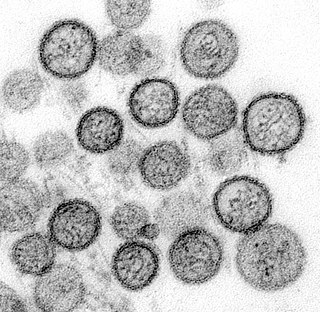
Sin Nombre virus (SNV) is the most common cause of hantavirus pulmonary syndrome (HPS) in North America. Sin Nombre virus is transmitted mainly by the eastern deer mouse. In its natural reservoir, SNV causes an asymptomatic, persistent infection and is spread through excretions, fighting, and grooming. Humans can become infected by inhaling aerosols that contain rodent saliva, urine, or feces, as well as through bites and scratches. In humans, infection leads to HPS, an illness characterized by an early phase of mild and moderate symptoms such as fever, headache, and fatigue, followed by sudden respiratory failure. The case fatality rate from infection is high, at 30–50%.

Nodaviridae is a family of nonenveloped positive-strand RNA viruses. Vertebrates and invertebrates serve as natural hosts. Diseases associated with this family include: viral encephalopathy and retinopathy in fish. There are nine species in the family, assigned to two genera.

Potyviridae is a family of positive-strand RNA viruses that encompasses more than 30% of known plant viruses, many of which are of great agricultural significance. The family has 12 genera and 235 species, three of which are unassigned to a genus.

Tombusviridae is a family of single-stranded positive sense RNA plant viruses. There are three subfamilies, 17 genera, and 95 species in this family. The name is derived from Tomato bushy stunt virus (TBSV).
Closterovirus, also known as beet yellows viral group, is a genus of viruses, in the family Closteroviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 17 species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: yellowing and necrosis, particularly affecting the phloem. This genus has a probably worldwide distribution and includes among other viral species the Beet yellows virus and Citrus tristeza virus, rather economically important plant diseases. At least some species require vectors such as aphids or mealybugs for their transmission from plant to plant.
Andes virus (ANDV) is the most common cause of hantavirus pulmonary syndrome (HPS) in South America. Andes virus is transmitted mainly by the long-tailed pygmy rice rat. In its natural reservoir, ANDV causes an asymptomatic, persistent infection and is spread through excretions, fighting, and grooming. Humans can become infected by inhaling aerosols that contain rodent saliva, urine, or feces, as well as through bites and scratches. In humans, infection leads to HPS, an illness characterized by an early phase of mild and moderate symptoms such as fever, headache, and fatigue, followed by sudden respiratory failure. The case fatality rate from infection is high, at about 40%.

Crinivirus, formerly the lettuce infectious yellows virus group, is a genus of viruses, in the family Closteroviridae. They are linear, single-stranded positive sense RNA viruses. There are 14 species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: yellowing and necrosis, particularly affecting the phloem.
Kobuvirus is a genus of viruses in the order Picornavirales, in the family Picornaviridae. Humans and cattle serve as natural hosts. There are six species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: gastroenteritis. The genus was named because of the virus particles' lumpy appearance by electron microscopy; "kobu" means "knob" in Japanese.
Luteovirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Tombusviridae. There are 13 species in this genus. Plants serve as natural hosts. The geographical distribution of Luteoviruses is widespread, with the virus primarily infecting plants via transmission by aphid vectors. The virus only replicates within the host cell and not within the vector. The name 'luteovirus' arises from the Latin luteus, which is translated as 'yellow'. Luteovirus was given this name due to the symptomatic yellowing of the plant that occurs as a result of infection.

Orthonairovirus is a genus of viruses in the family Nairoviridae of the order Bunyavirales which includes viruses with circular, negative-sense single stranded RNA. The name is derived from the Nairobi sheep disease which affects the gastrointestinal tracts of sheep and goats. All viruses in this genus are tick-borne viruses with human or other vertebrate hosts.

Benyvirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Benyviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are four species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: BNYVV: rhizomania.

