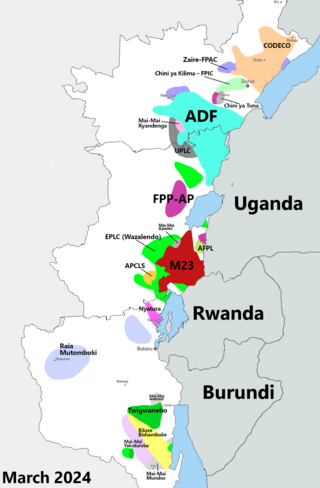
The Kivu conflict is an umbrella term for a series of protracted armed conflicts in the North Kivu and South Kivu provinces in the eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo which have occurred since the end of the Second Congo War. Including neighboring Ituri province, there are more than 120 different armed groups active in the eastern Democratic Republic of Congo. Currently, some of the most active rebel groups include the Allied Democratic Forces, the Cooperative for the Development of the Congo, the March 23 Movement, and many local Mai Mai militias. In addition to rebel groups and the governmental FARDC troops, a number of national and international organizations have intervened militarily in the conflict, including the United Nations force known as MONUSCO, and an East African Community regional force.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1304, adopted unanimously on 16 June 2000, after recalling resolutions 1234 (1999), 1258 (1999), 1273 (1999), 1279 (1999), 1291 (1999) and 1296 (2000) on situation in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Council demanded the immediate withdrawal of Ugandan, Rwandan, Congolese opposition and other armed groups from Kisangani in the Democratic Republic of the Congo.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1493, adopted unanimously on 28 July 2003, after recalling all resolutions on the situation in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the council extended the mandate of the United Nations Mission in the Democratic Republic of Congo (MONUC) until 30 July 2004 and raised its troop level from 8,700 to 10,800.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1533, adopted unanimously on 12 March 2004, after recalling all previous resolutions on the situation in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the council established a committee to monitor an arms embargo imposed on all foreign and Congolese forces in the east of the country.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1552, adopted unanimously on 27 July 2004, after recalling all previous resolutions on the situation in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, including resolutions 1493 (2003) and 1533 (2004), the council extended the arms embargo against movements and armed groups in the country until 31 July 2005.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1946, adopted unanimously on October 15, 2010, after recalling previous resolutions on the situation in Côte d'Ivoire, including resolutions 1880 (2009), 1893 (2009), 1911 (2010) and 1933 (2010), the Council extended sanctions against the country, including an arms embargo and ban on the trading of diamonds, for a further six months.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1565, adopted unanimously on 1 October 2004 after recalling all previous resolutions on the situation in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, extended the mandate of the United Nations Mission in the Democratic Republic of Congo (MONUC) until 31 March 2005 and authorised an additional deployment of 5,900 troops and police. It reaffirmed the commitment to respect the “sovereignty, territorial integrity and political independence [sic]” of Congo and States in the region.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1952, adopted unanimously on November 29, 2010, after recalling previous resolutions on the situation in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, including resolutions 1807 (2008), 1857 (2008) and 1896 (2009), the Council renewed an arms embargo and related targeted sanctions for a further period until November 30, 2011.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1592, adopted unanimously on 30 March 2005, after recalling all previous resolutions on the situation in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, including Resolution 1565 (2004), the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Mission in the Democratic Republic of Congo (MONUC) until 1 October 2005.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1596, adopted unanimously on 18 April 2005, after recalling all previous resolutions on the situation in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, including resolutions 1493 (2003), 1533 (2004), 1552 (2004), 1565 (2004) and 1592 (2005), the council expanded the arms embargo to include all recipients of weapons in the country, and imposed a travel ban and asset freeze on those violating the embargo.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1643, adopted unanimously on 15 December 2005, after recalling previous resolutions on the situation in Côte d'Ivoire, the Council extended an arms embargo and travel and financial restrictions against the country until 15 December 2006, and included a ban on the trade of diamonds.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1649, adopted unanimously on 21 December 2005, after recalling all previous resolutions on the situation in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, including resolutions 1533 (2004), 1565 (2004), 1592 (2005), 1596 (2005) and 1616 (2005), 1621 (2005) and 1628 (2005), the council extended and expanded sanctions against the country until 31 July 2006, and demanded that foreign fighters disarm or face sanctions.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1698, adopted unanimously on July 31, 2006, after recalling all previous resolutions concerning the situation in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, including resolutions 1493 (2003), 1533 (2004), 1552 (2004), 1565 (2004), 1592 (2005), 1596 (2005), 1616 (2005), 1649 (2005) and 1654 (2006), the Council renewed sanctions against the country until July 31, 2007.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 2002, adopted unanimously on July 29, 2011, after recalling resolutions 733 (1992), 1519 (2003), 1558 (2004), 1587 (2004), 1630 (2005), 1676 (2006), 1724 (2006), 1744 (2007), 1766 (2007), 1772 (2007), 1801 (2008), 1811 (2008), 1844 (2008), 1853 (2008), 1862 (2009), 1907 (2009), 1916 (2010) and 1972 (2011), the Council tightened sanctions against Eritrea and Somalia to include individuals and entities recruiting or using child soldiers in the Somali Civil War, in addition to those responsible for attacks against schools and hospitals in Somalia.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 1771 was unanimously adopted on 10 August 2007.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 1896 was unanimously adopted on 30 November 2009.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 1807 was unanimously adopted on 31 March 2008.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 1857 was unanimously adopted on 22 December 2008.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 2021 was unanimously adopted on 29 November 2011.

The March 23 Movement, often abbreviated as M23 and also known as the Congolese Revolutionary Army, is a Congolese Tutsi-led rebel military group. Based in eastern areas of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), it operates mainly in the province of North Kivu, which borders both Uganda and Rwanda. The M23 rebellion of 2012 to 2013 against the DRC government led to the displacement of large numbers of people. On 20 November 2012, M23 took control of Goma, a provincial capital with a population of a million people, but it was requested to evacuate it by the International Conference on the Great Lakes Region because the DRC government had finally agreed to negotiate. In late 2012, Congolese troops, along with UN troops, retook control of Goma, and M23 announced a ceasefire and said that it wanted to resume peace talks.
















