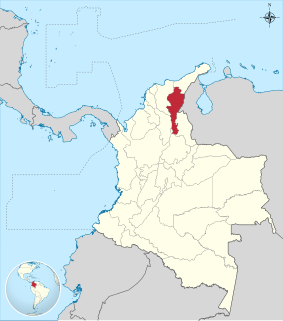
Cesar Department or simply Cesar is a department of Colombia located in the north of the country in the Caribbean region, bordering to the north with the Department of La Guajira, to the west with the Department of Magdalena and Department of Bolivar, to the south with Department of Santander, to the west with the Department of North Santander, and to the east with the country of Venezuela. The department capital city is Valledupar.
The Pueblo Revolt of 1680—also known as Popé's Rebellion—was an uprising of most of the indigenous Pueblo people against the Spanish colonizers in the province of Santa Fe de Nuevo México, present day New Mexico. The Pueblo Revolt killed 400 Spanish and drove the remaining 2,000 settlers out of the province.

San Juan del Cesar is a municipality and town located in the La Guajira Department, Colombia.

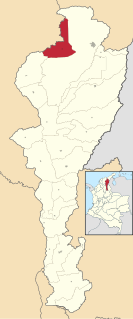
Los Robles La Paz or simply La Paz is a municipality and a town in the Department of Cesar, Colombia. The town is close to the Capital city of the Department of Cesar; Valledupar. The municipality of La Paz borders to the north with La Guajira Department, to the northeast with the municipality of Manaure. To the east with the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela sharing the Serranía del Perijá mountain range. To the south with the municipality of Codazzi, southwest with the municipality of El Paso, Cesar. To the west with the municipality of San Diego and to the northwest with the municipality of Valledupar.

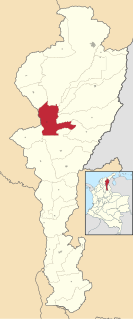
Chimichagua is a city and municipality in the central region of the Department of Cesar, Colombia. Approximately one third of the municipality of Chimichagua is water. The municipality seat lies by the Cienaga de Zapatosa marshes.

Chiriguaná is a city and municipality in the Department of Cesar, Colombia.
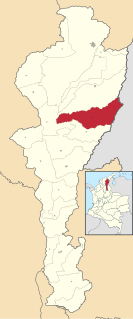
Becerril or Becerril de Campos is a town and municipality of the Colombian Department of Cesar.
Bosconia is a town and municipality in the Colombian Department of Cesar.

Urumita is a town and municipality of the Colombian Department of La Guajira.

Patillal is a village and corregimiento in the municipality of Valledupar within the Colombian Department of Cesar. The town lies on the steps of the Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta with a semiarid terrain.

Tourism in Cesar Department refers to the tourism in the Colombian Department of Cesar. Tourism developed primarily in Valledupar during the middle of the 20th century after the creation of Cesar Department, but had its precedents in religious peregrination during the holy week, Catholic church tradition with peregrines going to Valledupar to celebrate processions, religious masses, saint of Ecce Homo veneration, the Virgen del Carmen, among others, these peregrinations were also popular in Atanquez a small village enclaved in the Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta, were the local culture inherited from the Spanish and Indigenous develop the "devil dancers".
The History of Valledupar refers to the historical events related to the Colombian city of Valledupar. The region of what is now Valledupar was prior to the Spanish conquest of the Americas inhabited by numerous indigenous tribes pertaining to three major language families; the Arawaks, Kalina (Caribs) and Chibchas.

Atanquez or San Sebastian is a Colombian town and corregimiento of Valledupar in the Department of Cesar. Atanquez is located on the Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta mountain range at approximately 2,000 m over sea level. Atanquez is known for being predominantly inhabited by the indigenous ethnic group Kankuamos among others and mestizo groups.

The Chimilas or Ette Ennaka are an indigenous people in the Andes of north-eastern Colombia. Their Chimila language is part of the Chibcha language family; there were estimated to be around 1000 speakers in 1998. At the time of the Spanish Conquest the Ariguaní River valley was the strategic centre of their territory. On the Serranía del Perijá mountains the Yukpas were also part of the Chimila confederation of tribes.
Guatapurí is a Colombian town and corregimiento of Valledupar in the Department of Cesar. Atanquez is located on the Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta mountain range at approximately 2,000 m over the sea level. Guatapurí is known for being predominantly inhabited by the indigenous ethnic group Kankuamos among others and mestizo groups.
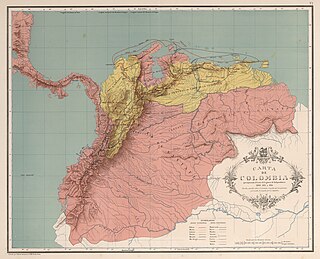
The Magdalena Campaign was a military operation from late 1812 to early 1813 led by the independentists Simón Bolívar and Pierre Labatut against royalists and the crown of Spain in New Granada. The campaign resulted in the revolutionary United Provinces of New Grenada taking control of the Magdalena River, which connects the port city of Cartagena with the interior of Colombia.