
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international peace and security, recommending the admission of new UN members to the General Assembly, and approving any changes to the UN Charter. Its powers as outlined in the United Nations Charter include establishing peacekeeping operations, enacting international sanctions, and authorizing military action. The UNSC is the only UN body with authority to issue resolutions that are binding on member states.

The United Nations General Assembly, UNGA; French: Assemblée générale des Nations unies, AGDNU is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN), serving as its main deliberative, policymaking, and representative organ. Currently in its 79th session, its powers, composition, functions, and procedures are set out in Chapter IV of the United Nations Charter.

The member states of the United Nations comprise 193 sovereign states. The United Nations (UN) is the world's largest intergovernmental organization. All members have equal representation in the UN General Assembly.

A United Nations Security Council resolution (UNSCR) is a United Nations resolution adopted by the Security Council (UNSC), the United Nations (UN) 15-member body charged with "primary responsibility for the maintenance of international peace and security".
A United Nations General Assembly resolution is a decision or declaration voted on by all member states of the United Nations in the General Assembly.

A United Nations resolution is a formal text adopted by a United Nations (UN) body. Although any UN body can issue resolutions, in practice most resolutions are issued by the Security Council or the General Assembly, in the form of United Nations Security Council resolutions and United Nations General Assembly resolutions, respectively.
The United Nations General Assembly has granted observer status to international organizations, entities, and non-member states, to enable them to participate in the work of the United Nations General Assembly, though with limitations. The General Assembly determines the privileges it will grant to each observer, beyond those laid down in a 1986 Conference on treaties between states and international organizations. Exceptionally, the European Union (EU) was in 2011 granted the right to speak in debates, to submit proposals and amendments, the right of reply, to raise points of order and to circulate documents, etc. As of May 2011, the EU is the only international organization to hold these enhanced rights, which has been likened to the rights of full membership, short of the right to vote.

The United Nations Security Council veto power is the power of the five permanent members of the UN Security Council to veto any decision other than a "procedural" decision.
Chapter VII of the United Nations Charter sets out the UN Security Council's powers to maintain peace. It allows the Council to "determine the existence of any threat to the peace, breach of the peace, or act of aggression" and to take military and nonmilitary action to "restore international peace and security".

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1680, adopted on May 17, 2006, after recalling previous resolutions on Lebanon, including 425 (1978), 426 (1978), 520 (1982), 1559 (2004) and 1655 (2005), the Council strongly encouraged Syria to respond positively to Lebanon's request to delineate borders and establish diplomatic relations, with the purpose of asserting Lebanon's sovereignty, territorial integrity and political independence.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1737 was unanimously passed by the United Nations Security Council on 23 December 2006.

The African Union-United Nations Hybrid Operation in Darfur was a joint African Union (AU) and United Nations (UN) peacekeeping mission formally approved by United Nations Security Council Resolution 1769 on 31 July 2007, to bring stability to the war-torn Darfur region of Sudan while peace talks on a final settlement continue.

Resolution 1973 was adopted by the United Nations Security Council on 17 March 2011 in response to the First Libyan Civil War. The resolution formed the legal basis for military intervention in the Libyan Civil War, demanding "an immediate ceasefire" and authorizing the international community to establish a no-fly zone and to use all means necessary short of foreign occupation to protect civilians.

The United Nations Supervision Mission in Syria (UNSMIS) was a United Nations peacekeeping mission in Syria, set up in 2012 as a result of United Nations Security Council Resolution 2043 in response to the Syrian Civil War. It was commanded by Norwegian Major General Robert Mood until 20 July 2012 followed by Lieutenant General Babacar Gaye from Senegal. Although observers remain in the country, Mood suspended their mission on June 16, 2012, citing "escalating violence". Observers will conduct no further patrols and stay in their current positions until the suspension is lifted. On 20 July 2012, the Security Council extended UNSMIS for a final period of 30 days. According to resolution 2059, the Council would only consider more extensions in the event that the Secretary-General reports and the Security Council confirms the cessation of the use of heavy weapons and a reduction in the level of violence sufficient by all sides to allow UNSMIS to implement its mandate.

The permanent members of the United Nations Security Council are the five sovereign states to whom the UN Charter of 1945 grants a permanent seat on the UN Security Council: China, France, Russia, United Kingdom, and United States.

The Republic of Korea and the Democratic People's Republic of Korea were simultaneously admitted to the United Nations (UN) in 1991. On 8 August 1991, the UN Security Council passed Resolution 702, recommending both states to the General Assembly for membership. On 17 September 1991, the General Assembly admitted both countries under Resolution 46/1.
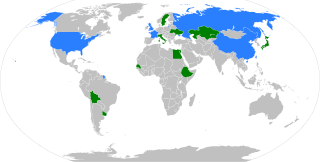
The 2016 United Nations Security Council election was held on 28 June during the 70th session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The elections were for five non-permanent seats on the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 2017. In accordance with the Security Council's rotation rules, whereby the ten non-permanent UNSC seats rotate among the various regional blocs into which UN member states traditionally divide themselves for voting and representation purposes, the five available seats were allocated as follows:

United Nations General Assembly Resolution ES‑11/1 is a resolution of the eleventh emergency special session of the United Nations General Assembly, adopted on 2 March 2022. It deplored Russia's invasion of Ukraine and demanded a full withdrawal of Russian forces and a reversal of its decision to recognise the self-declared People's Republics of Donetsk and Luhansk.












