
U Antliae is a variable star in the constellation Antlia. It is a carbon star surrounded by two thin shells of dust.

Kappa Cassiopeiae is a star in the constellation Cassiopeia.

R Centauri is a Mira variable star in the constellation Centaurus.

HD 95109 is a Classical Cepheid variable, a type of variable star, in the constellation Carina. Its apparent magnitude is 6.86.

V385 Andromedae is a variable star in the constellation Andromeda, about 360 parsecs (1,200 ly) away. It is a red giant over a hundred times larger than the sun. It has an apparent magnitude around 6.4, just about visible to the naked eye in ideal conditions.

R Arae is an Algol-type eclipsing binary in the constellation Ara. Located approximately 298 parsecs (970 ly) distant, it normally shines at magnitude 6.17, but during eclipses can fall as low as magnitude 7.32. It has been suggested by multiple studies that mass transfer is occurring between the two stars of this system, and the period of eclipses seems to be increasing over time. The primary is a blue-white main sequence star of spectral type B5V that is 5 times as massive as the Sun, while the secondary is a yellow-white star of spectral type F1IV that is 1.5 times as massive as the Sun. Stellar material is being stripped off the secondary and accreting on the primary.

PU Aurigae is an irregular variable star located in the constellation Auriga. A red giant, it varies by 0.1 magnitude around magnitude 5.64. Located around 560 light-years distant, it shines with a luminosity approximately 1,523 times that of the Sun and has a surface temperature of 3,482 K.
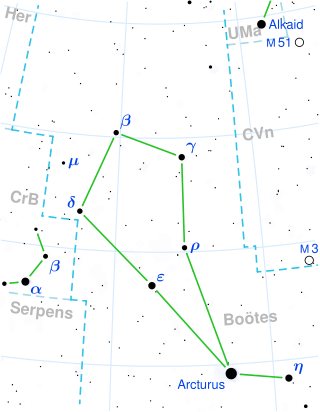
HD 123657, or BY Boötis, is a variable star of magnitude 4.98–5.33V. This makes it a dim naked eye star. The star is located near the end of the handle of the Big Dipper, but just within the boundaries of the constellation Boötes.

W Andromedae is a variable star in the constellation of Andromeda. It is classified as a Mira variable and S-type star, and varies from an apparent visual magnitude of 14.6 at minimum brightness to a magnitude of 6.7 at maximum brightness, with a period of approximately 397.3 days. The star is losing mass due to stellar winds at a rate of 2.79×10−7M☉/yr.

V4381 Sagittarii is a variable star in the constellation Sagittarius. A white supergiant of spectral type A2/A3Iab, it is an Alpha Cygni variable that varies between apparent photographic magnitudes 6.57 and 6.62. Its visual apparent magnitude is about 6.54.

HD 110432 is a Be star in the south-east of Crux, behind the center of the southern hemisphere's dark Coalsack Nebula. It has a stellar classification of B1IVe, which means it is a subgiant star of class B that displays emission lines in its spectrum. This is a variable star of the Gamma Cassiopeiae type, indicating it is a shell star with a circumstellar disk of gas about the equator, and has the variable star designation BZ Crucis. It is not known to be a member of a binary system, although it is probably a member of the open cluster NGC 4609. This star is moderately luminous in the X-ray band, with a variable energy emission of 1032–33 erg s−1 in the range 0.2−12 keV. The X-ray emission may be caused by magnetic activity, or possibly by accretion onto a white dwarf companion.

U Camelopardalis is a semiregular variable star in the constellation Camelopardalis. Based on parallax measurements made by the Hipparcos spacecraft, it is located about 3,000 light-years away from the Earth. Its apparent visual magnitude is about 8, which is dim enough that it cannot be seen with the unaided eye.

Eta Piscis Austrini is binary star system in the southern constellation of Piscis Austrinus. As of 2000, the two components had an angular separation of 1.818 arc seconds along a position angle of 113.4°. The pair have a combined apparent visual magnitude of +5.43, which is bright enough to be seen with the naked eye. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 3.99 mas as seen from the Earth, the system is located roughly 820 light years from the Sun.

QZ Puppis is a class B2.5V star in the constellation Puppis. Its apparent magnitude is 4.5 and it is approximately 650 light years away based on parallax.

MX Puppis is a class B1.5IV star in the constellation Puppis. Its apparent magnitude varies irregularly between magnitude 4.6 and 4.9 and it is classified as a Gamma Cassiopeiae variable. It is approximately 930 light years away based on parallax.

Y Centauri or Y Cen is a semiregular variable star in the constellation of Centaurus.

R Leonis Minoris is a Mira variable type star in the constellation Leo Minor. It ranges between apparent magnitude 6.3 and 13.2, and spectral types M6.5e to M9.0e (Tc:), over a period of 372 days.

AC Herculis, is an RV Tauri variable and spectroscopic binary star in the constellation of Hercules. It varies in brightness between apparent magnitudes 6.85 and 9.0.

V528 Carinae is a variable star in the constellation Carina.

T Leporis is a variable star in the constellation of Lepus, the Hare. It is located half a degree from ε Leporis in the sky; its distance is approximately 1,100 light years from the Solar System. It has the spectral type M6ev, and is a Mira variable — as is R Leporis, in the same constellation — whose apparent magnitude varies between +7.40 and +14.30 with a period of 368.13 days.



















