Related Research Articles

The Tupolev Tu-114 Rossiya is a retired large turboprop-powered long-range airliner designed by the Tupolev design bureau and built in the Soviet Union from May 1955. The aircraft was the largest and fastest passenger plane at that time and also had the longest range, at 10,900 km (6,800 mi). It has held the official title of fastest propeller-driven aircraft since 1960.

The Tupolev Tu-85 was a Soviet prototype strategic bomber based on the Tu-4, an unlicensed, reverse engineered copy of the Boeing B-29 Superfortress. It was the ultimate development of the B-29 family, being over 50% heavier than its progenitor and had nearly double the range. Only two prototypes were built before the program was cancelled in favor of the turboprop powered Tupolev Tu-95 bomber which could cover the same range at a far higher speed.
The Tupolev Tu-70 was a Soviet passenger variant of the Tu-4 bomber, an unlicensed, reverse engineered copy of the Boeing B-29 Superfortress. Designed immediately after the end of World War II, it used a number of components from Boeing B-29s that had made emergency landings in the Soviet Union after bombing Japan. It had the first pressurized fuselage in the Soviet Union and first flew on 27 November 1946. The aircraft was successfully tested, recommended for serial production, but ultimately not produced because of more pressing military orders and because Aeroflot had no requirement for such an aircraft. A military cargo aircraft version was the Tupolev Tu-75.

The Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-105, part of the Spiral program, was a crewed test vehicle to explore low-speed handling and landing. It was a visible result of a Soviet project to create an orbital spaceplane. The MiG 105 was nicknamed "Lapot", for the shape of its nose.

The Tupolev Tu-14, was a Soviet twinjet light bomber derived from the Tupolev '73', the failed competitor to the Ilyushin Il-28 'Beagle'. It was used as a torpedo bomber by the mine-torpedo regiments of Soviet Naval Aviation between 1952–1959 and exported to the People's Republic of China.

The BisnovatR-4 was an early Soviet long-range air-to-air missile. It was used primarily as the sole weapon of the Tupolev Tu-128 interceptor, matching its RP-S Smerch ('Tornado') radar.
The Tupolev Tu-125 was an unrealized project to develop a new long-range supersonic bomber for the Soviet Air Force. Development commenced in 1958 to replace the newest Tu-22. The "Tu-125" designation was an internal one used by the Tupolev design bureau. Since the aircraft was never built, it never received a military designation.
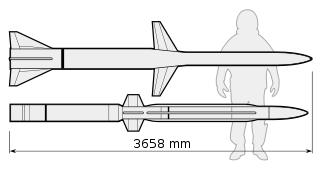
The AIM-152 Advanced Air-to-Air Missile (AAAM) was a long-range air-to-air missile developed by the United States. The AIM-152 was intended to serve as the successor to the AIM-54 Phoenix. The program went through a protracted development stage but was never adopted by the United States Navy, due to the ending of the Cold War and the reduction in threat of its perceived primary target, Soviet supersonic bombers. Development was cancelled in 1992.

The Tupolev Tu-95LAL experimental aircraft which flew from 1961 to 1965 was a modified Tupolev Tu-95 Soviet bomber aircraft, analogous to the United States' earlier Convair NB-36H. It was intended to see whether a nuclear reactor could be used to power an aircraft, primarily testing airborne operation of a reactor and shielding for components and crew. The reactor did not actually power the aircraft.

Sukhoi-Gulfstream S-21 was a projected Russian-American supersonic business jet.

The Lavochkin La-250 "Anakonda" was a high-altitude interceptor aircraft prototype developed in the Soviet Union by the Lavochkin design bureau in the 1950s. Its nickname "Anaconda" was invented during the flight test and referred to both the elongated body shape as well as the relatively critical flight characteristics of the machine.
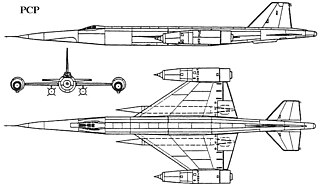
The Tsybin RSR was a Soviet design for an advanced, long-range, Mach 3 strategic reconnaissance aircraft.

The Tupolev Tu-123 Yastreb was one of the earliest Soviet reconnaissance drones that began development in 1960. Sometimes referred to as the "DBR-1", it was introduced into active service in 1964.

The Raduga Kh-26 KSR-5 was a long-range, air-launched cruise missile and anti ship missile developed by the Soviet Union. It was essentially a scaled down version of the Kh-22 'Kitchen', built to be carried by the less capable Tu-16.

The Tupolev Tu-244 was a proposed supersonic transport (SST) aircraft, developed from the Tu-144. It implemented novel features such as cryogenic fuel to enable flight distances of up to 10,000 km (6,200 mi) and would have carried up to 300 passengers. The project was cancelled in 1993.

The Tupolev Tu-2000 was a planned hypersonic flight experimental aircraft designed by the Tupolev design bureau. It was intended to test technologies for a single-stage-to-orbit aerospaceplane and also the Tupolev Tu-360 intercontinental bomber.
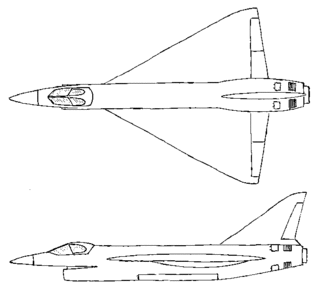
The Saab 36 was a cancelled Swedish supersonic bomber planned by Saab AB during the 1950s. The aircraft was intended to be able to carry an 800 kg free-falling nuclear weapon, but the Swedish nuclear weapons program was cancelled in the 1960s; the plans for the bomber had been cancelled in 1957. The Saab 36 was to be fitted with delta wings, as was the Saab 35 Draken fighter. The engine was to be a version of the British Bristol Olympus turbojet, the same engine powering the Avro Vulcan jet bomber.

The Reaction Engines Limited LAPCAT Configuration A2 is a design study for a hypersonic speed jet airliner intended to provide long range, high capacity commercial transportation.

The Tupolev Tu-1 was a prototype Soviet night fighter variant of the Tupolev Tu-2 medium bomber that first flew after the end of World War II. It was cancelled when its experimental Mikulin AM-43V engines reached the end of their service life.
The Tupolev Voron was a planned supersonic unmanned reconnaissance aircraft of the Soviet Union manufactured by the company Tupolev, largely based on or designed to compete with the Lockheed D-21.
References
- 1 2 Gordon, Yefim; Komissarov, Sergey (2013). Unflown wings : Soviet and Russian unrealized aircraft projects 1925-2010. Birmingham: Ian Allan Publishing Ltd. pp. 90-91. ISBN 978-1906537340.
- ↑ "360 (Ту-360)".
- ↑ Tu-2000
- ↑ " Tu-2000 ", astronautix.com , Retrieved 24 April 2010