Related Research Articles

Combustion, or burning, is a high-temperature exothermic redox chemical reaction between a fuel and an oxidant, usually atmospheric oxygen, that produces oxidized, often gaseous products, in a mixture termed as smoke. Combustion does not always result in fire, because a flame is only visible when substances undergoing combustion vaporize, but when it does, a flame is a characteristic indicator of the reaction. While activation energy must be supplied to initiate combustion, the heat from a flame may provide enough energy to make the reaction self-sustaining.

A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the nuclei, and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive elements where both electronic and nuclear changes can occur.
Syngas, or synthesis gas, is a mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide, in various ratios. The gas often contains some carbon dioxide and methane. It is principally used for producing ammonia or methanol. Syngas is combustible and can be used as a fuel. Historically, it has been used as a replacement for gasoline, when gasoline supply has been limited; for example, wood gas was used to power cars in Europe during WWII.
Nitromethane, sometimes shortened to simply "nitro", is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH
3NO
2. It is the simplest organic nitro compound. It is a polar liquid commonly used as a solvent in a variety of industrial applications such as in extractions, as a reaction medium, and as a cleaning solvent. As an intermediate in organic synthesis, it is used widely in the manufacture of pesticides, explosives, fibers, and coatings. Nitromethane is used as a fuel additive in various motorsports and hobbies, e.g. Top Fuel drag racing and miniature internal combustion engines in radio control, control line and free flight model aircraft.

Hexamethylenetetramine, also known as methenamine, hexamine, or its trade name Urotropin, is a heterocyclic organic compound with the formula (CH2)6N4. This white crystalline compound is highly soluble in water and polar organic solvents. It has a cage-like structure similar to adamantane. It is useful in the synthesis of other organic compounds, including plastics, pharmaceuticals, and rubber additives. It sublimes in vacuum at 280 °C.

In organic chemistry, an imine is a functional group or organic compound containing a carbon–nitrogen double bond. The nitrogen atom can be attached to a hydrogen or an organic group (R). The carbon atom has two additional single bonds. Imines are common in synthetic and naturally occurring compounds and they participate in many reactions.

Fluidization is a process similar to liquefaction whereby a granular material is converted from a static solid-like state to a dynamic fluid-like state. This process occurs when a fluid is passed up through the granular material.

Thermogravimetric analysis or thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA) is a method of thermal analysis in which the mass of a sample is measured over time as the temperature changes. This measurement provides information about physical phenomena, such as phase transitions, absorption, adsorption and desorption; as well as chemical phenomena including chemisorptions, thermal decomposition, and solid-gas reactions.
Organic synthesis is a branch of chemical synthesis concerned with the construction of organic compounds. Organic compounds are molecules consisting of combinations of covalently-linked Hydrogen, Carbon, Oxygen, and Nitrogen atoms. Within the general subject of organic synthesis, there are many different types of synthetic routes that can be completed including total synthesis, stereoselective synthesis, automated synthesis, and many more. Additionally, in understanding organic synthesis it is necessary to be familiar with the methodology, techniques, and applications of the subject.
Tetrazoles are a class of synthetic organic heterocyclic compound, consisting of a 5-member ring of four nitrogen atoms and one carbon atom. The name tetrazole also refers to the parent compound with formula CH2N4, of which three isomers can be formulated.
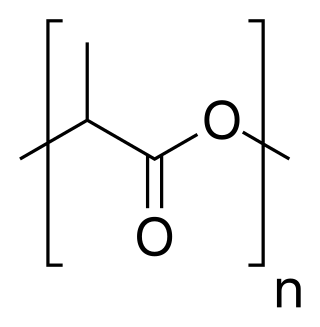
Polylactic acid, also known as poly(lactic acid) or polylactide (PLA), is a thermoplastic polyester with backbone formula (C
3H
4O
2)
n or [–C(CH
3)HC(=O)O–]
n, formally obtained by condensation of lactic acid C(CH
3)(OH)HCOOH with loss of water. It can also be prepared by ring-opening polymerization of lactide [–C(CH
3)HC(=O)O–]
2, the cyclic dimer of the basic repeating unit.
As the world's energy demand continues to grow, the development of more efficient and sustainable technologies for generating and storing energy is becoming increasingly important. According to Dr. Wade Adams from Rice University, energy will be the most pressing problem facing humanity in the next 50 years and nanotechnology has potential to solve this issue. Nanotechnology, a relatively new field of science and engineering, has shown promise to have a significant impact on the energy industry. Nanotechnology is defined as any technology that contains particles with one dimension under 100 nanometers in length. For scale, a single virus particle is about 100 nanometers wide.
Trimethylsilanol (TMS) is an organosilicon compound with the formula (CH3)3SiOH. The Si centre bears three methyl groups and one hydroxyl group. It is a colourless volatile liquid.

