A fern is a member of a group of vascular plants that reproduce via spores and have neither seeds nor flowers. The polypodiophytes include all living pteridophytes except the lycopods, and differ from mosses and other bryophytes by being vascular, i.e., having specialized tissues that conduct water and nutrients and in having life cycles in which the branched sporophyte is the dominant phase. Ferns have complex leaves called megaphylls, that are more complex than the microphylls of clubmosses. Most ferns are leptosporangiate ferns. They produce coiled fiddleheads that uncoil and expand into fronds. The group includes about 10,560 known extant species. Ferns are defined here in the broad sense, being all of the Polypodiopsida, comprising both the leptosporangiate (Polypodiidae) and eusporangiate ferns, the latter group including horsetails, whisk ferns, marattioid ferns, and ophioglossoid ferns.

Glossopteris [etymology: from Ancient Greek γλῶσσα + πτερίς ] is the largest and best-known genus of the extinct Permian order of seed ferns known as Glossopteridales. The genus Glossopteris refers only to leaves, within a framework of form genera used in paleobotany. Species of Glossopteris were the dominant trees of the middle- to high-latitude lowland vegetation across the supercontinent Gondwana during the Permian Period. Glossopteris fossils were critical in recognizing former connections between the various fragments of Gondwana: South America, Africa, India, Australia, New Zealand, and Antarctica.

Archaeopteris is an extinct genus of progymnosperm tree with fern-like leaves. A useful index fossil, this tree is found in strata dating from the Upper Devonian to Lower Carboniferous, the oldest fossils being 385 million years old, and had global distribution.

The Caytoniales are an extinct order of seed plants known from fossils collected throughout the Mesozoic Era, around 252 to 66 million years ago. They are regarded as seed ferns because they are seed-bearing plants with fern-like leaves. Although at one time considered angiosperms because of their berry-like cupules, that hypothesis was later disproven. Nevertheless, some authorities consider them likely ancestors or close relatives of angiosperms. The origin of angiosperms remains unclear, and they cannot be linked with any known seed plants groups with certainty.

Caytonia is an extinct genus of seed ferns.

Sagenopteris is a genus of extinct seed ferns from the Triassic to late Early Cretaceous.

Dicroidium is an extinct genus of fork-leaved seed ferns that were widely distributed over Gondwana during the Triassic. Their fossils are known from South Africa, the Arabian Peninsula, Australia, New Zealand, South America, Madagascar, the Indian subcontinent and Antarctica. They were first discovered in Triassic sediments of Tasmania by Morris in 1845. Fossils from the Umm Irna Formation in Jordan and in Pakistan indicate that these plants already existed in Late Permian. Late surviving members of the genus are known from the Early Jurassic (Sinemurian) of East Antarctica. Within paleobotany, Dicroidium is a form genus used to refers to the leaves, associated with ovuluate organs classified as Umkomasia and pollen organs classified as Pteruchus, while Dicroidum is also used collectively to refer to the whole plant.

Lepidopteris is a form genus for leaves of Late Permian to Late Triassic Period Pteridospermatophyta, or seed ferns, which lived from around 260 to 200 million years ago in what is now Australia, Antarctica, India, South America, South Africa, Russia and China. Nine species are currently recognized. Lepidopteris was a common and widespread seed fern, which survived the Permian-Triassic extinction event but succumbed to the Triassic-Jurassic extinction event. Lepidopteris callipteroides is especially common between the first two episodes of Permian-Triassic extinction event, and L. ottonis forms a comparable acme zone immediate before the Triassic-Jurassic extinction event. Lepidopteris would persist into the Early Jurassic in Patagonia, represented by the species Lepidopteris scassoi.

Umkomasia is a genus of seed bearing organs produced by corystosperm seed ferns, first based on fossils collected by Hamshaw Thomas from the Burnera Waterfall locality near the Umkomaas River of South Africa. He recognized on the basis of cuticular similarities that the same plant produced pollen organs Pteruchus and the leaves Dicroidium. Various other corystosperm seed bearing organs from the Jurassic and Cretaceous have been assigned to this genus, but recently have been given distinct genera, with Umkomasia being restricted to the Triassic.

Dicroidium odontopteroides was a common and widespread species of Dicroidium known from South Africa, Australia, New Zealand, South America and Antarctica. The species was first discovered in Triassic sediments of Tasmania and described by the palaeontologist John Morris in 1845.

Pteruchus africanus is a pollen organ of a seed fern (Pteridospermatophyta). It was first described by Hamshaw Thomas from the Umkomaas locality of South Africa.

Pteruchus is a form genus for pollen organs of the seed fern (Pteridospermatophyta family Umkomasiaceae. It was first described by Hamshaw Thomas from the Umkomaas locality of South Africa. It is associated with the seed bearing organs Umkomasia and Dicroidium leaves.

Peltaspermaceae is a natural family of seed ferns (Pteridospermatophyta) widespread in both northern and southern hemispheres coal measures of Permian and Triassic age. Peltasperms persisted in a relictual distribution in Patagonia during the Early Jurassic.

Moresnetiaceae is a natural family of seed ferns in the Division Pteridospermatophyta that appears in the North American and European Devonian to Carboniferous coal measures.

Caytonia nathorstii is an extinct species of seed ferns.
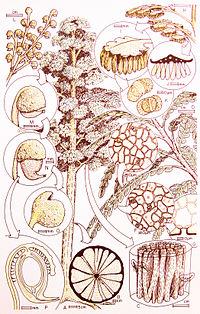
The Glossopteridaceae are an extinct family of plants belonging to Pteridospermatophyta, or seed ferns.

Corystospermaceae is a natural family of seed ferns (Pteridospermatophyta) also called Umkomasiaceae, and first based on fossils collected by Hamshaw Thomas from the Burnera Waterfall locality near the Umkomaas River of South Africa The leaves of Dicroidium were recognized by Alex Du Toit to unite all the countries of the Gondwana supercontinent during the Triassic: Africa, South America, India, and Australia. Subsequently, Dicroidium was found in the Triassic of Antarctica and New Zealand, and also the Permian Umm Irna Formation of Jordan. According to the form generic system of paleobotany, leaves are given separate generic names to ovulate and pollen organs, but the discovery of these reproductive organs in Africa by Thomas, and subsequently throughout Gondwana, strengthened Du Toit's concept of a continuous southern supercontinent. Corystospermaceae were also components of Jurassic and Cretaceous floras, declining in the Cretaceous presumably due to the rise of flowering plants, the last known representative of the group, Komlopteris cenozoicus, is known from the Eocene of Tasmania, at least 13 million years after the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event.

Stamnostoma is an extinct genus of seed ferns based on cupules with seeds. These are among the earliest known seed plants and of earliest Carboniferous (Tournaisian) age.

Dictyopteridium is an extinct genus of plants belonging to Glossopteridaceae, but the name is used only for compression fossils of elongate multiovulate reproductive structures adnate to Glossopteris leaves. Permineralized remains identical to Dictyopteridium have been referred to the organ genus Homevaleia

Lagenostoma is a genus of seed ferns (Pteridospermatophyta), based on ovules preserved in coal balls from the Six Inch Coal of the Hough Hill Colliery near Stalybridge, England. Distinctive stalked glands enabled Oliver and Scott to attribute these seeds to fernlike foliage of Sphenopteris hoeningshauseni in the same coal balls. This was the first recognition that some Carboniferous fernlike leaves had seeds, and so were not pteridophytes, but rather Pteridospermatophyta, or seed ferns. The realization that seed plants as well as spore plants had fernlike leaves was a major contribution to the evolutionary history of plants.