
Chelidae is one of three living families of the turtle suborder Pleurodira, and are commonly called Austro-South American side-neck turtles. The family is distributed in Australia, New Guinea, parts of Indonesia, and throughout most of South America. It is a large family of turtles with a significant fossil history dating back to the Cretaceous. The family is entirely Gondwanan in origin, with no members found outside Gondwana, either in the present day or as a fossil.

The Turonian is, in the ICS' geologic timescale, the second age in the Late Cretaceous Epoch, or a stage in the Upper Cretaceous Series. It spans the time between 93.9 ± 0.8 Ma and 89.8 ± 1 Ma. The Turonian is preceded by the Cenomanian Stage and underlies the Coniacian Stage.
The Coniacian is an age or stage in the geologic timescale. It is a subdivision of the Late Cretaceous Epoch or Upper Cretaceous Series and spans the time between 89.8 ± 1 Ma and 86.3 ± 0.7 Ma. The Coniacian is preceded by the Turonian and followed by the Santonian.
Asiamericana (AY-zha-MER-i-KAHN-a – is a dubious dinosaur genus known only from isolated teeth. It was named to recognize the occurrence of similar fossil teeth in Central Asia and North America. These regions once formed a connected land mass, during the Cretaceous period and were referred to as Asiamerica.

Evaniidae is a family of parasitoid wasps also known as ensign wasps, nightshade wasps, hatchet wasps, or cockroach egg parasitoid wasps. They number around 20 extant genera containing over 400 described species, and are found all over the world except in the polar regions. The larvae of these solitary wasps are parasitoids that feed on cockroaches and develop inside the egg-cases, or oothecae, of their hosts.

Pliosauridae is a family of plesiosaurian marine reptiles from the Latest Triassic to the early Late Cretaceous of Australia, Europe, North America and South America. The family is more inclusive than the archetypal short-necked large headed species that are placed in the subclade Thalassophonea, with basal forms resembling other plesiosaurs with long necks. They became extinct during the early Late Cretaceous and were subsequently replaced by the mosasaurs. It was formally named by Harry G. Seeley in 1874.

Dallasaurus is a basal mosasauroid from the Upper Cretaceous of North America. Along with Russellosaurus, Dallasaurus is one of the two oldest mosasauroid taxa currently known from North America. It is also one of the smallest known mosasaurine, measuring up to 1 m (3.3 ft) in length and 2 kg (4.4 lb) in body mass.

Nemonychidae is a small family of weevils, placed within the primitive weevil group because they have straight rather than geniculate (elbowed) antennae. They are often called pine flower weevils. As in the Anthribidae, the labrum appears as a separate segment to the clypeus, and the maxillary palps are long and projecting. Nemonychidae have all ventrites free, while Anthribidae have ventrites 1-4 connate or partially fused. Nemonychidae lack lateral carinae on the pronotum, while these are usually present, though may be short, in Anthribidae.

Brachauchenius is an extinct genus of pliosaurid that lived in North America and Morocco during the Late Cretaceous.

Sphagesauridae is a Gondwanan family of mesoeucrocodylians that lived during the Late Cretaceous. It was a clade of terrestrial crocodilians that evolved very mammal-like teeth and jaws. Both Sphagesaurus and Adamantinasuchus are known from the Turonian to Santonian of Brazil.

Iteaceae is a flowering plant family of trees and shrubs native to the eastern USA, southeastern Africa, and south and Southeastern Asia. Some older taxonomic systems place the genus Itea in the family Grossulariaceae. The APG III system of 2009 includes the former Pterostemonaceae in Iteaceae. Consequently, it now has two genera with a total of 18 known species.

Shaochilong is an extinct genus of carcharodontosaurid dinosaur from the mid-Cretaceous Ulansuhai Formation of China. The type species, S. maortuensis, was originally named Chilantaisaurus maortuensis, but was re-described and reclassified in 2009. It was one of the last known carcharodontosaurids to walk the earth. Alongside Mapusaurus from Argentina, they were the only members of the family to live until the end of the Turonian epoch.

Acanthoceratoidea, formerly Acanthocerataceae, is a superfamily of Upper Cretaceous ammonoid cephalopods belonging to the order Ammonitida, and comprising some 10 or so families.
The Cenomanian-Turonian boundary event, also known as the Cenomanian-Turonian extinction, Cenomanian-Turonian oceanic anoxic event, and referred to also as the Bonarelli event, was one of two anoxic extinction events in the Cretaceous period. Selby et al. in 2009 concluded the OAE 2 occurred approximately 91.5 ± 8.6 Ma, though estimates published by Leckie et al. (2002) are given as 93–94 Ma. The Cenomanian-Turonian boundary has been refined in 2012 to 93.9 ± 0.15 Ma There was a large carbon cycle disturbance during this time period. However, apart from the carbon cycle disturbance, there were also large disturbances in the oxygen and sulphur cycles of the ocean.

Thalassophonea is an extinct clade of pliosaurids from the Middle Jurassic to the early Late Cretaceous of Australia, Europe, North America and South America. Thalassophonea was erected by Roger Benson and Patrick Druckenmiller in 2013. The name is derived from Greek thalassa (θάλασσα), "sea", and phoneus (φονεύς), "murderer". It is a stem-based taxon defined as "all taxa more closely related to Pliosaurus brachydeirus than to Marmornectes candrewi". It includes the short necked and large headed taxa that typify the family.
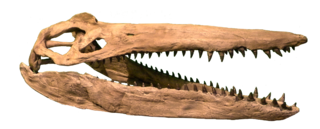
Megacephalosaurus is an extinct genus of short-necked pliosaur that inhabited the Western Interior Seaway of North America about 94 to 93 million years ago during the Turonian stage of the Late Cretaceous, containing the single species M. eulerti. It is named after its large head, which is the largest of any plesiosaur in the continent and measures up to 1.75 meters (5.7 ft) in length. Megacephalosaurus was one of the largest marine reptiles of its time with an estimated length of 6–9 meters (20–30 ft). Its long snout and consistently sized teeth suggest that it preferred a diet on smaller-sized prey.

Macrobaenidae is an extinct family of turtles, known from the Early Cretaceous to Paleogene of Laurasia. Their relationships to other turtles and whether or not they form a monophlyletic group are controversial. They are typically interpreted as stem or crown group cryptodires, but some more recent analyses have found them to lie outside crown group Testudines. Macrobaenids can be distinguished from other testudinatans by the presence of a carotid fenestra, cruciform plastron with strap-like epiplastra, and a lack of extragulars.

Naomichelys is an extinct genus of helochelydrid stem turtle known from the Cretaceous (Aptian-Campanian) of North America. It is the only member of the family known to be native to North America.

Goulmimichthys is an extinct genus of ray-finned fishes in the family Pachyrhizodontidae. The genus, first described by Cavin in 1995, is known from various Turonian age formations. The type species G. arambourgi from the Akrabou Formation in the El Rachidia Province of Morocco, and other fossils described are G. gasparini of the La Frontera Formation, Colombia, and G. roberti from the Agua Nueva Formation of Mexico.

Bachea is an extinct genus of ray-finned fish that lived during the Late Cretaceous in what is now central Colombia, South America. The type species is B. huilensis, described in 1997 by María Páramo from the Turonian of Huila, Colombia.

















