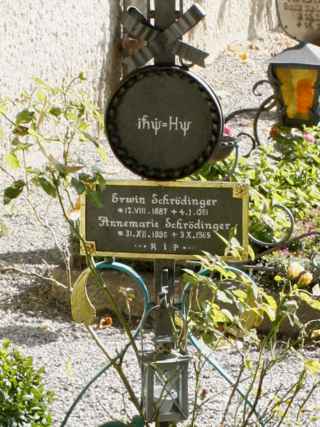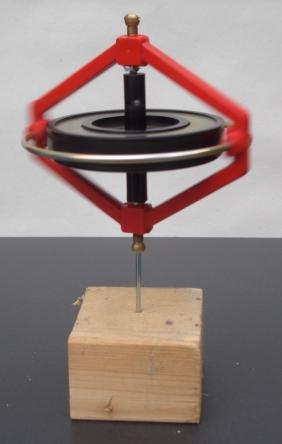
In physics, angular momentum is the rotational analog of linear momentum. It is an important physical quantity because it is a conserved quantity – the total angular momentum of a closed system remains constant. Angular momentum has both a direction and a magnitude, and both are conserved. Bicycles and motorcycles, flying discs, rifled bullets, and gyroscopes owe their useful properties to conservation of angular momentum. Conservation of angular momentum is also why hurricanes form spirals and neutron stars have high rotational rates. In general, conservation limits the possible motion of a system, but it does not uniquely determine it.

The blue whale is a marine mammal and a baleen whale. Reaching a maximum confirmed length of 29.9 meters (98 ft) and weighing up to 199 tonnes, it is the largest animal known ever to have existed. The blue whale's long and slender body can be of various shades of greyish-blue dorsally and somewhat lighter underneath. Four subspecies are recognized: B. m. musculus in the North Atlantic and North Pacific, B. m. intermedia in the Southern Ocean, B. m. brevicauda in the Indian Ocean and South Pacific Ocean, and B. m. indica in the Northern Indian Ocean. There is also a population in the waters off Chile that may constitute a fifth subspecies.

A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms, when they share electrons, is known as covalent bonding. For many molecules, the sharing of electrons allows each atom to attain the equivalent of a full valence shell, corresponding to a stable electronic configuration. In organic chemistry, covalent bonding is much more common than ionic bonding.

The cat, commonly referred to as the domestic cat or house cat, is the only domesticated species in the family Felidae. Recent advances in archaeology and genetics have shown that the domestication of the cat occurred in the Near East around 7500 BC. It is commonly kept as a house pet and farm cat, but also ranges freely as a feral cat avoiding human contact. It is valued by humans for companionship and its ability to kill vermin. Because of its retractable claws it is adapted to killing small prey like mice and rats. It has a strong flexible body, quick reflexes, sharp teeth, and its night vision and sense of smell are well developed. It is a social species, but a solitary hunter and a crepuscular predator. Cat communication includes vocalizations like meowing, purring, trilling, hissing, growling, and grunting as well as cat body language. It can hear sounds too faint or too high in frequency for human ears, such as those made by small mammals. It also secretes and perceives pheromones.

The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) is an alphabetic system of phonetic notation based primarily on the Latin script. It was devised by the International Phonetic Association in the late 19th century as a standardized representation of speech sounds in written form. The IPA is used by lexicographers, foreign language students and teachers, linguists, speech–language pathologists, singers, actors, constructed language creators, and translators.

An inductor, also called a coil, choke, or reactor, is a passive two-terminal electrical component that stores energy in a magnetic field when electric current flows through it. An inductor typically consists of an insulated wire wound into a coil.

Ketamine is a dissociative anesthetic used medically for induction and maintenance of anesthesia. It is also used as a treatment for depression, and as a pain management tool. Ketamine is a novel compound that was derived from phencyclidine in 1962 in pursuit of a safer anesthetic with fewer hallucinogenic effects.
In mathematics, the Laplace transform, named after its discoverer Pierre-Simon Laplace, is an integral transform that converts a function of a real variable to a function of a complex variable . The transform has many applications in science and engineering, mostly as a tool for solving linear differential equations. In particular, it transforms ordinary differential equations into algebraic equations and convolution into multiplication. For suitable functions f, the Laplace transform is defined by the integral
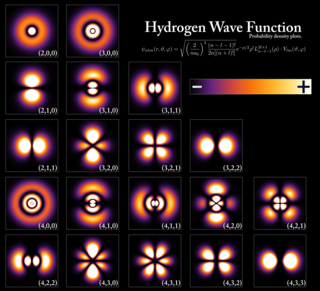
Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that describes the behavior of nature at and below the scale of atoms. It is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry, quantum field theory, quantum technology, and quantum information science.
Structured Query Language (SQL) is a domain-specific language used in programming and designed for managing data held in a relational database management system (RDBMS), or for stream processing in a relational data stream management system (RDSMS). It is particularly useful in handling structured data, i.e., data incorporating relations among entities and variables.

