of compounds containing carbon bonded to any group 2 element. By far the most common group 2 organometallic compounds are the magnesium-containing Grignard reagents which are widely used in organic chemistry. Other organometallic group 2 compounds are rare and are typically limited to academic interests.

Organonickel chemistry is a branch of organometallic chemistry that deals with organic compounds featuring nickel-carbon bonds. They are used as a catalyst, as a building block in organic chemistry and in chemical vapor deposition. Organonickel compounds are also short-lived intermediates in organic reactions. The first organonickel compound was nickel tetracarbonyl Ni(CO)4, reported in 1890 and quickly applied in the Mond process for nickel purification. Organonickel complexes are prominent in numerous industrial processes including carbonylations, hydrocyanation, and the Shell higher olefin process.

Tetraphenylcyclopentadienone is an organic compound with the formula (C6H5)4C4CO. It is a dark purple to black crystalline solid that is soluble in organic solvents. It is an easily made building block for many organic and organometallic compounds.
Organoiron chemistry is the chemistry of iron compounds containing a carbon-to-iron chemical bond. Organoiron compounds are relevant in organic synthesis as reagents such as iron pentacarbonyl, diiron nonacarbonyl and disodium tetracarbonylferrate. While iron adopts oxidation states from Fe(−II) through to Fe(VII), Fe(IV) is the highest established oxidation state for organoiron species. Although iron is generally less active in many catalytic applications, it is less expensive and "greener" than other metals. Organoiron compounds feature a wide range of ligands that support the Fe-C bond; as with other organometals, these supporting ligands prominently include phosphines, carbon monoxide, and cyclopentadienyl, but hard ligands such as amines are employed as well.
Organosodium chemistry is the chemistry of organometallic compounds containing a carbon to sodium chemical bond. The application of organosodium compounds in chemistry is limited in part due to competition from organolithium compounds, which are commercially available and exhibit more convenient reactivity.

Carbene C−H insertion in organic chemistry concerns the insertion reaction of a carbene into a carbon–hydrogen bond. This organic reaction is of some importance in the synthesis of new organic compounds.

In organic chemistry, a xylylene (sometimes quinone-dimethide) is any of the constitutional isomers having the formula C6H4(CH2)2. These compounds are related to the corresponding quinones and quinone methides by replacement of the oxygen atoms by CH2 groups. ortho- and para-xylylene are best known, although neither is stable in solid or liquid form. The meta form is a diradical. Certain substituted derivatives of xylylenes are however highly stable, such as tetracyanoquinodimethane and the xylylene dichlorides.
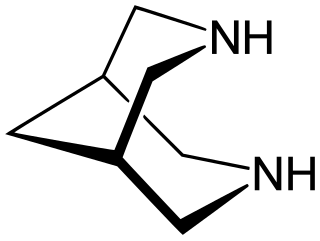
Bispidine (3,7-diazabicyclo[3.3.1]nonane) is an organic compound that is classified as a bicyclic diamine. Although synthetic, it is related structurally to natural alkaloid sparteine. It is a white crystalline solid. It has been widely investigated as a chelating agent. Many derivatives are known.










