| UN Security Council Resolution 971 | |
|---|---|
This apartment block accommodated refugees from Abkhazia | |
| Date | 12 January 1995 |
| Meeting no. | 3,488 |
| Code | S/RES/971 (Document) |
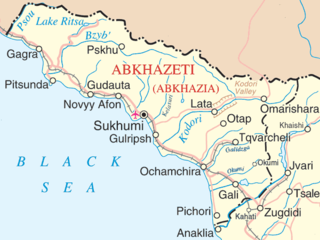
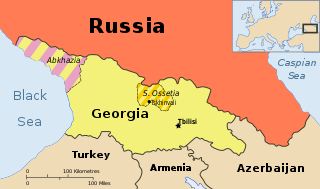
| Subject | Abkhazia, Georgia |
Voting summary | 15 voted for None voted against None abstained |
| Result | Adopted |
| Security Council composition | |
Permanent members | |
Non-permanent members | |
United Nations Security Council resolution 971, adopted unanimously on 12 January 1995, after reaffirming resolutions 849 (1993), 854 (1993), 858 (1993), 876 (1993), 881 (1993), 892 (1993), 896 (1994), 901 (1994), 906 (1994), 934 (1994) and 937 (1994), the Council extended the United Nations Observer Mission in Georgia (UNOMIG) until 15 May 1995. [1]
United Nations Security Council resolution 849, adopted unanimously on 9 July 1993, after noting with concern the recent fighting around Sukhumi in the disputed region of Abkhazia, the Council requested the Secretary-General Boutros Boutros-Ghali to send his Special Envoy to the region in order to reach agreement for a ceasefire between Abkhazia and Georgia, and once implemented, authorised a dispatch of 50 military observers. It was the first Security Council resolution on the conflict.

United Nations Security Council resolution 854, adopted unanimously on 6 August 1993, after recalling Resolution 849 (1993) which concerned a deployment of military observers if a ceasefire was observed between Abkhazia and Georgia, the Council noted that a ceasefire had been signed and approved a dispatch of 10 military observers to the area to observe the implementation of the ceasefire.

United Nations Security Council resolution 858, adopted unanimously on 24 August 1993, after recalling resolutions 849 (1993) and 854 (1993) and noting a ceasefire between Abkhazia and Georgia and commitments to withdraw forces, the Council established the United Nations Observer Mission in Georgia (UNOMIG) for an initial period of 90 days pending further extension.
Contents
The Security Council reaffirmed the sovereignty and territorial integrity of Georgia and the right to return of all refugees, on which an agreement was signed. The parties were urged not to undertake any unilateral actions that would impede the political process. There was a lack of progress on a comprehensive peace settlement and a slow return of refugees. In this regard the parties were called upon to work towards a settlement, particularly on the issue of the political status of Abkhazia. The Council expressed satisfaction at the co-operation between UNOMIG and the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) peacekeeping force.

Sovereignty is the full right and power of a governing body over itself, without any interference from outside sources or bodies. In political theory, sovereignty is a substantive term designating supreme authority over some polity.
Territorial integrity is the principle under international law that prohibits states from the use of force against the "territorial integrity or political independence" of another state. It is enshrined in Article 2(4) of the UN Charter and has been recognized as customary international law. Conversely it states that imposition by force of a border change is an act of aggression. It is a political term, for example when applied to a nation-state like Iraq, which has borders which were imposed at the end of WWI.

Georgia is a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia. Located at the crossroads of Western Asia and Eastern Europe, it is bounded to the west by the Black Sea, to the north by Russia, to the south by Turkey and Armenia, and to the southeast by Azerbaijan. The capital and largest city is Tbilisi. Georgia covers a territory of 69,700 square kilometres (26,911 sq mi), and its 2017 population is about 3.718 million. Georgia is a unitary semi-presidential republic, with the government elected through a representative democracy.
After extending the mandate of UNOMIG until 15 May 1995, the Secretary-General Boutros Boutros-Ghali was requested to report on the situation in Abkhazia and Georgia within two months from the adoption of the current resolution. Both parties, particularly the Abkhaz side, were urged to comply with their commitments concerning refugees and displaced persons. The Secretary-General was asked to co-operate with the CIS force in taking additional steps to ensure the return of refugees and displaced persons, while Member States were called upon to contribute to the voluntary fund established by the Agreement on a Cease-fire and Separation of Forces. [2]

Boutros Boutros-Ghali was an Egyptian politician and diplomat who was the sixth Secretary-General of the United Nations (UN) from January 1992 to December 1996. An academic and former Vice Foreign Minister of Egypt, Boutros-Ghali oversaw the UN at a time when it dealt with several world crises, including the breakup of Yugoslavia and the Rwandan genocide. He was then the first Secretary-General of the Organisation internationale de la Francophonie from 16 November 1997 to 31 December 2002.
The Agreement on a Cease-fire and Separation of Forces was signed by parties to the Georgian-Abkhazian conflict in Moscow on 14 May 1994. Also known as the 1994 Moscow Agreement, it was witnessed by United Nations, Russian Federation and Conference on Security and Cooperation in Europe representatives. The agreement was recognised in United Nations Security Council Resolution 934.