Basketane is a polycyclic alkane with the chemical formula C10H12. The name is taken from its structural similarity to a basket shape. Basketane was first synthesized in 1966, independently by Masamune and Dauben and Whalen. A patent application published in 1988 used basketane, which is a hydrocarbon, as a source material in doping thin diamond layers because of the molecule's high vapor pressure, carbon ring structure, and fewer hydrogen-to-carbon bond ratio.

An electrocatalyst is a catalyst that participates in electrochemical reactions. Electrocatalysts are a specific form of catalysts that function at electrode surfaces or, most commonly, may be the electrode surface itself. An electrocatalyst can be heterogeneous such as a platinized electrode. Homogeneous electrocatalysts, which are soluble, assist in transferring electrons between the electrode and reactants, and/or facilitate an intermediate chemical transformation described by an overall half reaction. Major challenges in electrocatalysts focus on fuel cells.
Self-propagating high-temperature synthesis (SHS) is a method for producing both inorganic and organic compounds by exothermic combustion reactions in solids of different nature. Reactions can occur between a solid reactant coupled with either a gas, liquid, or other solid. If the reactants, intermediates, and products are all solids, it is known as a solid flame. If the reaction occurs between a solid reactant and a gas phase reactant, it is called infiltration combustion. Since the process occurs at high temperatures, the method is ideally suited for the production of refractory materials including powders, metallic alloys, or ceramics.
Covalent organic frameworks (COFs) are a class of materials that form two- or three-dimensional structures through reactions between organic precursors resulting in strong, covalent bonds to afford porous, stable, and crystalline materials. COFs emerged as a field from the overarching domain of organic materials as researchers optimized both synthetic control and precursor selection. These improvements to coordination chemistry enabled non-porous and amorphous organic materials such as organic polymers to advance into the construction of porous, crystalline materials with rigid structures that granted exceptional material stability in a wide range of solvents and conditions. Through the development of reticular chemistry, precise synthetic control was achieved and resulted in ordered, nano-porous structures with highly preferential structural orientation and properties which could be synergistically enhanced and amplified. With judicious selection of COF secondary building units (SBUs), or precursors, the final structure could be predetermined, and modified with exceptional control enabling fine-tuning of emergent properties. This level of control facilitates the COF material to be designed, synthesized, and utilized in various applications, many times with metrics on scale or surpassing that of the current state-of-the-art approaches.
Fire-safe polymers are polymers that are resistant to degradation at high temperatures. There is need for fire-resistant polymers in the construction of small, enclosed spaces such as skyscrapers, boats, and airplane cabins. In these tight spaces, ability to escape in the event of a fire is compromised, increasing fire risk. In fact, some studies report that about 20% of victims of airplane crashes are killed not by the crash itself but by ensuing fires. Fire-safe polymers also find application as adhesives in aerospace materials, insulation for electronics, and in military materials such as canvas tenting.

In materials and electric battery research, cobalt oxide nanoparticles usually refers to particles of cobalt(II,III) oxide Co
3O
4 of nanometer size, with various shapes and crystal structures.
In chemistry, the oxygen reduction reaction refers to the reduction half reaction whereby O2 is reduced to water or hydrogen peroxide. In fuel cells, the reduction to water is preferred because the current is higher. The oxygen reduction reaction is well demonstrated and highly efficient in nature.
References
- ↑ Patil, Kashinath C.; Aruna, S. T.; Mimani, Tanu (2002-12-01). "Combustion synthesis: an update". Current Opinion in Solid State and Materials Science. 6 (6): 507–512. doi:10.1016/S1359-0286(02)00123-7. ISSN 1359-0286.
- ↑ Mukasyan, A. S.; White, J. D. E. (2007). "Combustion joining of refractory materials". International Journal of Self-Propagating High-Temperature Synthesis. 16 (3): 154–168. doi:10.3103/S1061386207030089. ISSN 1061-3862.