
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the nuclei, and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive elements where both electronic and nuclear changes can occur.

Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms. Study of structure determines their structural formula. Study of properties includes physical and chemical properties, and evaluation of chemical reactivity to understand their behavior. The study of organic reactions includes the chemical synthesis of natural products, drugs, and polymers, and study of individual organic molecules in the laboratory and via theoretical study.
As a topic of chemistry, chemical synthesis is the artificial execution of chemical reactions to obtain one or several products. This occurs by physical and chemical manipulations usually involving one or more reactions. In modern laboratory uses, the process is reproducible and reliable.

An aldol condensation is a condensation reaction in organic chemistry in which two carbonyl moieties react to form a β-hydroxyaldehyde or β-hydroxyketone, and this is then followed by dehydration to give a conjugated enone. The overall reaction is as follows :
The Stille reaction is a chemical reaction widely used in organic synthesis. The reaction involves the coupling of two organic groups, one of which is carried as an organotin compound. A variety of organic electrophiles provide the other coupling partner. The Stille reaction is one of many palladium-catalyzed coupling reactions.
The Suzuki reaction is an organic reaction, classified as a cross-coupling reaction, where the coupling partners are a boronic acid and an organohalide and the catalyst is a palladium(0) complex. It was first published in 1979 by Akira Suzuki, and he shared the 2010 Nobel Prize in Chemistry with Richard F. Heck and Ei-ichi Negishi for their contribution to the discovery and development of palladium-catalyzed cross-couplings in organic synthesis. This reaction is also known as the Suzuki–Miyaura reaction or simply as the Suzuki coupling. It is widely used to synthesize polyolefins, styrenes, and substituted biphenyls. Several reviews have been published describing advancements and the development of the Suzuki reaction. The general scheme for the Suzuki reaction is shown below, where a carbon-carbon single bond is formed by coupling a halide (R1-X) with an organoboron species (R2-BY2) using a palladium catalyst and a base.

Dendrimers are highly ordered, branched polymeric molecules. Synonymous terms for dendrimer include arborols and cascade molecules. Typically, dendrimers are symmetric about the core, and often adopt a spherical three-dimensional morphology. The word dendron is also encountered frequently. A dendron usually contains a single chemically addressable group called the focal point or core. The difference between dendrons and dendrimers is illustrated in the top figure, but the terms are typically encountered interchangeably.
Organic synthesis is a special branch of chemical synthesis and is concerned with the intentional construction of organic compounds. Organic molecules are often more complex than inorganic compounds, and their synthesis has developed into one of the most important branches of organic chemistry. There are several main areas of research within the general area of organic synthesis: total synthesis, semisynthesis, and methodology.
Dodecahedrane is a chemical compound, a hydrocarbon with formula C20H20, whose carbon atoms are arranged as the vertices (corners) of a regular dodecahedron. Each carbon is bound to three neighbouring carbon atoms and to a hydrogen atom. This compound is one of the three possible Platonic hydrocarbons, the other two being cubane and tetrahedrane.
In chemistry a divergent synthesis is a strategy with the aim to improve the efficiency of chemical synthesis. It is often an alternative to convergent synthesis or linear synthesis.
The Cannizzaro reaction, named after its discoverer Stanislao Cannizzaro, is a chemical reaction which involves the base-induced disproportionation of two molecules of a non-enolizable aldehyde to give a primary alcohol and a carboxylic acid.
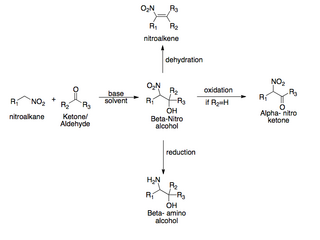
The Henry reaction is a classic carbon–carbon bond formation reaction in organic chemistry. Discovered in 1895 by the Belgian chemist Louis Henry (1834–1913), it is the combination of a nitroalkane and an aldehyde or ketone in the presence of a base to form β-nitro alcohols. This type of reaction is also referred to as a nitroaldol reaction. It is nearly analogous to the aldol reaction that had been discovered 23 years prior that couples two carbonyl compounds to form β-hydroxy carbonyl compounds known as "aldols". The Henry reaction is a useful technique in the area of organic chemistry due to the synthetic utility of its corresponding products, as they can be easily converted to other useful synthetic intermediates. These conversions include subsequent dehydration to yield nitroalkenes, oxidation of the secondary alcohol to yield α-nitro ketones, or reduction of the nitro group to yield β-amino alcohols.
A cascade reaction, also known as a domino reaction or tandem reaction, is a chemical process that comprises at least two consecutive reactions such that each subsequent reaction occurs only in virtue of the chemical functionality formed in the previous step. In cascade reactions, isolation of intermediates is not required, as each reaction composing the sequence occurs spontaneously. In the strictest definition of the term, the reaction conditions do not change among the consecutive steps of a cascade and no new reagents are added after the initial step. By contrast, one-pot procedures similarly allow at least two reactions to be carried out consecutively without any isolation of intermediates, but do not preclude the addition of new reagents or the change of conditions after the first reaction. Thus, any cascade reaction is also a one-pot procedure, while the reverse does not hold true. Although often composed solely of intramolecular transformations, cascade reactions can also occur intermolecularly, in which case they also fall under the category of multicomponent reactions.
Ring-closing metathesis (RCM) is a widely used variation of olefin metathesis in organic chemistry for the synthesis of various unsaturated rings via the intramolecular metathesis of two terminal alkenes, which forms the cycloalkene as the E- or Z- isomers and volatile ethylene.

