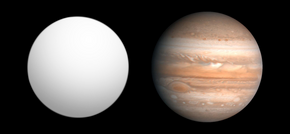
XO-3b is an exoplanet with about 11.79 times the mass of Jupiter, and it orbits its parent star in about 3.2 days. The radius of this object is 1.217 times that of Jupiter. Astronomers announced their discovery on May 30, 2007, at the American Astronomical Society in Honolulu, Hawaii. Its discovery is attributed to the combined effort of amateur and professional astronomers working together on the XO Project using a telescope located on the Haleakala summit in Hawaii.

TrES-4b is an extrasolar planet, and one of the largest exoplanets ever found. It was discovered in 2006, and announced in 2007, by the Trans-Atlantic Exoplanet Survey, using the transit method. It is approximately 1,400 light-years (430 pc) away orbiting the star GSC 02620-00648, in the constellation Hercules.

HAT-P-4b is a confirmed extrasolar planet orbiting the star HAT-P-4 over 1000 light years away in Boötes constellation. It was discovered by transit on October 2, 2007, which looks for slight dimming of stars caused by planets that passed in front of them. It is the fourth planet discovered by the HATNet Project. It is also called BD+36 2593b, TYC 2569-01599-1b, 2MASS J15195792+3613467b, SAO 64638b.

WASP-3b is an extrasolar planet orbiting the star WASP-3 located approximately 800 light-years away in the constellation Lyra. It was discovered via the transit method by SuperWASP, and follow up radial velocity observations confirmed that WASP-3b is a planet. The planet's mass and radius indicate that it is a gas giant with a similar bulk composition to Jupiter. WASP-3b has such an orbital distance around its star to classify it in the class of planets known as hot Jupiters and has an atmospheric temperature of approximately 1983 K.

WASP-4b is an exoplanet, specifically a hot Jupiter, approximately 891 light-years away in the constellation of Phoenix.

WASP-5b is an exoplanet orbiting the star WASP-5 located approximately 1000 light-years away in the constellation Phoenix. The planet's mass and radius indicate that it is a gas giant with a similar bulk composition to Jupiter. The small orbital distance of WASP-5 b around its star means it belongs to a class of planets known as hot Jupiters. The planetary equilibrium temperature would be 1717 K, but the measured dayside temperature is higher, with a 2015 study finding 2500±100 K and a 2020 study finding 2000±90 K.
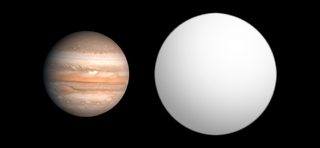
HAT-P-7b is an extrasolar planet discovered in 2008. It orbits very close to its host star and is larger and more massive than Jupiter. Due to the extreme heat that it receives from its star, the dayside temperature is predicted to be 2,630–2,880 K K, while nightside temperatures are 2,211–2,238 K. HAT-P-7b is also one of the darkest planets ever observed, with an albedo of less than 0.03—meaning it absorbs more than 97% of the visible light that strikes it.

WASP-6b, also named Boinayel, is an exoplanet approximately 650 light years away in the constellation Aquarius. It was discovered in 2008, by the WASP survey, by astronomical transit across its parent star WASP-6. This planet orbits at only 4% of the Earth-Sun distance. The planet has a mass half that of Jupiter, but its insolation has forced a thermal expansion of its radius to greater than that of Jupiter. Thus, this planet is an inflated hot Jupiter. Starspots on the host star WASP-6 helped to refine the measurements of the mass and the radius of the planet.
WASP-7, also identified as HD 197286, is a type F star located about 520 light years away in the constellation Microscopium. This star is a little larger and about 28% more massive than the Sun and is also brighter and hotter. At magnitude 9 the star cannot be seen by the naked eye but is visible through a small telescope.

WASP-8b is an exoplanet orbiting the star WASP-8A in the constellation of Sculptor. The star is similar to the Sun and forms a binary star with a red dwarf star (WASP-8B) of half the Sun's mass that orbits WASP-8A 4.5 arcseconds away. The system is 294 light-years away and is therefore located closer to Earth than many other star systems that are known to feature planets similar to WASP-8b. The planet and its parent star were discovered in the SuperWASP batch -6b to -15b. On 1 April 2008, Dr. Don Pollacco of Queen's University Belfast announced them at the RAS National Astronomy Meeting.

