| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name Anthra[10,1,2-cde]benzo[rst]pentaphene-5,10-dione | |
| Other names Dibenzanthrone, Tinon Dark Blue BOA, Ahcovat Dark Blue BO, Violanthrone A, Bianthrone A, Irgalite Blue 2R, Paradone Dark Blue | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.775 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C34H16O2 | |
| Molar mass | 456.48964 |
| Appearance | dark blue solid |
| Density | 1.53 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 492 °C (decomposes) |
| −204.8·10−6 cm3/mol | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
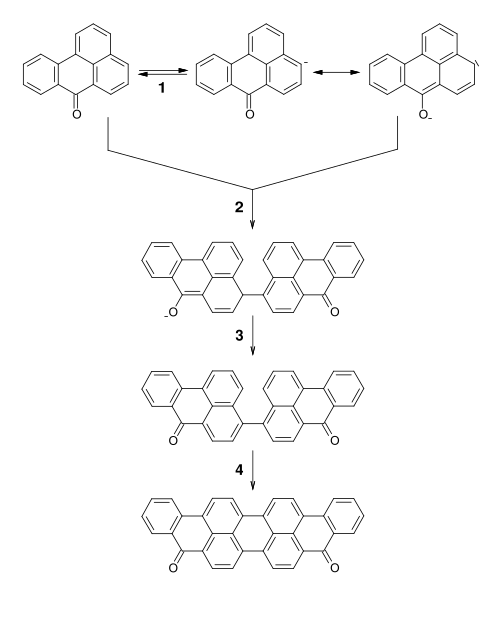
Violanthrone, also known as dibenzanthrone, is an organic compound that serves as a vat dye and a precursor to other vat dyes. X-ray crystallography confirms that the molecule is planar with C2v symmetry. [1] Isomeric with violanthrone is isoviolanthrone, which has a centrosymmetric structure. [2]