
Interstate 95 (I-95) is the main north–south Interstate Highway on the East Coast of the United States, running from U.S. Route 1 (US 1) in Miami, Florida, north to the Houlton–Woodstock Border Crossing between Maine and the Canadian province of New Brunswick. The highway largely parallels the Atlantic coast and US 1, except for the portion between Savannah, Georgia, and Washington, D.C., and the portion between Portland and Houlton in Maine, both of which follow a more direct inland route.

Interstate 85 (I-85) is a major Interstate Highway in the Southeastern United States. Its southern terminus is at an interchange with I-65 in Montgomery, Alabama; its northern terminus is an interchange with I-95 in Petersburg, Virginia, near Richmond. It is nominally north–south as it carries an odd number, but it is physically oriented northeast–southwest and covers a larger east–west span than north–south. While most Interstates that end in a "5" are cross-country, I-85 is primarily a regional route serving five southeastern states: Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, Georgia, and Alabama.

The Greater Richmond Region, the Richmond metropolitan area or Central Virginia, is a region and metropolitan area in the U.S. state of Virginia, centered on Richmond. The U.S. Office of Management and Budget (OMB) defines the area as the Richmond, VA Metropolitan Statistical Area, a Metropolitan Statistical Area (MSA) used by the U.S. Census Bureau and other entities. The OMB defines the area as comprising 17 county-level jurisdictions, including the independent cities of Richmond, Petersburg, Hopewell, and Colonial Heights. As of 2020, it had a population of 1,314,434, making it the 44th largest MSA in the country.
The Virginia Department of Transportation (VDOT) is the agency of the state government responsible for transportation in the state of Virginia in the United States. VDOT is headquartered at the Virginia Department of Highways Building in downtown Richmond. VDOT is responsible for building, maintaining, and operating the roads, bridges, and tunnels in the commonwealth. It is overseen by the Commonwealth Transportation Board, which has the power to fund airports, seaports, rail, and public transportation.

The Henry G. Shirley Memorial Highway, often shortened to Shirley Highway, consists of a 17.3-mile (27.8 km) portion of Interstates 95 and 395 in the U.S. Commonwealth of Virginia. Shirley Highway was the first limited-access freeway in Virginia. Begun in 1941, the road was completed from U.S. Route 1 in Colchester, Virginia, just north of Woodbridge, to the 14th Street Bridge over the Potomac River between Virginia and Washington, D.C. in 1952.

State Route 895, also known as the Pocahontas Parkway and Pocahontas 895, is a controlled-access toll road in the U.S. state of Virginia. It connects the junction of Interstate 95 and State Route 150 in Chesterfield County with Interstate 295 near Richmond International Airport in Henrico County, forming part of a southeastern bypass of Richmond. Due to a quirk in the evolution of the road, the long-planned designation of Interstate 895 could not be used.

State Route 6 is a primary state highway in the U.S. state of Virginia. Known for most of its length as River Road, the state highway runs 102.26 miles (164.57 km) from U.S. Route 250 in Afton east to SR 161 in Richmond. SR 6 is one of the main highways of mountainous Nelson County, where the highway runs north–south from its beginning to US 29. From Scottsville to Richmond, the state highway parallels the James River. SR 6 is a major suburban highway through southwestern Henrico County and the main street of Richmond's West End.

State Route 161 is a primary state highway in and near Richmond, Virginia, United States. It extends from an interchange with Interstate 95 (I-95) in the independent city of Richmond north to an intersection with U.S. Route 1 in the Lakeside area of central Henrico County.
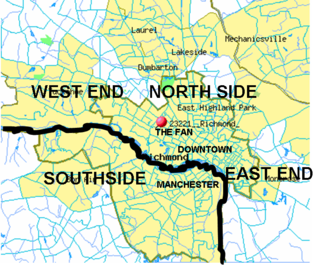
The Southside of Richmond is an area of the Metropolitan Statistical Area surrounding Richmond, Virginia. It generally includes all portions of the City of Richmond that lie south of the James River, and includes all of the former city of Manchester. Depending on context, the term "Southside of Richmond" can include some northern areas of adjacent Chesterfield County, Virginia in the Richmond-Petersburg region. With minor exceptions near Bon Air, VA, the Chippenham Parkway forms the border between Chesterfield County and the City of Richmond portions of Southside, with some news agencies using the term "South Richmond" to refer to the locations in Southside located in the city proper.

World War II Veteran's Memorial Bridge is a twin-span 3,642-foot-long (1,110 m) bridge which carries State Route 288 across the James River between Powhatan County and Goochland County in Virginia. State Route 288 forms a semi-circumferential beltway around the southwestern quadrant of the Richmond metropolitan area connecting with Interstate 95 on the southern end and Interstate 64 on the northern end.