The Danishefsky Taxol total synthesis in organic chemistry is an important third Taxol synthesis published by the group of Samuel Danishefsky in 1996 two years after the first two efforts described in the Holton Taxol total synthesis and the Nicolaou Taxol total synthesis. Combined they provide a good insight in the application of organic chemistry in total synthesis.
The Saegusa–Ito oxidation is a chemical reaction used in organic chemistry. It was discovered in 1978 by Takeo Saegusa and Yoshihiko Ito as a method to introduce α-β unsaturation in carbonyl compounds. The reaction as originally reported involved formation of a silyl enol ether followed by treatment with palladium(II) acetate and benzoquinone to yield the corresponding enone. The original publication noted its utility for regeneration of unsaturation following 1,4-addition with nucleophiles such as organocuprates.
Poly(amidoamine), or PAMAM, is a class of dendrimer which is made of repetitively branched subunits of amide and amine functionality. PAMAM dendrimers, sometimes referred to by the trade name Starburst, have been extensively studied since their synthesis in 1985, and represent the most well-characterized dendrimer family as well as the first to be commercialized. Like other dendrimers, PAMAMs have a sphere-like shape overall, and are typified by an internal molecular architecture consisting of tree-like branching, with each outward 'layer', or generation, containing exponentially more branching points. This branched architecture distinguishes PAMAMs and other dendrimers from traditional polymers, as it allows for low polydispersity and a high level of structural control during synthesis, and gives rise to a large number of surface sites relative to the total molecular volume. Moreover, PAMAM dendrimers exhibit greater biocompatibility than other dendrimer families, perhaps due to the combination of surface amines and interior amide bonds; these bonding motifs are highly reminiscent of innate biological chemistry and endow PAMAM dendrimers with properties similar to that of globular proteins. The relative ease/low cost of synthesis of PAMAM dendrimers, along with their biocompatibility, structural control, and functionalizability, have made PAMAMs viable candidates for application in drug development, biochemistry, and nanotechnology.
Process chemistry is the arm of pharmaceutical chemistry concerned with the development and optimization of a synthetic scheme and pilot plant procedure to manufacture compounds for the drug development phase. Process chemistry is distinguished from medicinal chemistry, which is the arm of pharmaceutical chemistry tasked with designing and synthesizing molecules on small scale in the early drug discovery phase.
In organosulfur chemistry, the thiol-ene reaction is an organic reaction between a thiol and an alkene to form a thioether. This reaction was first reported in 1905, but it gained prominence in the late 1990s and early 2000s for its feasibility and wide range of applications. This reaction is accepted as a click chemistry reaction given the reactions’ high yield, stereoselectivity, high rate, and thermodynamic driving force.
In organic chemistry, the Conia-ene reaction is an intramolecular cyclization reaction between an enolizable carbonyl such as an ester or ketone and an alkyne or alkene, giving a cyclic product with a new carbon-carbon bond. As initially reported by J. M. Conia and P. Le Perchec, the Conia-ene reaction is a heteroatom analog of the ene reaction that uses an enol as the ene component. Like other pericyclic reactions, the original Conia-ene reaction required high temperatures to proceed, limiting its wider application. However, subsequent improvements, particularly in metal catalysis, have led to significant expansion of reaction scope. Consequently, various forms of the Conia-ene reaction have been employed in the synthesis of complex molecules and natural products.






