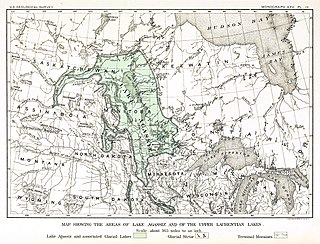
Lake Agassiz was a large glacial lake in central North America. Fed by glacial meltwater at the end of the last glacial period, its area was larger than all of the modern Great Lakes combined, although its mean depth was not as great as that of many major lakes today.

The Continental Divide National Scenic Trail is a United States National Scenic Trail with a length measured by the Continental Divide Trail Coalition of 3,028 miles (4,873 km) between the U.S. border with Chihuahua, Mexico and the border with Alberta, Canada. Frequent route changes and a large number of alternate routes result in the actual hiking distance to be between 2,700 miles (4,300 km) and 3,150 miles (5,070 km). The CDT follows the Continental Divide of the Americas along the Rocky Mountains and traverses five U.S. states — Montana, Idaho, Wyoming, Colorado, and New Mexico. In Montana near the Canadian border the trail crosses Triple Divide Pass (near Triple Divide Peak, from which waters may flow to either the Arctic Ocean, Atlantic Ocean or Pacific Ocean.

Lake Missoula was a prehistoric proglacial lake in western Montana that existed periodically at the end of the last ice age between 15,000 and 13,000 years ago. The lake measured about 7,770 square kilometres (3,000 sq mi) and contained about 2,100 cubic kilometres (500 cu mi) of water, half the volume of Lake Michigan.

Flathead Lake is a large natural lake in northwest Montana and is the largest natural freshwater lake by surface area that is west of the source of the Missouri River in the contiguous United States.

The Anaconda–Pintler Wilderness is located in southwestern Montana, in the northwestern United States. It runs for 40 miles (64 km) along both sides of the crest of the Anaconda Range, covering almost 250 square miles (650 km2). To the north are the Sapphire Mountains, and to the south is the Big Hole Valley. Elevations range from about 5,000 feet (1,500 m) up to 10,793 feet (3,290 m) at West Goat Peak. West Pintler Peak, located in a more commonly visited area, rises to 9,894 feet (3,016 m). Visitors can most easily access this area via trailheads at Pintler Lake to the south, and at Lutz Creek and Moose Lake to the north. The wilderness lies in parts of Deer Lodge, Granite, Ravalli, and Beaverhead counties.

The Livingston Range is a mountain range located primarily in Glacier National Park in the U.S. state of Montana, and in the extreme southeastern section of the Canadian province of British Columbia. The range is 36 miles (58 km) long and 28 miles (45 km) wide. Over 15 summits exceed 9,000 ft (2,700 m) above sea level, and the highest point is Kintla Peak at 10,101 feet (3,079 m).

Kintla Peak is a pyramidal peak in the Livingston Range of Glacier National Park in the U.S. state of Montana. It is the tallest mountain in the Livingston Range and the third-tallest in the park. It is also the most northerly peak and land area in the contiguous United States above 10,000 ft (3,000 m). The Agassiz Glacier lies below it to the southeast.

Kinnerly Peak is located in the Livingston Range, Glacier National Park in the U.S. state of Montana. It is approximately 1 mile (1.6 km) north of Kintla Peak, the highest peak in the Livingston Range, and 3 miles (4.8 km) south of the Canada–United States border. Both peaks are in the remote northwest corner of the park. Kinnerly Peak is the eighth tallest peak in Glacier National Park.

Blodgett Canyon is located in southwestern Montana in the northwestern United States. It is one of more than two dozen scenic canyons deeply carved into the eastern flanks of the Bitterroot Range in Bitterroot National Forest. Starting from a group of peaks at over 8,500 feet along the Idaho/Montana border, the canyon steeply drops to Blodgett Lake at 6,800 feet. After running northeast for about a mile, it turns due east and descends for a total of about 12 miles (19 km) to the Bitterroot Valley. A trailhead is located at the mouth of the canyon, just west of the community of Hamilton and at an elevation of 4,000 feet (m).

