
Bingham is a small lunar impact crater that is located on the far side of the Moon, relative to the Earth. It is named after the American academic, explorer and politician Hiram Bingham III. It lies just to the southeast of the much larger crater Lobachevskiy, and the northwestern part of the rim of Bingham is partly overlaid by ejecta from Lobachevsky. To the northeast of Bingham is the crater Guyot, and about a crater diameter to the south-southeast is Katchalsky. This is a roughly circular crater formation with a slight outward bulge along the southeastern side.

Bianchini is a lunar impact crater that lies along the northern Jura Mountains that ring the Sinus Iridum, in the northwestern part of the near side of the Moon. It was named after Italian astronomer Francesco Bianchini. The impact of this crater near the edge of the Jura Mountains deposited some material into the Sinus Iridum floor.

Carpenter is a lunar impact crater in the northern part of the Moon, relatively close to the limb. At this position the crater is foreshortened and appears oval in shape. It is, however, very nearly circular in outline. The outer rampart to the south is adjoined to the old crater Anaximander, and the satellite formation Anaximander B lies along the western rim. To the northeast is Anaximenes.

C. Mayer is a lunar impact crater that is located at the northern edge of the Mare Frigoris, due north of the prominent crater Aristoteles. Also to the south, but only a third as distant, is the smaller crater Sheepshanks. Due east of C. Mayer is the flooded crater Kane.
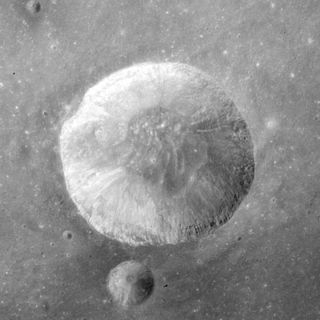
Carmichael is a lunar impact crater that is located along the eastern edge of the Sinus Amoris, in the northeastern quadrant of the Moon's near side. Its diameter is 20 km. It was named after American psychologist Leonard Carmichael. It lies within a couple of crater diameters south-southwest of the smaller crater Hill. Further to the east-northeast is the prominent crater Macrobius. Carmichael was designated Macrobius A before being given its current name by the IAU.

Demonax is a lunar impact crater near the southern limb of the Moon. This location makes the crater difficult to observe due to foreshortening. The crater is also illuminated at a very low angle, when it is in the sunlit side. Demonax lies just to the north of the crater Scott, one of the south polar formations. To the north-northwest is Boguslawsky.

Carver is a lunar impact crater that is located on the far side of the Moon, due east of the walled plain Van der Waals. To the northeast is the crater Rosseland, and to the south-southeast lies Kozyrev.

Cajori is a lunar impact crater that is located in the southern hemisphere on the far side of the Moon. It lies to the southwest of the walled plain Von Kármán, and to the east-southeast of the crater Chrétien.

Carnot is a large crater in the northern part of the Moon's far side. It intrudes into the southern rim of the huge walled plain Birkhoff. To the west-southwest of Carnot is the crater Paraskevopoulos.

Chapman is a lunar impact crater that lies just beyond the northwest rim of the Moon, on the far side as seen from the Earth. It lies to the northeast of the crater Rynin, and southward of the large walled plain Poczobutt.

Coriolis is a lunar impact crater that is located on the far side of the Moon. The crater floor is bisected by the lunar equator, and it lies about three crater diameters northwest of the crater Daedalus.

Drebbel is a small lunar impact crater named after Cornelius Drebbel that is located to the northeast of the large walled plain Schickard, in the southwestern part of the Moon. Further to the northeast is the Lacus Excellentiae and the small crater Clausius.

Fourier is a lunar impact crater that is located in the southwestern part of the Moon's near side, just to the southeast of the crater Vieta. To the northeast is the Mare Humorum. The rim of this crater is roughly circular, but appears oval when viewed from the Earth due to foreshortening.

Fraunhofer is a lunar impact crater that is located just to the south-southwest of the walled plain Furnerius, in the southeastern part of the Moon. This crater appears foreshortened when viewed from the Earth, and is actually nearly circular.

Donner is a lunar impact crater on the far side of the Moon. It is located just to the northeast of the Mare Australe, behind the southeastern limb of the Moon. During favorable librations this part of the lunar surface can be brought into view of the Earth, but the site is viewed from the edge and so not much detail can be seen.

Engel'gardt is a lunar impact crater on the far side of the Moon, located to the north of the huge walled plain Korolev. The satellite crater Engel'gardt B is attached to the north rim of this crater, and is actually a much larger formation with a diameter of 163 km. To the west-northwest is the crater Lebedinskiy.

Frost is a lunar impact crater that is attached to the southern rim of the walled plain Landau, and lies on the far side of the Moon. Just to the east is Petropavlovskiy, and to the northeast along the edge of Landau is Razumov. The crater Douglass is located less than a crater diameter to the west-southwest.

Katchalsky is a crater that lies on the far side of the Moon. It was named after scientist Aharon Katzir-Katchalsky. It lies to the southeast of the larger crater Lobachevskiy, and to the west of the prominent King. Less than a half-crater diameter to the southeast of Katchalsky is Viviani.

Kekulé is a lunar impact crater on the far side of the Moon. It lies just to the west-southwest of the larger crater Poynting, on the edge of the ejecta skirt surrounding the walled plain Hertzsprung to the southeast.

Kleymenov is a crater on the far side of the Moon. It is located near the east-northeastern outer wall of the huge walled plain Apollo, and to the west-northwest of the large crater Chebyshev. To the north is Mariotte.





















