
The geography of Iraq is diverse and falls into five main regions: the desert, Upper Mesopotamia, the northern highlands of Iraq, Lower Mesopotamia, and the alluvial plain extending from around Tikrit to the Persian Gulf.
Transport in Iraq consists of railways, highways, waterways, pipelines, ports and harbors, marines and airports.

Kuwait is a country in West Asia, bordering the Persian Gulf, between Iraq and Saudi Arabia. Kuwait is located at the far northwestern corner of the Persian Gulf. Kuwait is 17,820 square kilometres in size. At its most distant points, it is about 200 km (120 mi) north to south, and 170 km (110 mi) east to west. Kuwait has 10 islands. Kuwait's area consists mostly of desert.

Basra is a city in southern Iraq located on the Shatt al-Arab. It had an estimated population of 1.4 million in 2018. Basra is also Iraq's main port, although it does not have deep water access, which is handled at the port of Umm Qasr. However, there is ongoing construction of Grand Faw Port on the coast of Basra, which is considered a national project for Iraq and will become one of the largest ports in the world and the largest in the Middle East, in addition, the port will strengthen Iraq's geopolitical position in the region and the world. Furthermore, Iraq is planning to establish a large naval base in the Faw peninsula.

The Shatt al-Arab is a river of some 200 kilometres (120 mi) in length that is formed at the confluence of the Euphrates and Tigris rivers in the town of al-Qurnah in the Basra Governorate of southern Iraq. The southern end of the river constitutes the Iran–Iraq border down to its mouth, where it discharges into the Persian Gulf. The Shatt al-Arab varies in width from about 232 metres (761 ft) at Basra to 800 metres (2,600 ft) at its mouth. It is thought that the waterway formed relatively recently in geological time, with the Tigris and Euphrates originally emptying into the Persian Gulf via a channel further to the west. Kuwait's Bubiyan Island is part of the Shatt al-Arab delta.

This is a timeline of the events surrounding the United States-led invasion of Iraq in 2003.

Umm Qasr is a port city in southern Iraq. It stands on the canalised Khawr az-Zubayr, part of the Khawr Abd Allah estuary which leads to the Persian Gulf. It is separated from the border of Kuwait by a small inlet. A bridge across the waterway linked the port with Kuwait prior to the 1991 Persian Gulf War.

Basra Governorate, also called Basra Province, is a governorate in southern Iraq in the region of Arabian Peninsula, bordering Kuwait to the south and Iran to the east. The capital is the city of Basra, located in the Basrah district. Other districts of Basra include Al-Qurna, Al-Zubair, Al-Midaina, Shatt Al-Arab, Abu Al-Khaseeb and Al-Faw located on the Persian Gulf. It is the only governorate with a coastline.
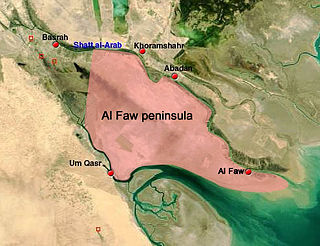
The Al-Faw peninsula is a peninsula in the Persian Gulf, located in the extreme southeast of Iraq. The marshy peninsula is 20 km (12 mi) southeast of Iraq's third largest city, Basra, and is part of a delta for the Shatt al-Arab river, formed by the confluence of the major Euphrates and Tigris rivers. The al-Faw peninsula borders Iran to the northeast, with the cities of Abadan and Khorramshahr on the opposite side of the Shatt al-Arab, and Kuwait to the southwest, opposite from Bubiyan Island and Warbah Island, near the Iraqi city of Umm Qasr.

