
The Peace and Security Council (PSC) is the organ of the African Union in charge of enforcing union decisions. It is patterned somewhat after the United Nations Security Council. The PSC is also the main pillar of the African Peace and Security Architecture (APSA), and works with other pillars of the APSA in order to promote "peace, security and stability in Africa". The specific goal of the Peace and Security Council (PSC) is the "prevention, management and resolution of conflicts". To achieve these goals, it involves subsidiary organizations such as the Military Staff Committee and the Committee of Experts.

The United Nations Security Council veto power is the power of the five permanent members of the UN Security Council to veto any decision other than a "procedural" decision.
The responsibility to protect is a global political commitment which was endorsed by the United Nations General Assembly at the 2005 World Summit in order to address its four key concerns to prevent genocide, war crimes, ethnic cleansing and crimes against humanity. The doctrine is regarded as a unanimous and well-established international norm over the past two decades.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1244, adopted on 10 June 1999, after recalling resolutions 1160 (1998), 1199 (1998), 1203 (1998) and 1239 (1999), authorised an international civil and military presence in the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia and established the United Nations Interim Administration Mission in Kosovo (UNMIK). It followed an agreement by Yugoslav President Slobodan Milošević to terms proposed by President of Finland Martti Ahtisaari and former Prime Minister of Russia Viktor Chernomyrdin on 8 June, involving withdrawal of all Yugoslav state forces from Kosovo.

Peace enforcement is the use of various tactics, most notably military force to compel peace in a conflict, generally against the will of combatants. Peace enforcement missions permit the use of non-defensive armed force, unlike peacekeeping operations. Only the United Nations, through its Security Council per Chapter VII of its charter, has the ability to authorize peace enforcement missions.
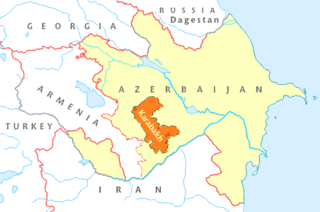
United Nations Security Council resolution 874, adopted unanimously on 14 October 1993, reaffirmed sovereignty and territorial integrity of the Azerbaijani Republic and of all other States in the region, called for the preservation of the ceasefire, cessation of hostilities and withdrawal of forces from recently occupied districts of the Republic of Azerbaijan, and reaffirmed resolutions 822 (1993) and 853 (1993). The Council expressed its concern at "...the conflict in and around the Nagorny Karabakh region of the Azerbaijani Republic, and of the tensions between the Republic of Armenia and the Azerbaijani Republic...", and called upon the parties to observe the ceasefire agreed with by the government of Russia and OSCE Minsk Group.

United Nations Security Council resolution 788, adopted unanimously on 19 November 1992, after determining that the deterioration of the situation in Liberia constituted a threat to international peace and security, the council imposed an arms embargo on the country for the purposes of establishing peace and stability.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1125, adopted unanimously on 6 August 1997, after expressing concern at the situation facing the Central African Republic, the Council authorised the continuation of the Inter-African Mission to Monitor the Implementation of the Bangui Agreements (MISAB) mission in the country for a further three months.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1197, adopted unanimously on 18 September 1998, after reaffirming its primary responsibility to maintain international peace and security, the Council addressed co-operation efforts with the Organisation of African Unity (OAU).

United Nations Security Council resolution 1209, adopted unanimously on 19 November 1998, after recalling resolutions 1170 (1998) and 1196 (1998) on Africa, the Council addressed illicit arms flows on the continent.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1301, adopted on 31 May 2000, after recalling all previous resolutions on the question of the Western Sahara, in particular resolutions 1108 (1997) and 1292 (2000), the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Mission for the Referendum in Western Sahara (MINURSO) until 31 July 2000.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1350, adopted unanimously on 27 April 2001, after recalling resolutions 808 (1993), 827 (1993), 1166 (1998) and 1329 (2000), the Council forwarded a list of nominees for permanent judges at the International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia (ICTY) to the General Assembly for consideration.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 2016 was unanimously adopted on 27 October 2011 on the situation of Libya during the Libyan Civil War.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 2033 was unanimously adopted on 12 January 2012 on relationship with African Union relating to conflict prevention.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 2056 was unanimously adopted on 5 July 2012.

The Mali War is an ongoing conflict that started in January 2012 between the northern and southern parts of Mali in Africa. On 16 January 2012, several insurgent groups began fighting a campaign against the Malian government for independence or greater autonomy for northern Mali, which they called Azawad. The National Movement for the Liberation of Azawad (MNLA), an organization fighting to make this area of Mali an independent homeland for the Tuareg people, had taken control of the region by April 2012.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 2085, adopted unanimously on 20 December 2012, authorized the deployment of the African-led International Support Mission to Mali (AFISMA). The resolution recalled previous resolutions regarding the Northern Mali conflict, including resolutions 2056 and 2071 in authorizing action. According to Ban Ki-moon, the resolution "aimed at the full restoration of Mali’s constitutional order and territorial integrity."
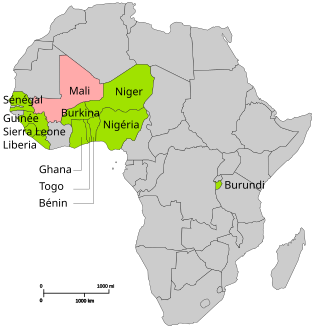
The African-led International Support Mission to Mali (AFISMA) was an Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) organized military mission sent to support the government of ECOWAS member nation Mali against Islamist rebels in the Northern Mali conflict. The mission was authorized with UN Security Council Resolution 2085, passed on 20 December 2012, which "authorizes the deployment of an African-led International Support Mission in Mali (AFISMA) for an initial period of one year. The AFISMA mission transferred its authority to MINUSMA on 1 July 2013, that is, AFISMA mission ended and MINUSMA mission began, with AFISMA troops becoming MINUSMA troops.

The following is a timeline of major events during the Northern Mali conflict.

















