
Smilodon is a genus of the extinct machairodont subfamily of the felids. It is one of the most famous prehistoric mammals and the best known saber-toothed cat. Although commonly known as the saber-toothed tiger, it was not closely related to the tiger or other modern cats. Smilodon lived in the Americas during the Pleistocene epoch. The genus was named in 1842 based on fossils from Brazil; the generic name means "scalpel" or "two-edged knife" combined with "tooth". Three species are recognized today: S. gracilis, S. fatalis, and S. populator. The two latter species were probably descended from S. gracilis, which itself probably evolved from Megantereon. The hundreds of individuals obtained from the La Brea Tar Pits in Los Angeles constitute the largest collection of Smilodon fossils.
The radula is an anatomical structure used by mollusks for feeding, sometimes compared to a tongue. It is a minutely toothed, chitinous ribbon, which is typically used for scraping or cutting food before the food enters the esophagus. The radula is unique to the molluscs, and is found in every class of mollusc except the bivalves, which instead use cilia, waving filaments that bring minute organisms to the mouth.

Megalodon, meaning "big tooth", is an extinct species of mackerel shark that lived approximately 23 to 3.6 million years ago (mya), during the Early Miocene to the Pliocene. It was formerly thought to be a member of the family Lamnidae and a close relative of the great white shark. However, it is now classified into the extinct family Otodontidae, which diverged from the great white shark during the Early Cretaceous. Its genus placement is still debated, authors placing it in either Carcharocles, Megaselachus, Otodus, or Procarcharodon. This is because transitional fossils have been found showing that megalodon is the final chronospecies of a lineage of giant sharks originally of the genus Otodus which evolved during the Paleocene.
The giant hutias are an extinct group of large rodents known from fossil and subfossil material in the est Indies. One species, Amblyrhiza inundata, is estimated to have weighed between 50 and 200 kg, big specimens being as large as an American black bear. This is twice as large as the capybara, the largest rodent living today, but still much smaller than Josephoartigasia monesi, the largest rodent known. These animals were probably used as a food source by the pre-Columbian peoples of the Caribbean. All giant hutias are in a single family, Heptaxodontidae, which contains no living species; this grouping seems to be paraphyletic and arbitrary, however.

Apodemus is a genus of Muridae. The name is unrelated to that of the Mus genus, instead being derived from the Greek ἀπό-δημος.

The greater white-toothed shrew is a small insectivorous mammal found in Europe and North Africa. It is the most common of the white-toothed shrews. This species is found along the Mediterranean, Netherlands, Belgium, Ireland, Germany and Portugal; in addition, the Osorio shrew of the Canary island of Gran Canaria, originally described as a separate species, was later discovered to be a population of introduced greater white-toothed shrew. Furthermore, a subspecies of the greater white-toothed shrew, Crocidura russula ibicensis, is found on the Mediterranean island of Ibiza. In April 2008, the greater white-toothed shrew was discovered in Ireland as well. Its preferred habitats are grassland and woodland. It is slightly larger than the lesser white-toothed shrew but otherwise very similar and can often be distinguished only by close inspection of its teeth which are unpigmented.

The Negros shrew is a white-toothed shrew found only on the island of Negros in the Philippines. It is locally called the katsurí and is listed as a critically endangered species due to habitat loss and a restricted range.
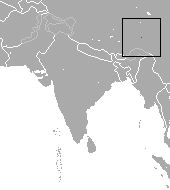
Kozlov's shrew is a red-toothed shrew found only at the Mekong River, Tibet, China. This shrew is listed as a data deficient species.
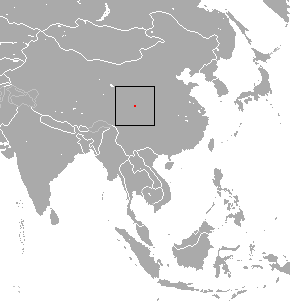
Salenski's shrew is a red-toothed shrew found only in northern Sichuan, China, where it is known from Wolong National Nature Reserve. It is listed as a critically endangered species due to habitat loss and a restricted range.

The genus Crocidura is one of nine genera of the shrew subfamily Crocidurinae. Members of the genus are commonly called white-toothed shrews or musk shrews, although both also apply to all of the species in the subfamily. With over 180 species, Crocidura contains the most species of any mammal genus. The name Crocidura means "woolly tail", because the tail of Crocidura species are covered in short hairs interspersed with longer ones.

Batomys is a genus of rodent endemic to the Philippines. It has six extant described species.
Physogaleus is a small genus of prehistoric shark that lived from the Eocene to Miocene epochs.

The Dsinezumi shrew, also known as the Japanese white-toothed shrew, is a species of musk shrew found in Japan and on Korea's Jeju Island. It is widespread, and considered to be of "least concern" by the IUCN.

The small-toothed sportive lemur, or small-toothed weasel lemur, is a primate species in the family Lepilemuridae that—like all extant lemurs—is endemic to Madagascar. The species lives in dense rainforest in southeastern Madagascar, and can be found in Ranomafana and Andringitra National Parks. Described in 1894, it was considered either a subspecies or taxonomic synonym of the weasel sportive lemur throughout most of the 20th century. Phylogenetic studies not only support its species status, but also suggest that it is the only eastern Malagasy sportive lemur that is more closely related to western than to other eastern species.
The Hispaniolan edible rat is a recently extinct species of rodent in the family Echimyidae. It is the only species in the genus Brotomys. It was endemic to the island of Hispaniola in the Caribbean, in what is today the Dominican Republic. Its natural habitat was subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests.

The Taiwanese mole shrew is one of four species of red-toothed shrews in the genus Anourosorex. This species is endemic to Taiwan.
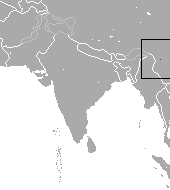
The pygmy brown-toothed shrew is a species of shrew in the order Eulipotyphla. It is distributed in China. C. parva was initially thought to be the same as Chodsigoa lamula, but it was found to be a separate species.

The Indochinese shrew is a species of white-toothed shrew native to Southeast Asia. It was first identified in 1922 by Herbert C. Robinson and C. Boden Kloss. The species is often taxonomized as a subspecies Horsfield's shrew, but bears a different range, occurring in Myanmar, Vietnam, and the Yunnan province of China. C. indochinensis is on the smaller end of shrews, with dark brownish gray fur and a long, slender tail.