Transportation in the Commonwealth of Virginia is by land, sea and air. Virginia's extensive network of highways and railroads were developed and built over a period almost 400 years, beginning almost immediately after the founding of Jamestown in 1607, and often incorporating old established trails of the Native Americans.

Transportation in Richmond, Virginia and its immediate surroundings include land, sea and air modes. This article includes the independent city and portions of the contiguous counties of Henrico and Chesterfield. While almost all of Henrico County would be considered part of the Richmond area, southern and eastern portions of Chesterfield adjoin the three smaller independent cities of Petersburg, Hopewell, and Colonial Heights, collectively commonly called the Tri-Cities area. A largely rural section of southwestern Chesterfield may be considered not a portion of either suburban area.

State Route 164 is a 7.27-mile-long (11.70 km) primary state highway in the U.S. state of Virginia that connects the northern parts of Suffolk and Portsmouth with Newport News and Hampton via Interstate 664 (I-664) with Downtown Portsmouth and Norfolk through either the Downtown or Midtown Tunnels.

Interstate 95 (I-95) runs 179 miles (288 km) within the commonwealth of Virginia between its borders with North Carolina and Maryland. I-95 meets the northern terminus of I-85 in Petersburg and is concurrent with I-64 for three miles (4.8 km) in Richmond. Although I-95 was originally planned as a highway through Washington, D.C., it was rerouted along the eastern portion of the Capital Beltway concurrent with I-495. From Petersburg to Richmond, I-95 utilized most of the Richmond–Petersburg Turnpike, a former toll road. In addition to Richmond, the route also runs through the medium-sized cities of Emporia, Petersburg, Colonial Heights, Fredericksburg, and Alexandria.

U.S. Route 1 (US 1) is a major north–south U.S. Route that serves the East Coast of the United States. In the U.S. state of Virginia, US 1 runs north–south through South Hill, Petersburg, Richmond, Fredericksburg, and Alexandria on its way from North Carolina to the 14th Street bridges into the District of Columbia. It is completely paralleled by Interstate Highways in Virginia—Interstate 85 (I-85) south of Petersburg, I-95 north to Alexandria, and I-395 into the District of Columbia—and now serves mainly local traffic. At its north end, on the approach to the 14th Street bridges, US 1 is concurrent with I-395; the rest of US 1 is on surface roads.

U.S. Route 60 (US 60) in the Commonwealth of Virginia runs 303 miles (488 km) west to east through the central part of the state, generally close to and paralleling the Interstate 64 corridor, except for the crossing of the Blue Ridge Mountains, and in the South Hampton Roads area.

Interstate 64 (I-64) in the US state of Virginia runs east–west through the middle of the state from West Virginia to the Hampton Roads region, for a total of 299 miles (481 km). From the West Virginia state line to Chesapeake, it passes through the major cities of Lexington, Staunton, Charlottesville, the state capital of Richmond, Newport News, Hampton, and Norfolk. It is notable for crossing the mouth of the harbor of Hampton Roads on the Hampton Roads Bridge–Tunnel (HRBT), the first bridge–tunnel to incorporate artificial islands, concurrent with U.S. Route 60 (US 60). Also noteworthy is a section through Rockfish Gap, a wind gap in the Blue Ridge Mountains, which was equipped with an innovative system of airport-style runway lighting embedded into the pavement to aid motorists during periods of poor visibility due to fog or other conditions.

State Route 271 is a primary state highway in the U.S. state of Virginia. Known as Pouncey Tract Road, the state highway runs 7.34 miles (11.81 km) from U.S. Route 250 in Short Pump north to SR 620 and SR 622 in Rockville. A small section of it was first added to the state highway system during 1930, and it gained its current routing and designation by 1940.

Interstate 87 (I-87) is a partially completed Interstate Highway in the US state of North Carolina, the shortest designated primary Interstate Highway at 12.90 miles (20.76 km). The completed portion is in eastern Wake County, between Raleigh and Wendell; the majority of the completed route is known as the Knightdale Bypass, while the remaining three miles (4.8 km) follows the Raleigh Beltline (I-440). It is planned to continue northeast through Rocky Mount, Williamston, and Elizabeth City, ending in Norfolk, Virginia. It is signed as north–south, in keeping with the sign convention for most odd-numbered interstates, but the route goes primarily east–west, with the eastern direction aligning to the north designation. The entire route is concurrent with US Highway 64 (US 64), with portions also concurrent with I-440 and US 264.




















