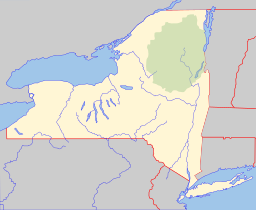
Harrietstown is a town in Franklin County, New York, United States. The total population was 5,709 at the 2010 census, of whom 3,879 lived in the village of Saranac Lake on the eastern side of the town.

Seneca Ray Stoddard (1844–1917) was an American landscape photographer known for his photographs of New York's Adirondack Mountains. He was also a naturalist, a writer, a poet, an artist, and a cartographer. His writings and photographs helped to popularize the Adirondacks.

Eagle Island Camp, also known as Camp Eagle Island or simply EIC, is a youth summer camp and former Girl Scout camp located on Eagle Island on Upper Saranac Lake in New York's Adirondack region. The site is listed on the National Register of Historic Places.

The Great Camps of the Adirondack Mountains refers to the grandiose family compounds of cabins that were built in the latter half of the nineteenth century on lakes in the Adirondacks such as Spitfire Lake and Rainbow Lake. The camps were summer homes for the wealthy, where they could relax, host or attend parties, and enjoy the wilderness. In time, however, this was accomplished without leaving the comforts of civilization behind; some great camps even contained a bowling alley or movie theatre.

Adirondack Architecture refers to the rugged architectural style generally associated with the Great Camps within the Adirondack Mountains area in New York. The builders of these camps used native building materials and sited their buildings within an irregular wooded landscape. These camps for the wealthy were built to provide a primitive, rustic appearance while avoiding the problems of in-shipping materials from elsewhere.
Lake Clear is a hamlet and a lake in Franklin County, New York, United States. The area is named for 940-acre (3.8 km2) Lake Clear, part of the original Seven Carries canoe route. It is located in the town of Harrietstown.

The High Peaks Wilderness Area, the largest Forest Preserve unit in the U.S. state of New York, is located in three counties and six towns in the Adirondack Park: Harrietstown in Franklin County, North Elba, Keene, North Hudson and Newcomb in Essex County and Long Lake in Hamilton County.

742-acre (3.00 km2) Upper St. Regis Lake is a part of the St. Regis River in the Adirondacks in northern New York State. Along with Lower St. Regis Lake and Spitfire Lake, it became famous in the late 19th century as a summer playground of America's power elite, drawn to the area by its scenic beauty and by the rustic charms of Paul Smith's Hotel. It is the site of many grand old summer "cottages" and Great Camps, including Marjorie Merriweather Post's Topridge. Frederick W. Vanderbilt, Anson Phelps Stokes and Whitelaw Reid were among the summer residents. "The camps of many of these families began as tent colonies, with separate units for sleeping, dining, games, and so on, and evolved into permanent structures built with understated taste."

Knollwood Club is an Adirondack Great Camp on Shingle Bay, Lower Saranac Lake, near the village of Saranac Lake, New York, USA. It was built in 1899–1900 by William L. Coulter, who had previously created a major addition to Alfred G. Vanderbilt's Sagamore Camp. The "club" consisted of a boathouse, "casino", and six identical 2+1⁄2-story shingle cottages, which were distinguished by unique twig work facades.

Lower Saranac Lake is one of three connected lakes, part of the Saranac River, near the village of Saranac Lake in the Adirondacks in northern New York. With Middle Saranac Lake and Upper Saranac Lake, a 17-mile (27 km) paddle with only one portage is possible. The Saranac Lake Islands Public Campground provides 87 campsites on inlands in Lower and Middle Saranac Lake. In addition to the Saranac River, it is fed by nearby Lake Colby, Fish Creek, and Lilly Pad Pond. Lower Saranac Lake is located in the town of Harrietstown, New York. The lake, along with both Upper and Middle Saranac Lakes, is also part of the 740-mile Northern Forest Canoe Trail, which begins in Old Forge, NY and ends in Fort Kent, ME.