The lion is a large cat of the genus Panthera native to Africa and India. It has a muscular, broad-chested body; short, rounded head; round ears; and a hairy tuft at the end of its tail. It is sexually dimorphic; adult male lions are larger than females and have a prominent mane. It is a social species, forming groups called prides. A lion's pride consists of a few adult males, related females, and cubs. Groups of female lions usually hunt together, preying mostly on large ungulates. The lion is an apex and keystone predator; although some lions scavenge when opportunities occur and have been known to hunt humans, lions typically do not actively seek out and prey on humans.

The cheetah is a large cat with a tawny to creamy white or pale buff fur that is marked with evenly spaced, solid black spots. Its head is small and rounded, with a short snout and black tear-like facial streaks. It reaches 67–94 cm (26–37 in) at the shoulder, and the head-and-body length is between 1.1 and 1.5 m. Adults weigh between 21 and 72 kg. It is the fastest land animal, capable of running at 80 to 98 km/h ; it has evolved specialized adaptations for speed, including a light build, long thin legs and a long tail.

Samuel Leroy Jackson is an American actor. One of the most widely recognized actors of his generation, the films in which he has appeared have collectively grossed over $27 billion worldwide, making him the highest-grossing leading actor of all time. In 2022, he received the Academy Honorary Award as "a cultural icon whose dynamic work has resonated across genres and generations and audiences worldwide".
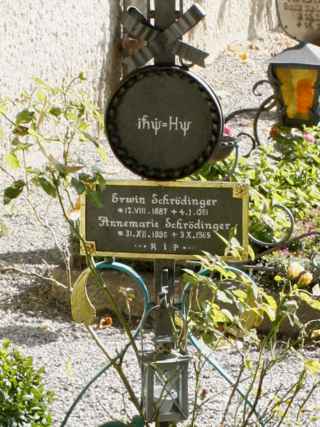
The Schrödinger equation is a linear partial differential equation that governs the wave function of a quantum-mechanical system. Its discovery was a significant landmark in the development of quantum mechanics. It is named after Erwin Schrödinger, who postulated the equation in 1925 and published it in 1926, forming the basis for the work that resulted in his Nobel Prize in Physics in 1933.
Some Buddhist terms and concepts lack direct translations into English that cover the breadth of the original term. Below are given a number of important Buddhist terms, short definitions, and the languages in which they appear. In this list, an attempt has been made to organize terms by their original form and give translations and synonyms in other languages along with the definition.

Young's modulus is a mechanical property of solid materials that measures the tensile or compressive stiffness when the force is applied lengthwise. It is the modulus of elasticity for tension or axial compression. Young's modulus is defined as the ratio of the stress applied to the object and the resulting axial strain in the linear elastic region of the material.
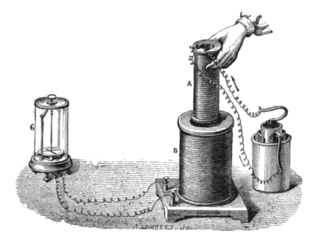
Faraday's law of induction is a law of electromagnetism predicting how a magnetic field will interact with an electric circuit to produce an electromotive force (emf). This phenomenon, known as electromagnetic induction, is the fundamental operating principle of transformers, inductors, and many types of electric motors, generators and solenoids.
In machine learning, backpropagation is a gradient estimation method used to train neural network models. The gradient estimate is used by the optimization algorithm to compute the network parameter updates.
L, or l, is the 12th letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is el, plural els.

Opecoelidae is a family of trematodes. It is the largest digenean family with over 90 genera and nearly 900 species, almost solely found in marine and freshwater teleost fishes. It was considered by Bray et al. to belong in the superfamily Opecoeloidea Ozaki, 1925 or the Brachycladioidea Odhner, 1905.