 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name Tris(2,4-di-tert-butylphenyl) phosphite | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.046.084 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C42H63O3P | |
| Molar mass | 646.937 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Melting point | 181–184 °C (358–363 °F; 454–457 K) |
| <0.1 g/100g | |
| Solubility in n-hexane | 14 g/100g |
| Solubility in ethyl acetate | 5 g/100g |
| Solubility in chloroform | 58 g/100g |
| Solubility in toluene | 40 g/100g |
| Solubility in methanol | <0.5 g/100g |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
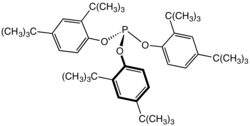
Tris(2,4-di-tert-butylphenyl)phosphite is an organophosphorus compound with the formula [(C4H9)2C6H3O]3P. This white solid is a widely used stabilizer in polymers where it functions as a secondary antioxidant. It also reduces discoloration (yellowing) of plastics. The compound is a phosphite ester formed by the reaction of 2,4-di-tert-butylphenol with phosphorus trichloride. [1] It is an approved food contact materials in the US. [2]