
RFA Sir Galahad (L3005) was a Round Table-class landing ship logistics vessel belonging to the Royal Fleet Auxiliary (RFA) of the United Kingdom. The ship saw service in the Falklands War of 1982, where she was bombed and set afire at Fitzroy on 8 June.

USS Ponce, was an Austin-class amphibious transport dock, formerly in service with the United States Navy. She has been the only ship of the Navy named for Ponce in the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, which in turn was named after the Spanish explorer Juan Ponce de León, the first governor of Puerto Rico and the European discoverer of Florida. Her keel was laid down on 31 October 1966 by the Lockheed Shipbuilding and Construction Company of Seattle, Washington. She was launched on 20 May 1970 sponsored by Florence W. Hyland, the wife of Admiral John J. Hyland, and commissioned on 10 July 1971. She spent most of her career based on the East Coast and operating in the Atlantic Ocean and Mediterranean Sea, serving in Operation Desert Shield and supporting US operations in the 2011 Libyan Civil War.

RFA Sir Bedivere (L3004) was a Landing Ship Logistic of the Round Table class. She saw service in the Falklands War, the Persian Gulf and Sierra Leone. In 2009, she was commissioned into the Brazilian Navy and renamed NDCC Almirante Saboia (G-25), where she saw service in Haiti.

RFA Sir Percivale (L3036) was a Round Table class landing ship logistics (LSL) vessel belonging to the Royal Fleet Auxiliary of the United Kingdom.

TV Sir Tristram (L3505) formerly RFA Sir Tristram, is a Round Table-class landing ship logistics that was converted to a Special Forces Training Vessel in 2008. She was launched in 1966, and accepted into British Army service in 1967. As with others of her class, she was transferred to the Royal Fleet Auxiliary in 1970, and was crewed by British officers and Hong Kong Chinese sailors. The ship saw service in the Falklands War of 1982, and was badly damaged at Fitzroy on 8 June.

RFA Bayleaf (A109) was a Leaf-class support tanker of the Royal Fleet Auxiliary (RFA), the naval auxiliary fleet of the United Kingdom, which served with the fleet for 30 years, tasked with providing fuel, food, fresh water, ammunition and other supplies to Royal Navy vessels around the world.

NRP Bérrio (A5210) was a fleet support tanker of the Portuguese Navy. She was built by Swan Hunter in 1969 at Hebburn, England as RFA Blue Rover (A270) of the Rover-class and from 1970 to 1993 was part of the British Royal Fleet Auxiliary. In 1982 during her British service she participated in the Falklands War.

RFA Sir Lancelot (L3029) was the lead ship and prototype of the Round Table class landing ship logistics, an amphibious warfare design operated by the British Armed Forces.

HMAS Choules (L100) is a Bay-class landing ship that served with the Royal Fleet Auxiliary (RFA) from 2006 to 2011, before being purchased by the Royal Australian Navy (RAN). The vessel was built as RFA Largs Bay by Swan Hunter in Wallsend, Tyne and Wear. She was named after Largs Bay in Ayrshire, Scotland, and entered service in November 2006. During her career with the RFA, Largs Bay served as the British ship assigned to patrol the Falkland Islands in 2008, and delivered relief supplies following the 2010 Haiti earthquake.

HMS Andromeda was a Leander-class frigate of the Royal Navy. She was built at HM Dockyard Portsmouth. She was launched on 24 May 1967 and commissioned into the Royal Navy on 2 December 1968. She took part in the Falklands War. She was sold to India in 1995, for use as a training ship, being renamed INS Krishna. She was finally decommissioned in May 2012.

The Round Table class, also known as the Sir Lancelot class, was a British ship class designed for amphibious warfare missions in support of the main amphibious warfare ships. They were designated landing ship logistics (LSL).

The Bay class is a ship class of four dock landing ships built for the British Royal Fleet Auxiliary (RFA) during the 2000s. They are based on the Dutch-Spanish Royal Schelde Enforcer design, and replaced the Round Table-class logistics ships. Two ships each were ordered from Swan Hunter and BAE Systems Naval Ships. Construction work started in 2002, but saw major delays and cost overruns, particularly at Swan Hunter's shipyard. In mid-2006, Swan Hunter was stripped of work, and the incomplete second ship was towed to BAE's shipyard for completion. All four ships, Largs Bay, Lyme Bay, Mounts Bay, and Cardigan Bay had entered service by 2007.

USS Hermitage (LSD-34) was a Thomaston-class dock landing ship of the United States Navy. She was named for The Hermitage, President Andrew Jackson's estate just outside Nashville, Tennessee.

USS Cayuga (LST-1186) was a Newport-class tank landing ship of the United States Navy which replaced the traditional bow door-design tank landing ships (LSTs). The vessel was constructed by the National Steel and Shipbuilding Company in San Diego, California and was launched in 1969 and commissioned in 1970. Cayuga took part in the Vietnam War and Gulf War in American service. Decommissioned in 1994, the LST was transferred to the Brazilian Navy the same year on loan and renamed NDCC Mattoso Maia. The ship was purchased by Brazil outright in 2001. Mattoso Maia took part in MINUSTAH before being taken out of service in 2023.

The Battle of Umm Qasr was the first military confrontation in the Iraq War. At the start of the war, one of the first objectives was the port of Umm Qasr. On 21 March 2003, as allied forces advanced across Southern Iraq, an amphibious landing force captured the new port area of Umm Qasr. The assault was spearheaded by Royal Marines of the British 3 Commando Brigade, augmented by U.S. Marines of the American 15th MEU and Polish JW GROM troops. Iraqi forces in the old town of Umm Qasr put up unexpectedly strong resistance, requiring several days' fighting before the area was cleared of defenders. The port was finally declared safe and reopened on 25 March 2003.

The 1982 British military campaign to recapture the Falkland Islands depended on complex logistical arrangements. The logistical difficulties of operating 7,000 nautical miles from home were formidable. The Argentine invasion of the Falkland Islands came at a time when the Royal Navy was experiencing a reduction in its amphibious capability, but it still possessed the aircraft carriers HMS Hermes and Invincible, the landing platform dock (LPD) ships HMS Fearless and Intrepid, and six landing ship logistics (LSL) ships. To provide the necessary logistic support, the Royal Navy's ships were augmented by ships taken up from trade (STUFT).

Umm Qasr Port is Iraq's only deep water port, part of the city of Umm Qasr.

Atlantic Causeway was a container ship, operated by Cunard, and one of the merchant vessels requisitioned by the British government to support British forces in the Falklands War in 1982.
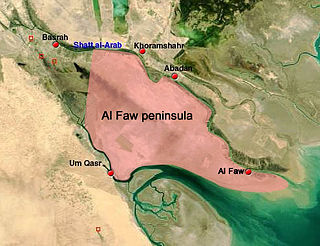
The Battle of Al Faw began on 20 March 2003 and continued for four days, as part of the 2003 invasion of Iraq.
























