
Stereochemistry, a subdiscipline of chemistry, studies the spatial arrangement of atoms that forms the structure of molecules and their manipulation. The study of stereochemistry focuses on the relationships between stereoisomers, which by definition have the same molecular formula and sequence of bonded atoms (constitution), but differ in the geometric positioning of the atoms in space. For this reason, it is also known as 3D chemistry—the prefix "stereo-" means "three-dimensionality".
In chemistry, a racemic mixture or racemate is one that has equal amounts of left- and right-handed enantiomers of a chiral molecule or salt. Racemic mixtures are rare in nature, but many compounds are produced industrially as racemates.

In chemistry, an enantiomer – also called optical isomer, antipode, or optical antipode – is one of a pair of molecular entities which are mirror images of each other and non-superposable. Enantiomers of each other are much like one's right and left hands; without mirroring one of them, hands cannot be superposed onto each other. It is solely a relationship of chirality and the permanent three-dimensional relationships among molecules or other chemical structures: no amount of re-orientiation of a molecule as a whole or conformational change converts one chemical into its enantiomer. Chemical structures with chirality rotate plane-polarized light. A mixture of equal amounts of each enantiomer, a racemic mixture or a racemate, does not rotate light.

In stereochemistry, a stereocenter of a molecule is an atom (center), axis or plane that is the focus of stereoisomerism; that is, when having at least three different groups bound to the stereocenter, interchanging any two different groups creates a new stereoisomer. Stereocenters are also referred to as stereogenic centers.

Ethanolamine is a naturally occurring organic chemical compound with the formula HOCH
2CH
2NH
2 or C
2H
7NO. The molecule is bifunctional, containing both a primary amine and a primary alcohol. Ethanolamine is a colorless, viscous liquid with an odor reminiscent of ammonia.

In chemistry, a molecule or ion is called chiral if it cannot be superposed on its mirror image by any combination of rotations, translations, and some conformational changes. This geometric property is called chirality. The terms are derived from Ancient Greek χείρ (cheir) 'hand'; which is the canonical example of an object with this property.

Enantioselective synthesis, also called asymmetric synthesis, is a form of chemical synthesis. It is defined by IUPAC as "a chemical reaction in which one or more new elements of chirality are formed in a substrate molecule and which produces the stereoisomeric products in unequal amounts."
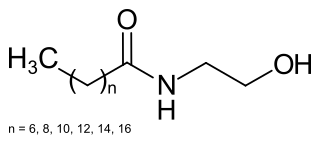
Cocamide MEA, or cocamide monoethanolamine, is a solid, off-white to tan compound, often sold in flaked form. The solid melts to yield a pale yellow viscous clear liquid. It is a mixture of fatty acid amides which is produced from the fatty acids in coconut oil when reacted with ethanolamine.

Dimethylethanolamine is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2NCH2CH2OH. It is bifunctional, containing both a tertiary amine and primary alcohol functional groups. It is a colorless viscous liquid. It is used in skin care products for improving skin tone and also taken orally as a nootropic. It is prepared by the ethoxylation of dimethylamine.
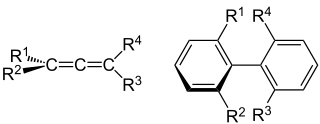
In chemistry, axial chirality is a special case of chirality in which a molecule contains two pairs of chemical groups in a non-planar arrangement about an axis of chirality so that the molecule is not superposable on its mirror image. The axis of chirality is usually determined by a chemical bond that is constrained against free rotation either by steric hindrance of the groups, as in substituted biaryl compounds such as BINAP, or by torsional stiffness of the bonds, as in the C=C double bonds in allenes such as glutinic acid. Axial chirality is most commonly observed in substituted biaryl compounds wherein the rotation about the aryl–aryl bond is restricted so it results in chiral atropisomers, as in various ortho-substituted biphenyls, and in binaphthyls such as BINAP.
![<span class="mw-page-title-main">Sulfonium</span> Cation of the form [SR3]+](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/62/%28CH3%293S%2B_in_the_BPh4-_salt_%28code_HEYZAM%29.png/320px-%28CH3%293S%2B_in_the_BPh4-_salt_%28code_HEYZAM%29.png)
In organic chemistry, a sulfonium ion, also known as sulphonium ion or sulfanium ion, is a positively-charged ion featuring three organic substituents attached to sulfur. These organosulfur compounds have the formula [SR3]+. Together with a negatively-charged counterion, they give sulfonium salts. They are typically colorless solids that are soluble in organic solvent.
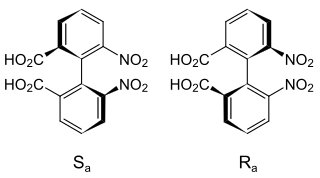
Atropisomers are stereoisomers arising because of hindered rotation about a single bond, where energy differences due to steric strain or other contributors create a barrier to rotation that is high enough to allow for isolation of individual conformers. They occur naturally and are important in pharmaceutical design. When the substituents are achiral, these conformers are enantiomers (atropoenantiomers), showing axial chirality; otherwise they are diastereomers (atropodiastereomers).