The Cook–Folsom–Peterson Expedition of 1869 was the first organized expedition to explore the region that became Yellowstone National Park. The privately financed expedition was carried out by David E. Folsom, Charles W. Cook and William Peterson of Diamond City, Montana, a gold camp in the Confederate Gulch area of the Big Belt Mountains east of Helena, Montana. The journals kept by Cook and Folsom, as well as their personal accounts to friends were of significant inspirational value to spur the organization of the Washburn-Langford-Doane Expedition which visited Yellowstone in 1870.

The geography of New York state varies widely. Most of New York is dominated by farms, forests, rivers, mountains, and lakes. New York's Adirondack Park is larger than any U.S. National Park in the contiguous United States. Niagara Falls, on the Niagara River as it flows from Lake Erie to Lake Ontario, is a popular attraction. The Hudson River begins near Lake Tear of the Clouds and flows south through the eastern part of the state without draining lakes George or Champlain. Lake George empties at its north end into Lake Champlain, whose northern end extends into Canada, where it drains into the Richelieu River and then the St. Lawrence. Four of New York City's five boroughs are on the three islands at the mouth of the Hudson River: Manhattan Island, Staten Island, and Brooklyn and Queens on Long Island.

Balsam Lake Mountain is one of the Catskill Mountains, located in the Town of Hardenburgh, New York, United States. It is the westernmost of the range's 35 High Peaks. Its exact height has not been determined, but the highest contour line on topographic maps, 3,720 feet (1,130 m), is usually given as its elevation.

The following articles relate to the history, geography, geology, flora, fauna, structures and recreation in Glacier National Park (U.S.), the U.S. portion of the Waterton-Glacier International Peace Park.

Long Knife Peak is located in the Clark Range, Glacier National Park in the U.S. state of Montana. Though much of the mountain slopes extend into the Canadian Province of British Columbia, the main summit is in the U.S. Long Knife Peak rises more than a vertical 1 mile (1.6 km) above Upper Kintla Lake. It is also the most northerly peak and land area in the contiguous United States above 9,000 feet (2,743 m). Long Knife Peak is on an east west ridgeline identified as the "Boundary Mountains" on the USGS 7.5 minute topo quad and this extended ridge, with peak 8864, also contains the most northerly named (numbered) peak and land area in the contiguous United States above 8,000 feet (2,438 m).

Numa Peak is located in the Livingston Range, Glacier National Park in the U.S. state of Montana. The small Baby Glacier is below the peak to the immediate northeast. Numa Peak is the high point along Numa Ridge and rises almost 5,000 feet (1,500 m) above Bowman Lake.

Parke Peak is located in the Livingston Range, Glacier National Park in the U.S. state of Montana. Harris Glacier is immediately northeast of Parke Peak.

Baby Glacier is a glacier located in the U.S. state of Montana in Glacier National Park. Baby Glacier is situated in a cirque on the northeast slope of Numa Peak at an elevation between 7,200 feet (2,200 m) and 6,800 feet (2,100 m) above sea level. The glacier covers approximately 19 acres (0.077 km2) and does not meet the threshold of 25 acres (0.10 km2) often cited as being the minimum size to qualify as an active glacier. Between 1966 and 2005, Baby Glacier lost a third of its surface area.

Kintla Glacier is in Glacier National Park in the U.S. state of Montana. The glacier is situated on a plateau 2 miles (3.2 km) southwest of Kintla Peak at an elevation between 8,700 feet (2,700 m) and 7,700 feet (2,300 m) above sea level. The glacier has numerous crevasses and is actually two glaciers with a combined area of 280 acres (110 ha) as of 2005. This is a 34 percent decrease in area from 1966.

Smoky Dome, at 10,095 feet (3,077 m) above sea level is the highest peak in the Soldier Mountains of Idaho. Smoky Dome is located northwest of Fairfield in Camas County and Sawtooth National Forest.