Al-Fāw is a port town on Al-Faw Peninsula in Iraq near the Shatt al-Arab and the Persian Gulf. The Al Faw Peninsula is part of the Basra Governorate.
The Khawr Abd Allah is today an estuary, but once was the point where the Shatt al-Arab emptied into the Persian Gulf. It is located in southern Iraq and northern Kuwait. Both countries' border divides the lower portion of the estuary, but adjacent to the port of Umm Qasr, the estuary becomes wholly Iraqi. The Shatt al-Arab is now the from which the rivers drain out and is east of the Khawr Abd Allah. As the estuary extends northwestward into Iraq, it changes its name to Khawr az-Zubayr at Umm Qasr. From that point, it links by canal again to the northwest and into the Tigris and Euphrates proper. It forms the northeastern coastline of Jazirat Bubiyan and the northern coastline of Jazirat Warbah. Both of these islands are officially Kuwait.

The Iraqi Naval Forces, or the Iraqi Navy, is the naval warfare service branch of the Armed forces of Iraq. Formed in 1937, initially as the Iraqi Coastal Defense Force, its primary responsibilities was the protection of Iraq's coastline and offshore assets, the official name was changed on 12 January 2005 to Iraqi Naval Forces

The Battle of Umm Qasr was the first military confrontation in the Iraq War. At the start of the war, one of the first objectives was the port of Umm Qasr. On 21 March 2003, as allied forces advanced across Southern Iraq, an amphibious landing force captured the new port area of Umm Qasr. The assault was spearheaded by Royal Marines of the British 3 Commando Brigade, augmented by U.S. Marines of the American 15th MEU and Polish JW GROM troops. Iraqi forces in the old town of Umm Qasr put up unexpectedly strong resistance, requiring several days' fighting before the area was cleared of defenders. The port was finally declared safe and reopened on 25 March 2003.
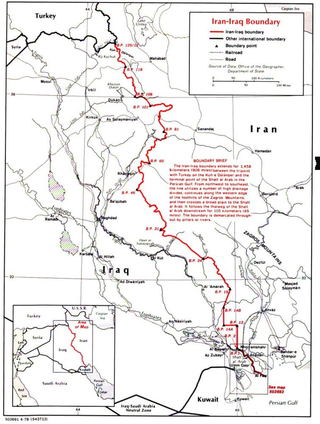
The Iran–Iraq border runs for 1,599 km (994 mi) from the tripoint with Turkey in the north down to the Shatt al-Arab waterway and out to the Persian Gulf in the south. Although the boundary was first determined in 1639, certain disputes continue, particularly surrounding navigation on the Shatt al-Arab.

The First Battle of al-Faw was a battle of the Iran–Iraq War, fought on the al-Faw peninsula between 10 February and 10 March 1986. The Iranian operation is considered to be one of Iran's greatest achievements in the Iran–Iraq War. The Iranians were able to capture the al-Faw peninsula, cutting off Iraqi access to the Persian Gulf in the process; this in turn hardened Iraqi attitudes to prosecute the war. The Faw peninsula was later recaptured by Iraqi forces near the end of the war.
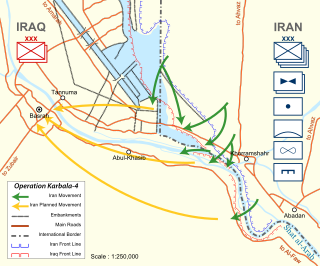
Operation Karbala-4 was an Iranian offensive in the Iran–Iraq War on the southern front. The operation was launched after the failure of Operation Karbala-2 and Operation Karbala-3 to move the Iraqi lines in an effort to capture Iraqi territory.

The Battle of Al Faw was one of the first battles of the Iraq War; it took place March 20-24, 2003.

The Sheikhdom of Kuwait was a sheikhdom which gained independence from the Khalidi Emirate of Al Hasa under Sabah I bin Jaber in the year 1752. The Sheikhdom became a British protectorate between 1899 and 1961 after the Anglo-Kuwaiti agreement of 1899 was signed between Sheikh Mubarak Al-Sabah and the British government in India due to threats to Kuwait's independence from the Ottoman Empire.
The Gulf War began on the 2 August 1990, when Iraq invaded Kuwait. The war was fought between the international coalition led by the United States of America against Iraq. Saddam Hussein's rationale behind the invasion is disputed and largely unknown. No Iraqi document has ever been discovered explicitly listing these.


















