
The former State Union of Serbia and Montenegro was represented at the Olympic Games on six occasions between 1996 and 2006, when the union was dissolved and Montenegro and Serbia each declared full independence.
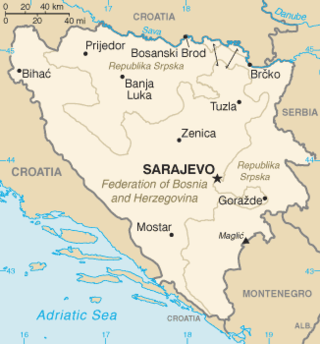
United Nations Security Council resolution 820, adopted on 17 April 1993, after reaffirming all previous resolutions on the topic for a lasting peace settlement in Bosnia and Herzegovina and the region, the council discussed the peace plan for Bosnia and Herzegovina and comprehensive steps to ensure its implementation.
United Nations Security Council resolution 838, adopted unanimously on 10 June 1993, after reaffirming Resolution 713 (1991) and all subsequent resolutions on the situation in the former Yugoslavia and in particular Bosnia and Herzegovina, the Council discussed options for the deployment of international observers on the borders of Bosnia and Herzegovina to ensure implementation of previous Security Council resolutions.
United Nations Security Council resolution 908, adopted unanimously on 31 March 1994, after reaffirming all resolutions on the situation in the former Yugoslavia and in particular Resolution 871 (1993), the council extended the mandate of the United Nations Protection Force (UNPROFOR) until 30 September 1994 and declared its intention to increase the number of personnel in the peacekeeping force.

United Nations Security Council resolution 943, adopted on 23 September 1994, after reaffirming all resolutions on the situation in Bosnia and Herzegovina, the Council suspended some restrictions against the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia and discussed the closure of the border between both countries.
United Nations Security Council resolution 967, adopted unanimously on 14 December 1994, after recalling all resolutions on the situation in the former Yugoslavia, in particular Resolution 757 (1992) and receiving letters from the chairman of the security council committee established in Resolution 727 (1992) and the United Nations Children's Fund which noted a resurgence in diphtheria and that the only available stocks of anti-serum to combat the condition were located in Serbia and Montenegro, the council, acting under Chapter VII of the United Nations Charter, authorised the export of 12,000 vials of diphtheria anti-serum from the country for a period of 30 days.
United Nations Security Council resolution 970, adopted on 12 January 1995, after reaffirming all resolutions on the situation in Bosnia and Herzegovina in particular Resolution 943 (1994) concerning the border closure between the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia and Bosnia and Herzegovina, the Council decided that measures in that resolution would be suspended for a further period of 100 days.

United Nations Security Council resolution 988, adopted on 21 April 1995, after reaffirming all resolutions on the situation in the former Yugoslavia, in particular resolutions 943 (1994) and 970 (1995), the Council noted measures by the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia to continue the border closure with Bosnia and Herzegovina and therefore extended the partial suspension of sanctions against Serbia and Montenegro for a further 75 days until 5 July 1995.

United Nations Security Council resolution 992, adopted unanimously on 11 May 1995, after reaffirming all resolutions on the situation in the former Yugoslavia, including 820 (1993), the Council addressed freedom of navigation in the Danube River.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1003, adopted on 5 July 1995, after reaffirming all resolutions on the situation in the former Yugoslavia, in particular resolutions 943 (1994), 970 (1995) and 988 (1995), the Council noted measures by the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia to continue the border closure with Bosnia and Herzegovina and therefore extended the partial suspension of sanctions against Serbia and Montenegro for an additional 75 days until 18 September 1995.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1021, adopted on November 22, 1995, after recalling all resolutions on the situation in the former Yugoslavia, particularly resolutions 713 (1991) and 727 (1992), the Council set a date of March 13, 1996, for the suspension of most aspects of the arms embargo on the former Yugoslavia. Resolution 1074 (1996) terminated the remaining measures of the embargo.
United Nations Security Council resolution 1022, adopted on 22 November 1995, after recalling all resolutions on the conflicts in the former Yugoslavia, the Council suspended measures in previous resolutions related to the former Yugoslavia.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1038, adopted unanimously on 15 January 1996, after recalling previous resolutions on Croatia including resolutions 779 (1992), 981 (1995) and 1025 (1995), the Council authorised the United Nations Mission of Observers in Prevlaka to continue monitoring the demilitarisation in the Prevlaka peninsula area of Croatia.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1066, adopted unanimously on 15 July 1996, after recalling previous resolutions on Croatia including resolutions 779 (1992), 981 (1995), 1025 (1995) and 1038 (1996), the Council authorised military observers to continue monitoring the demilitarisation in the Prevlaka peninsula area of Croatia until 15 January 1997.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1074, adopted unanimously on 1 October 1996, after recalling all resolutions on the conflicts in the former Yugoslavia and in particular Resolution 1022 (1995), the Council terminated all remaining measures against the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia from previous resolutions with immediate effect.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1082, adopted unanimously on 27 November 1996, after recalling previous resolutions including 1046 (1996) and 1058 (1996), the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Preventive Deployment Force (UNPREDEP) in Macedonia until 31 May 1997 and reduced its size.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1357, adopted unanimously on 21 June 2001, after recalling resolutions 1031 (1995), 1035 (1995), 1088 (1996), 1103 (1997), 1107 (1997), 1144 (1997), 1168 (1998), 1174 (1998), 1184 (1998), 1247 (1999) and 1305 (2000), the council extended the mandate of the United Nations Mission in Bosnia and Herzegovina (UNMIBH) for a period until 21 June 2002 and authorised states participating in the NATO-led Stabilisation Force (SFOR) to continue to do so for a further twelve months.
During the Yugoslav Wars of the 1990s and early 2000s, several rounds of international sanctions were imposed against the former Yugoslav republics of Serbia and Montenegro that formed a new country called the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia.
Serbia joined the United Nations on November 1, 2000, as the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. The previous Yugoslav state was one of the original 51 member states of the United Nations.

Democratic Federal Yugoslavia was a charter member of the United Nations from its establishment in 1945 as the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia until 1992 during the Yugoslav Wars. During its existence the country played a prominent role in the promotion of multilateralism and narrowing of the Cold War divisions in which various UN bodies were perceived as important vehicles. Yugoslavia was elected a non-permanent member of the United Nations Security Council on multiple occasions in periods between 1950 and 1951, 1956, 1972–1973, and 1988–1989, which was in total 7 years of Yugoslav membership in the organization. The country was also one of 17 original members of the Special Committee on Decolonization.
















