Related Research Articles

VMware, Inc. is an American cloud computing and virtualization technology company with headquarters in Palo Alto, California. VMware was the first commercially successful company to virtualize the x86 architecture.

NetApp, Inc. is an American hybrid cloud data services and data management company headquartered in San Jose, California. It has ranked in the Fortune 500 from 2012–2021. Founded in 1992 with an IPO in 1995, NetApp offers cloud data services for management of applications and data both online and physically.
The IBM SAN Volume Controller (SVC) is a block storage virtualization appliance that belongs to the IBM System Storage product family. SVC implements an indirection, or "virtualization", layer in a Fibre Channel storage area network (SAN).
Gluster Inc. was a software company that provided an open source platform for scale-out public and private cloud storage. The company was privately funded and headquartered in Sunnyvale, California, with an engineering center in Bangalore, India. Gluster was funded by Nexus Venture Partners and Index Ventures. Gluster was acquired by Red Hat on October 7, 2011.
Desktop virtualization is a software technology that separates the desktop environment and associated application software from the physical client device that is used to access it.

VMware ESXi is an enterprise-class, type-1 hypervisor developed by VMware for deploying and serving virtual computers. As a type-1 hypervisor, ESXi is not a software application that is installed on an operating system (OS); instead, it includes and integrates vital OS components, such as a kernel.
Virtual Iron Software, was located in Lowell, Massachusetts, sold proprietary software for virtualization and management of a virtual infrastructure. Co-founded by Alex Vasilevsky, Virtual Iron figured among the first companies to offer virtualization software to fully support Intel VT-x and AMD-V hardware-assisted virtualization.

oVirt is a free, open-source virtualization management platform. It was founded by Red Hat as a community project on which Red Hat Virtualization is based. It allows centralized management of virtual machines, compute, storage and networking resources, from an easy-to-use web-based front-end with platform independent access. KVM on x86-64, PowerPC64 and s390x architecture are the only hypervisors supported, but there is an ongoing effort to support ARM architecture in a future releases.
In computing, virtualization or virtualisation is the act of creating a virtual version of something at the same abstraction level, including virtual computer hardware platforms, storage devices, and computer network resources.

A storage area network (SAN) or storage network is a computer network which provides access to consolidated, block-level data storage. SANs are primarily used to access data storage devices, such as disk arrays and tape libraries from servers so that the devices appear to the operating system as direct-attached storage. A SAN typically is a dedicated network of storage devices not accessible through the local area network (LAN).
Wanova, Inc, headquartered in San Jose, California, provides software to help IT organizations manage, support and protect data on desktop and laptop computers. Wanova's primary product, Wanova Mirage, was designed as an alternative to server-hosted desktop virtualization technologies.
Cisco Unified Computing System (UCS) is a data center server computer product line composed of server hardware, virtualization support, switching fabric, and management software, introduced in 2009 by Cisco Systems. The products are marketed for scalability by integrating many components of a data center that can be managed as a single unit.

OpenNebula is a cloud computing platform for managing heterogeneous distributed data center infrastructures. The OpenNebula platform manages a data center's virtual infrastructure to build private, public and hybrid implementations of Infrastructure as a Service. The two primary uses of the OpenNebula platform are data center virtualization and cloud deployments based on the KVM hypervisor, LXD/LXC system containers, and AWS Firecracker microVMs. The platform is also capable of offering the cloud infrastructure necessary to operate a cloud on top of existing VMware infrastructure. In early June 2020, OpenNebula announced the release of a new Enterprise Edition for corporate users, along with a Community Edition. OpenNebula CE is free and open-source software, released under the Apache License version 2. OpenNebula CE comes with free access to maintenance releases but with upgrades to new minor/major versions only available for users with non-commercial deployments or with significant contributions to the OpenNebula Community. OpenNebula EE is distributed under a closed-source license and requires a commercial Subscription.
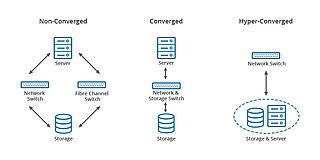
Converged storage is a storage architecture that combines storage and computing resources into a single entity. This can result in the development of platforms for server centric, storage centric or hybrid workloads where applications and data come together to improve application performance and delivery. The combination of storage and compute differs to the traditional IT model in which computation and storage take place in separate or siloed computer equipment. The traditional model requires discrete provisioning changes, such as upgrades and planned migrations, in the face of server load changes, which are increasingly dynamic with virtualization, where converged storage increases the supply of resources along with new VM demands in parallel.

StarWind Software, Inc. is a privately held Beverly, Massachusetts-based computer software and hardware appliance company specializing in storage virtualization and software-defined storage.
HP ConvergedSystem is a portfolio of system-based products from Hewlett-Packard (HP) that integrates preconfigured IT components into systems for virtualization, cloud computing, big data, collaboration, converged management, and client virtualization. Composed of servers, storage, networking, and integrated software and services, the systems are designed to address the cost and complexity of data center operations and maintenance by pulling the IT components together into a single resource pool so they are easier to manage and faster to deploy. Where previously it would take three to six months from the time of order to get a system up and running, it now reportedly takes as few as 20 days with the HP ConvergedSystem.
Software-defined storage (SDS) is a marketing term for computer data storage software for policy-based provisioning and management of data storage independent of the underlying hardware. Software-defined storage typically includes a form of storage virtualization to separate the storage hardware from the software that manages it. The software enabling a software-defined storage environment may also provide policy management for features such as data deduplication, replication, thin provisioning, snapshots and backup.

Dell Technologies PowerFlex, is a commercial software-defined storage product from Dell Technologies that creates a server-based storage area network (SAN) from local server storage using x86 servers. It converts this direct-attached storage into shared block storage than runs over an IP-based network.
A bare-metal server is a physical computer server that is used by one consumer, or tenant, only. Each server offered for rental is a distinct physical piece of hardware that is a functional server on its own. They are not virtual servers running in multiple pieces of shared hardware.
ONTAP or Data ONTAP or Clustered Data ONTAP (cDOT) or Data ONTAP 7-Mode is NetApp's proprietary operating system used in storage disk arrays such as NetApp FAS and AFF, ONTAP Select and Cloud Volumes ONTAP. With the release of version 9.0, NetApp decided to simplify the Data ONTAP name and removed word "Data" from it and remove 7-Mode image, therefore, ONTAP 9 is successor from Clustered Data ONTAP 8.
References
- ↑ "Virtual storage appliance (VSA)". Techtarget. November 1, 2012. Retrieved July 8, 2021.
- ↑ "Competitors and Alternatives to SANsymphony". Gartner. Retrieved July 8, 2021.
- ↑ "VDI hypervisor selection: Does it matter what you pick?". TechTarget. June 15, 2012. Retrieved July 29, 2021.
- 1 2 "Deploy a 2-node StarWind VSAN Free for VMware ESXi 6.5". Tech Coffee. April 18, 2017. Retrieved July 9, 2021.
- ↑ "VMware vSAN: What Is It, and How Does It Help Businesses?". BizTech Magazine. December 23, 2019. Retrieved August 3, 2021.
- 1 2 "VMware vSAN vs. SAN: What are the differences?". TechTarget. September 10, 2020. Retrieved July 29, 2021.
- ↑ "What is hybrid cloud? Everything you need to know". Tech Target. May 1, 2021. Retrieved July 9, 2021.
- ↑ "What Is Software Defined Storage? Features & Benefits". Enterprise Storage Forum. February 22, 2018. Retrieved July 8, 2021.