WASP-14b is an extrasolar planet discovered in 2008 by SuperWASP using the transit method. Follow-up radial velocity measurements showed that the mass of WASP-14b is almost eight times larger than that of Jupiter. The radius found by the transit observations show that it has a radius 25% larger than Jupiter. This makes WASP-14b one of the densest exoplanets known. Its radius best fits the model of Jonathan Fortney.

HD 17156 b, named Mulchatna by the IAU, is an extrasolar planet approximately 255 light-years away in the constellation of Cassiopeia. The planet was discovered orbiting the yellow subgiant star HD 17156 in April 2007. The planet is classified as a relatively cool hot Jupiter planet slightly smaller than Jupiter but slightly larger than Saturn. This highly-eccentric three-week orbit takes it approximately 0.0523 AU of the star at periastron before swinging out to approximately 0.2665 AU at apastron. Its eccentricity is about the same as 16 Cygni Bb, a so-called "eccentric Jupiter". Until 2009, HD 17156 b was the transiting planet with the longest orbital period.

HAT-P-9b, formally named Alef, is an exoplanet approximately 1500 light years away in the constellation Auriga. This planet was found by the transit method on June 26, 2008. It has a mass 78% that of Jupiter and a radius 140% that of Jupiter. As with most transiting planets, this planet is a hot Jupiter, meaning this Jupiter-like planet orbits extremely close to its parent star, taking only 3.92 days to orbit.

HAT-P-13b is an extrasolar planet approximately 700 light-years away in the constellation Ursa Major. The planet was discovered when it transited across its sun, HAT-P-13. This planet is a hot Jupiter with 0.851 times the mass of Jupiter and 1.28 radius. The planet has a lower mass, but its overall size is larger than Jupiter.

WASP-17b is an exoplanet in the constellation Scorpius that is orbiting the star WASP-17. Its discovery was announced on 11 August 2009. It is the first planet discovered to have a retrograde orbit, meaning it orbits in a direction counter to the rotation of its host star. This discovery challenged traditional planetary formation theory. In terms of diameter, WASP-17b is one of the largest exoplanets discovered and at half Jupiter's mass, this made it the most puffy planet known in 2010. On 3 December 2013, scientists working with the Hubble Space Telescope reported detecting water in the exoplanet's atmosphere.

WASP-19b, formally named Banksia, is an exoplanet, notable for possessing one of the shortest orbital periods of any known planetary body: 0.79 days or approximately 18.932 hours. It has a mass close to that of Jupiter, but by comparison has a much larger radius ; making it nearly the size of a low-mass star. It orbits the star WASP-19 in the Vela constellation. At the time of discovery it was the shortest period hot Jupiter discovered as planets with shorter orbital periods had a rocky, or metallic composition.
WASP-24b is a Hot Jupiter detected in the orbit of the F-type star WASP-24. The planet is approximately the same size and mass of Jupiter, but it orbits at approximately 4% of the mean distance between the Earth and the Sun every two days. WASP-24b was observed by SuperWASP starting in 2008; after two years of observations, follow-ups led to the collection of the information that led to the planet's discovery.
HAT-P-24b is an extrasolar planet discovered by the HATNet Project in 2010 orbiting the F8 dwarf star HAT-P-24. It is a hot Jupiter, with a mass three quarters that of Jupiter and a radius 20% larger.
Kepler-13 or KOI-13 is a stellar triple star system consisting of Kepler-13A, around which an orbiting hot Jupiter exoplanet was discovered with the Kepler spacecraft in 2011, and Kepler-13B a common proper motion companion star which has an additional star orbiting it.
HD 146389, is a star with a yellow-white hue in the northern constellation of Hercules. The star was given the formal name Irena by the International Astronomical Union in January 2020. It is invisible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 9.4 The star is located at a distance of approximately 446 light years from the Sun based on parallax, but is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −9 km/s. The star is known to host one exoplanet, designated WASP-38b or formally named 'Iztok'.