
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinters, distinguishing them from the organism's own healthy tissue. Many species have two major subsystems of the immune system. The innate immune system provides a preconfigured response to broad groups of situations and stimuli. The adaptive immune system provides a tailored response to each stimulus by learning to recognize molecules it has previously encountered. Both use molecules and cells to perform their functions.

Lemon balm, balm, common balm, or balm mint, is a perennial herbaceous plant in the mint family and native to south-central Europe, the Mediterranean Basin, Iran, and Central Asia, but now naturalized elsewhere.

Valerian is a perennial flowering plant native to Europe and Asia. In the summer when the mature plant may have a height of 1.5 metres (5 ft), it bears sweetly scented pink or white flowers that attract many fly species, especially hoverflies of the genus Eristalis. It is consumed as food by the larvae of some Lepidoptera species, including the grey pug.

Nicotine is a chiral alkaloid that is naturally produced in the nightshade family of plants and is widely used recreationally as a stimulant and anxiolytic. As a pharmaceutical drug, it is used for smoking cessation to relieve withdrawal symptoms. Nicotine acts as a receptor agonist at most nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs), except at two nicotinic receptor subunits where it acts as a receptor antagonist.

Thujone is a ketone and a monoterpene that occurs predominantly in two diastereomeric (epimeric) forms: (−)-α-thujone and (+)-β-thujone.

Aloysia citrodora, lemon verbena, is a species of flowering plant in the verbena family Verbenaceae, native to South America. Other common names include lemon beebrush. It was brought to Europe by the Spanish and the Portuguese in the 17th century and cultivated for its oil.

Verbena is a genus in the family Verbenaceae. It contains about 250 species of annual and perennial herbaceous or semi-woody flowering plants. The majority of the species are native to the Americas and Asia. Verbena officinalis, the common vervain or common verbena, is the type species and native to Europe.

Althaea officinalis, or marsh-mallow, is a perennial species indigenous to Europe, Western Asia, and North Africa, which is used in herbalism and as an ornamental plant. A confection made from the root since ancient Egyptian times evolved into today's marshmallow treat, but most modern marshmallow treats no longer contain any marsh-mallow root.

Valeric acid or pentanoic acid is a straight-chain alkyl carboxylic acid with the chemical formula CH
3(CH
2)
3COOH. Like other low-molecular-weight carboxylic acids, it has an unpleasant odor. It is found in the perennial flowering plant Valeriana officinalis, from which it gets its name. Its primary use is in the synthesis of its esters. Salts and esters of valeric acid are known as valerates or pentanoates. Volatile esters of valeric acid tend to have pleasant odors and are used in perfumes and cosmetics. Several, including ethyl valerate and pentyl valerate are used as food additives because of their fruity flavors.

The ventrolateral preoptic nucleus (VLPO), also known as the intermediate nucleus of the preoptic area (IPA), is a small cluster of neurons situated in the anterior hypothalamus, sitting just above and to the side of the optic chiasm in the brain of humans and other animals. The brain's sleep-promoting nuclei, together with the ascending arousal system which includes components in the brainstem, hypothalamus and basal forebrain, are the interconnected neural systems which control states of arousal, sleep, and transitions between these two states. The VLPO is active during sleep, particularly during non-rapid eye movement sleep, and releases inhibitory neurotransmitters, mainly GABA and galanin, which inhibit neurons of the ascending arousal system that are involved in wakefulness and arousal. The VLPO is in turn innervated by neurons from several components of the ascending arousal system. The VLPO is activated by the endogenous sleep-promoting substances adenosine and prostaglandin D2. The VLPO is inhibited during wakefulness by the arousal-inducing neurotransmitters norepinephrine and acetylcholine. The role of the VLPO in sleep and wakefulness, and its association with sleep disorders – particularly insomnia and narcolepsy – is a growing area of neuroscience research.

Verbena officinalis, the common vervain or common verbena, is a perennial herb native to Europe. It grows up to 70 cm high, with an upright habitus. The lobed leaves are toothed, and the delicate spikes hold clusters of two-lipped mauve flowers.

3-Methylbutanoic acid, also known as β-methylbutyric acid or more commonly isovaleric acid, is a branched-chain alkyl carboxylic acid with the chemical formula (CH3)2CHCH2CO2H. It is classified as a short-chain fatty acid. Like other low-molecular-weight carboxylic acids, it has an unpleasant odor. The compound occurs naturally and can be found in many foods, such as cheese, soy milk, and apple juice.

Pyrrolizidine alkaloids (PAs), sometimes referred to as necine bases, are a group of naturally occurring alkaloids based on the structure of pyrrolizidine. Pyrrolizidine alkaloids are produced by plants as a defense mechanism against insect herbivores. More than 660 PAs and PA N-oxides have been identified in over 6,000 plants, and about half of them exhibit hepatotoxicity. They are found frequently in plants in the Boraginaceae, Asteraceae, Orchidaceae and Fabaceae families; less frequently in the Convolvulaceae and Poaceae, and in at least one species in the Lamiaceae. It has been estimated that 3% of the world’s flowering plants contain pyrrolizidine alkaloids. Honey can contain pyrrolizidine alkaloids, as can grains, milk, offal and eggs. To date (2011), there is no international regulation of PAs in food, unlike those for herbs and medicines.
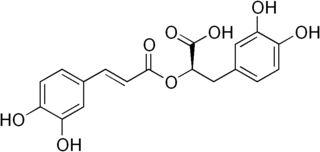
Rosmarinic acid is a chemical compound found in a variety of plants. It was found to exhibit photoprotective effect against ultraviolet C (UVC) damage when examined in vitro.

Valerenic acid is a sesquiterpenoid constituent of the essential oil of the valerian plant.

Verbena urticifolia, known as nettle-leaved vervain or white vervain, is a herbaceous plant in the vervain family (Verbenaceae). It belongs to the "true" vervains of genus Verbena.

Cornus officinalis, the Japanese cornel or Japanese cornelian cherry, is a species of flowering plant in the dogwood family Cornaceae. Despite its name it is native to China and Korea as well as Japan. It is not to be confused with C. mas, which is also known as the Cornelian cherry. It is not closely related to the true cherries of the genus Prunus.

Hyssopus officinalis or hyssop is a shrub in the Lamiaceae or mint family native to Southern Europe, the Middle East, and the region surrounding the Caspian Sea. Due to its purported properties as an antiseptic, cough reliever, and expectorant, it has been used in traditional herbal medicine.

Cuttlefish or cuttles are marine molluscs of the order Sepiida. They belong to the class Cephalopoda, which also includes squid, octopuses, and nautiluses. Cuttlefish have a unique internal shell, the cuttlebone, which is used for control of buoyancy.

Verbascoside is a caffeoyl phenylethanoid glycoside in which the phenylpropanoid caffeic acid and the phenylethanoid hydroxytyrosol form an ester and an ether bond respectively, to the rhamnose part of a disaccharide, namely β-(3′,4′-dihydroxyphenyl)ethyl-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl(1→3)-β-D-(4-O-caffeoyl)-glucopyranoside.




