Ethylenediamine (abbreviated as en when a ligand) is the organic compound with the formula C2H4(NH2)2. This colorless liquid with an ammonia-like odor is a basic amine. It is a widely used building block in chemical synthesis, with approximately 500,000 tonnes produced in 1998. Ethylenediamine is the first member of the so-called polyethylene amines.

Diethanolamine, often abbreviated as DEA or DEOA, is an organic compound with the formula HN(CH2CH2OH)2. Pure diethanolamine is a white solid at room temperature, but its tendencies to absorb water and to supercool often results in it being found in a colorless, viscous liquid state. Diethanolamine is polyfunctional, being a secondary amine and a diol. Like other organic amines, diethanolamine acts as a weak base. Reflecting the hydrophilic character of the secondary amine and hydroxyl groups, DEA is soluble in water. Amides prepared from DEA are often also hydrophilic. In 2013, the chemical was classified by the International Agency for Research on Cancer as "possibly carcinogenic to humans" (Group 2B).
In organic chemistry, spiro compounds are compounds that have at least two molecular rings sharing one common atom. Simple spiro compounds are bicyclic. The presence of only one common atom connecting the two rings distinguishes spiro compounds from other bicyclics. Spiro compounds may be fully carbocyclic or heterocyclic. One common type of spiro compound encountered in educational settings is a heterocyclic one— the acetal formed by reaction of a diol with a cyclic ketone.
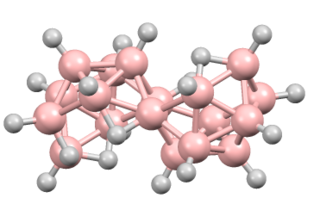
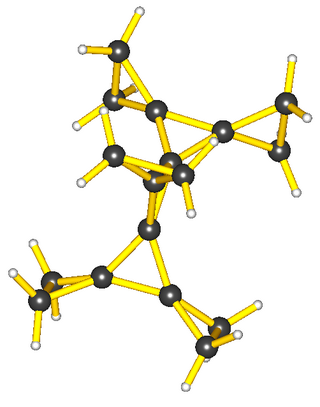
Octadecaborane is an inorganic compound, a boron hydride cluster with chemical formula B18H22. It is a colorless flammable solid, like many higher boron hydrides. Although the compound has no practical applications, its structure is of theoretical and pedagogical interest.

DIPAMP is an organophosphorus compound that is used as a ligand in homogeneous catalysis. It is a white solid that dissolves in organic solvents. Work on this compound by W. S. Knowles was recognized with the Nobel Prize in Chemistry. DIPAMP was the basis for one of the first industrial scale asymmetric hydrogenation, the synthesis of the drug L-DOPA.

In chemistry, isomers are molecules or polyatomic ions with identical molecular formula – that is, the same number of atoms of each element – but distinct arrangements of atoms in space. Isomerism refers to the existence or possibility of isomers.

Chirality is a property of asymmetry important in several branches of science. The word chirality is derived from the Greek χείρ (kheir), "hand", a familiar chiral object.
Alaninol is the organic compound with the formula CH3CH(NH2)CH2OH. A colorless solid, the compound is classified as an amino alcohol. It can be generated by converting the carboxylic group of alanine to an alcohol with a strong reducing agent such as lithium aluminium hydride. The compound is chiral, and as is normal for chiral compounds, the physical properties of the racemate differ somewhat from those of the enantiomers. It is a precursor to numerous chiral ligands used in asymmetric catalysis. The compound is an example of a 1,2-ethanolamine.








![<span class="mw-page-title-main">Sulfonium</span> Cation of the form [SR3]+](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/62/%28CH3%293S%2B_in_the_BPh4-_salt_%28code_HEYZAM%29.png/320px-%28CH3%293S%2B_in_the_BPh4-_salt_%28code_HEYZAM%29.png)