Potexvirus is a genus of pathogenic viruses in the order Tymovirales, in the family Alphaflexiviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 48 species in this genus, three of which are assigned to a subgenus. Diseases associated with this genus include: mosaic and ringspot symptoms. The genus name comes from POTato virus X).

Aspiviridae, formerly Ophioviridae, is a family of segmented negative-strand RNA viruses which infect plants. Member viruses are characterized by an elongated and highly filamentous and flexible nucleocapsid with helical symmetry. It is a monotypic taxon containing only one genus, Ophiovirus. Aspiviridae is also the only family in the order Serpentovirales, which in turn is the only order in the class Milneviricetes.
Ipomovirus is a genus of positive-strand RNA viruses in the family Potyviridae. Member viruses infect plants and are transmitted by whiteflies. The name of the genus is derived from Ipomoea – the generic name of sweet potato. There are seven species in this genus.
Hantaan virus (HTNV) is the main cause of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) in East Asia. Hantaan virus is transmitted by the striped field mouse In its natural reservoir, HTNV causes a persistent, asymptomatic infection and is spread through excretions, fighting, and grooming. Humans can become infected by inhaling aerosols that contain rodent saliva, urine, or feces, as well as through bites and scratches. In humans, infection causes such as fever and headache, as well as the appearance of spots on the skin, hepatitis, and renal symptoms such as kidney swelling, excess protein in urine, blood in urine, decreased urine production, and kidney failure. Rarely, HTNV infection affects the pituitary gland and can cause empty sella syndrome. The case fatality rate from infection is up to 6.3%.

Fig mosaic emaravirus (FMV) is a segmented, negative sense, single-stranded RNA virus that is determined to be the causal agent of fig mosaic disease (FMD) in fig plants, Ficus carica. It is a member of the genus Emaravirus and order Bunyavirales and is transmitted mainly by the eriophyid mite Aceria ficus. FMV can cause a range of symptoms varying in severity, including leaf chlorosis, deformity, and mosaic or discoloration patterns, as well as premature fruit drop.

Emaravirus is a genus of negative-strand RNA viruses which infect plants. The plant virus group is the sole genus in the family Fimoviridae. The genus has 21 species.
Negative-strand RNA viruses are a group of related viruses that have negative-sense, single-stranded genomes made of ribonucleic acid (RNA). They have genomes that act as complementary strands from which messenger RNA (mRNA) is synthesized by the viral enzyme RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp). During replication of the viral genome, RdRp synthesizes a positive-sense antigenome that it uses as a template to create genomic negative-sense RNA. Negative-strand RNA viruses also share a number of other characteristics: most contain a viral envelope that surrounds the capsid, which encases the viral genome, −ssRNA virus genomes are usually linear, and it is common for their genome to be segmented.

The Blueberry mosaic associated ophiovirus (B1MaV) is a plant virus which infects blueberry plants, causing a discoloration of the leaves of the plants in a mosaic-like pattern. The disease is found in blueberry plants in many regions of North America, as well as South America, Europe, New Zealand, and South Africa. Within these regions the virus is most often found in high blueberry-yielding areas, but can be spread to other locations. Blueberry mosaic associatedophiovirus is one of seven species in the genus Ophiovirus. It is a member of the Aspiviridae family, in the Serpentovirales order, and in the Milnevircetes class. The Ophioviridae viruses are characterized by a flexible and elongated nucleocapsid that is composed mostly of filamentous structures and is helically symmetrical. It also has a non-enveloped protein capsid that is capable of coiling around itself allowing for a super-coiled structure and the helical symmetry. The virus has the potential to be symptomatic or asymptomatic within plants causing the display of symptoms in only a few plants, but the ability to transmit the virus unknowingly in many plants. B1MaV often remains asymptomatic for long periods of time after initial infection allowing for blind transmission.

Botourmiaviridae is a family of positive-strand RNA viruses which infect plants and fungi. The family includes four genera: Ourmiavirus, Botoulivirus, Magoulivirus and Scleroulivirus. Members of genus Ourmiavirus infect plants and the other genera infect fungi. The member viruses have genomes which range from 2900 to 4800 nucleotides.