Spitfire Lake is a part of the St. Regis River in the Adirondacks in northern New York State and is 250-acre (1.0 km2) in area. Along with Upper and Lower St. Regis Lake, it became famous in the late 19th century as a summer playground of America's power elite, drawn to the area by its scenic beauty and by the rustic charms of Paul Smith's Hotel. It is the site of many grand old summer "cottages" and Great Camps; Frederick W. Vanderbilt, Anson Phelps Stokes and Whitelaw Reid were among the summer residents. "The camps of many of these families began as tent colonies, with separate units for sleeping, dining, games, and so on, and evolved into permanent structures built with understated taste."

Moss Ledge is an Adirondack Great Camp designed by William L. Coulter in 1898 for Isabel Ballantine of New York City. Ballantine was the granddaughter of Newark beer baron, John Holmes Ballantine.

Prospect Point Camp is an Adirondack Great Camp notable for its unusual chalets inspired by hunting lodges. William L. Coulter's design is a significant example of the Adirondack Rustic style. It is located on a bluff overlooking the northern reaches of Upper Saranac Lake, near Eagle Island Camp and Moss Ledge, two other Coulter designs. Its grand scale is typical of the opulent camps of the area in the great camp era. The camp was built for New York copper magnate and financier Adolph Lewisohn.

Between 1873 and 1945, Saranac Lake, New York became a world-renowned center for the treatment of tuberculosis, using a treatment that involved exposing patients to as much fresh air as possible under conditions of complete bed-rest. In the process, a specific building type, the "Cure Cottage", developed, built by residents seeking to capitalize on the town's fame, by physicians, and often by the patients themselves. Many of these structures are extant, and their historic value has been recognized by listing on The National Register of Historic Places.

The Seven Carries is an historic canoe route from Paul Smith's Hotel to the Saranac Inn through what is now known as the Saint Regis Canoe Area in southern Franklin County, New York in the Adirondack Park. The route was famous with sportsmen and tourists from major east-coast cities from the late 19th century through the 1930s; interest has revived in recent years. Despite the name, the route consists of only six carries, or portages.
The Saranac Inn was a large, luxurious hotel located on a peninsula at the northern end of the Upper Saranac Lake in the town of Santa Clara in the Adirondacks in New York State, United States. It was frequented by US Presidents Grover Cleveland and Chester A. Arthur and New York Governor Charles Evans Hughes. It closed in 1962, and burned to the ground in 1978.

William Lincoln Coulter (1865–1907) was an American architect who came to Saranac Lake, New York in the spring of 1896 in an effort to cure his tuberculosis, and stayed to design some of the finest Adirondack Great Camps and Cure Cottages in the area. Among the camps he designed were Knollwood Club, Camp Eagle Island and Prospect Point Camp; Camp Eagle Island has been designated a US National Historic Landmark. In Saranac Lake, in 1903, he designed a house at 147 Park Avenue for Thomas Bailey Aldrich, editor of the Atlantic Monthly, that wits dubbed "The Porcupine" because it had so many fine points and belonged to a "quill pusher". He also designed the Coulter Cottage, built between 1897 and 1899.

The Adirondack Canoe Classic, also known as the 90-miler, is a three-day, 90-mile (140 km) canoe race from Old Forge to Saranac Lake in the Adirondacks of New York, United States. The race has drawn as many as 500 competitors from California to Florida, New Zealand and Canada paddling 250 canoes, kayaks and guideboats. Included in the ninety mile length is 5.25 miles (8.45 km) of carries.

William G. Distin (1884–1970), an architect of Saranac Lake, New York, was an early associate of Great Camp designer William L. Coulter who went on to design a number of Adirondack Great Camps.

4,077-acre Long Lake is a 14-mile (23 km) lake in the town of Long Lake in Hamilton County, New York in the United States; the average width is half a mile. It is part of the Raquette River, which flows in a straight, northeast-trending valley. NY 30 crosses at a narrows 4 miles (6.4 km) from the south end where the hamlet of Long Lake is located. There are two public beaches and a state boat launch. More than half of the shoreline is part of the New York State Forest preserve. The northern end of the lake is undeveloped. The lake is also part of the 740-mile Northern Forest Canoe Trail, which begins in Old Forge, NY and ends in Fort Kent, ME. The Long Lake Camp for the Arts is based on the west side of the lake.