
Belarus, officially the Republic of Belarus, formerly known by its Russian name Byelorussia or Belorussia, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe bordered by Russia to the northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Its capital and most populous city is Minsk. Over 40% of its 207,600 square kilometres (80,200 sq mi) is forested. Its major economic sectors are service industries and manufacturing. Until the 20th century, different states at various times controlled the lands of modern-day Belarus, including the Principality of Polotsk, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, and the Russian Empire.

Minsk is the capital and largest city of Belarus, situated on the Svislač and the Nyamiha Rivers. As the capital, Minsk has a special administrative status in Belarus and is the administrative centre of Minsk Region (voblasć) and Minsk District (rajon). The population in January 2018 was 1,982,444, making Minsk the 11th most populous city in Europe. Minsk is the administrative capital of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) and seat of its Executive Secretary.

A trolleybus is an electric bus that draws power from dual overhead wires using spring-loaded trolley poles. Two wires, and two trolley poles, are required to complete the electrical circuit. This differs from a tram or streetcar, which normally uses the track as the return path, needing only one wire and one pole. They are also distinct from other kinds of electric buses, which usually rely on batteries. Power is most commonly supplied as 600-volt direct current, but there are exceptions.

Minsk Automobile Plant (MAZ), is a state-run automotive manufacturer association in Belarus, one of the largest in Eastern Europe.

Europe has an extensive number of tramway networks. Some of these networks have been upgraded to light rail standards, called Stadtbahn in Germany, premetros in Belgium, sneltram in the Netherlands, elétrico in Portugal and fast trams in some other countries.

Trolza, formerly known as the Uritsky factory or simply Uritsky, is a trolleybus manufacturer in Russia, located in Engels, Saratov oblast. In the Soviet era it was known as ZiU or Uritsky factory.

Servicio de Transportes Eléctricos del Distrito Federal (STE) is a public transport agency responsible for the operation of all trolleybus and light rail services in Mexico City. As its name implies, its routes use only electrically powered vehicles. It was created on 31 December 1946 and is owned by the Mexican Federal District government. STE is overseen by a broader Federal District authority, Secretaría de Transportes y Vialidad, which also regulates the city's other public transport authorities, including Sistema de Transporte Colectivo, Red de Transporte de Pasajeros del Distrito Federal and Metrobús, as well as other forms of transportation in the district. STE's passenger vehicle fleet consists exclusively of trolleybuses and light rail vehicles, and in 2007 its network carried 88 million passengers, of which 67 million were on trolleybus services and 21 million on light rail.
Mexicana de Autobuses, S.A., or MASA, was a major bus and coach manufacturer located in Mexico. Formed in 1959, it was owned by the Mexican government until being privatized in 1988. It was the country's second-largest bus manufacturer when it was acquired by Volvo, in 1998, and renamed Volvo Buses de México, S.A.

Mafersa S.A. is a Brazilian manufacturer of passenger rail cars, buses and trolleybuses, and related components. It was founded in 1944 and was located in the city of São Paulo. At the end of 1997 it became a subsidiary of Alstom.

The Bradford trolleybus system served the city of Bradford, Yorkshire, England for much of the 20th century. It was one of the first two trolleybus systems to be opened in the United Kingdom, along with the Leeds system.
The Nottinghamshire and Derbyshire trolleybus system once linked the city of Nottingham, in the county of Nottinghamshire, England, with Ripley, in the neighbouring county of Derbyshire. Opened on 7 January 1932, it replaced the Nottinghamshire and Derbyshire tramway, between the same termini.

The Chieti trolleybus system forms part of the public transport network of the city and comune of Chieti, in the region of Abruzzo, central Italy. In operation since 2009, the system comprises one urban route.
The Ashgabat trolleybus system formed part of the public transport network in Ashgabat, the capital city of Turkmenistan. It was the only trolleybus system ever in that country.

Trolleybuses in São Paulo provide a portion of the public transport service in Greater São Paulo, in the state of São Paulo, Brazil, with two independent trolleybus systems. The SPTrans system opened in 1949 and serves the city of São Paulo, while the Empresa Metropolitana de Transportes Urbanos de São Paulo (EMTU) system opened in 1988 and serves suburban areas to the southeast of the city proper. Worldwide, São Paulo is one of only two metropolitan areas possessing two independent trolleybus systems, the other being Naples, Italy.

The Shanghai trolleybus system is a system of trolleybuses forming part of the public transport network in the city of Shanghai, China. Of more than 300 trolleybus systems in operation worldwide, the Shanghai system is the oldest. The system turned 100 years old in November 2014 and was the first trolleybus system anywhere in the world to reach that milestone.
As of 2012 there were around 300 cities or metropolitan areas where trolleybuses were operated, and more than 500 additional trolleybus systems have existed in the past. For complete lists of trolleybus systems by location, with dates of opening and closure, see List of trolleybus systems and the related lists indexed there.
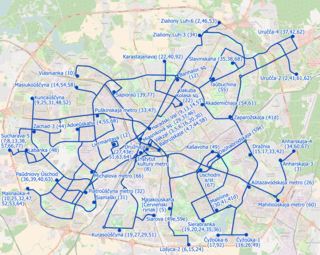
The Minsk trolleybus system serves the city of Minsk, the capital of Belarus. The system was opened in September 19, 1952. Nowadays it has more than 60 lines. The system is operated by the "Minsktrans" state enterprise.














