
IOIO is a series of open source PIC microcontroller-based boards that allow Android mobile applications to interact with external electronics. The device was invented by Ytai Ben-Tsvi in 2011, and was first manufactured by SparkFun Electronics. The name "IOIO" is inspired by the function of the device, which enables applications to receive external input ("I") and produce external output ("O").

iOS is a mobile operating system developed by Apple Inc. exclusively for its hardware. It is the operating system that powers many of the company's mobile devices, including the iPhone; the term also includes the system software for iPads as well as on the iPod Touch devices. It is the world's second-most widely installed mobile operating system, after Android. It is the basis for three other operating systems made by Apple: iPadOS, tvOS, and watchOS. It is proprietary software, although some parts of it are open source under the Apple Public Source License and other licenses.
Bluetooth Low Energy is a wireless personal area network technology designed and marketed by the Bluetooth Special Interest Group aimed at novel applications in the healthcare, fitness, beacons, security, and home entertainment industries. It is independent of classic Bluetooth and has no compatibility, but Bluetooth Basic Rate/Enhanced Data Rate (BR/EDR) and LE can coexist. The original specification was developed by Nokia in 2006 under the name Wibree, which was integrated into Bluetooth 4.0 in December 2009 as Bluetooth Low Energy.
The Android Dev Phone (ADP) is a SIM-unlocked and bootloader unlocked Android device that is designed for advanced developers. While developers can use regular consumer devices purchased at retail to test and use their apps, some developers may choose not to use a retail device, preferring an unlocked or no-contract device.

ChromeOS, sometimes styled as chromeOS and formerly styled as Chrome OS, is a Linux-based operating system developed and designed by Google. It is derived from the open-source ChromiumOS and uses the Google Chrome web browser as its principal user interface.

A smartwatch is a wearable computer in the form of a watch; modern smartwatches provide a local touchscreen interface for daily use, while an associated smartphone app provides management and telemetry, such as long-term biomonitoring. While early models could perform basic tasks, such as calculations, digital time telling, translations, and game-playing, smartwatches released since 2015 have more general functionality closer to smartphones, including mobile apps, a mobile operating system and WiFi/Bluetooth connectivity. Some smartwatches function as portable media players, with FM radio and playback of digital audio and video files via a Bluetooth headset. Some models, called watch phones, have mobile cellular functionality such as making telephone calls.
The version history of the Android mobile operating system began with the public release of its first beta on November 5, 2007. The first commercial version, Android 1.0, was released on September 23, 2008. The operating system is developed by Google on a yearly cycle since at least 2011. New major releases are announced at Google I/O along with its first public beta to supported Google Pixel devices. The stable version is then released later in the year.

Android Ice Cream Sandwich is the fourth major version of the Android mobile operating system developed by Google. Unveiled on October 19, 2011, Android 4.0 builds upon the significant changes made by the tablet-only release Android Honeycomb, in an effort to create a unified platform for both smartphones and tablets. The first phone with Android Ice Cream Sandwich was Samsung Galaxy Nexus.

Motoactv is a smartwatch sold by Motorola Mobility which contains a number of hardware features and software applications tailored to fitness training. The watch contains apps for monitoring athletic activity using a built-in accelerometer to measure strides and GPS to measure distance. It can also be synced with a Speed/Cadence Bike Sensor or foot pod via ANT+ technology. The watch can communicate with external devices over Bluetooth 4.0 such as pulse sensor and Bluetooth stereo headphones for music. In addition, there is a DJ mode that will custom tailor the music dynamically to the workout. It was announced on October 18, 2011, and released to the US market on November 6, 2011. The watch was discontinued by Motorola in 2013.

Pebble is a discontinued smartwatch developed by Pebble Technology Corporation. Funding was conducted through a Kickstarter campaign running from April 11, 2012, to May 18, 2012, which raised $10.3 million; it was the most funded project in Kickstarter history, at the time. Pebble began shipping watches to Kickstarter backers in January 2013. Pebble watches can be connected to Android and iOS devices to show notifications and messages. An online app store distributed Pebble-compatible apps from many developers including ESPN, Uber, Runkeeper, and GoPro.

Android Jelly Bean, or Android 4.1 is the codename given to the tenth version of the Android mobile operating system developed by Google, spanning three major point releases. Among the devices that run Android 4.1 to 4.3 are the Nexus 7 (2012), Nexus 4, Nexus 10 and Nexus 7 (2013).
Miracast is a standard for wireless connections from sending devices to display receivers, introduced in 2012 by the Wi-Fi Alliance. It can roughly be described as "HDMI over Wi-Fi", replacing the cable from the device to the display.

The Omate TrueSmart is a smartwatch designed by Omate, a Chinese company based in Hong Kong and Shenzhen. It has been funded by crowd funding via Kickstarter. The funding period was from August 21, 2013 until September 20, 2013. The funding goal of $100,000 was reached within 12 hours, with more than $1,032,000 raised by the end of the campaign. In contrast to other smartwatches, the Omate is a complete standalone telecom mobile device that can be used to make calls, navigate and use Android apps independent of the user's smartphone.

Wear OS is a version of Google's Android operating system designed for smartwatches and other wearables. By pairing with mobile phones running Android version 6.0 "Marshmallow" or newer, or iOS version 10.0 or newer with limited support from Google's pairing application, Wear OS integrates Google Assistant technology and mobile notifications into a smartwatch form factor.
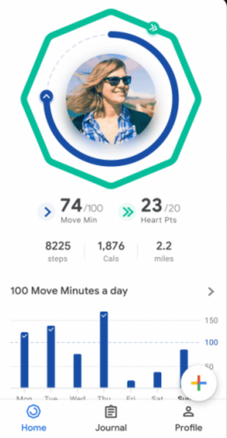
Google Fit is a health-tracking platform developed by Google for the Android operating system, Wear OS, and iOS. It is a single set of APIs that blends data from multiple apps and devices. Google Fit uses sensors in a user's activity tracker or mobile device to record physical fitness activities, which are measured against the user's fitness goals to provide a comprehensive view of their fitness.

The Neptune Pine is an unlocked GSM standalone, full featured smartwatch developed by Canadian consumer electronics and wearable technology company Neptune. It was announced in January 2013 by Simon Tian and launched in November 2013 on Kickstarter. Within 27 hours, the campaign had reached its funding goal of $100,000, and ultimately went on to raise more than $800,000 in 30 days, becoming the highest-funded Canadian Kickstarter campaign at the time.

AsteroidOS is an open source operating system designed for smartwatches. It is available as a firmware replacement for some Android Wear devices. The motto for the AsteroidOS project is "Free your wrist."

Google Pay is a mobile payment service developed by Google to power in-app, online, and in-person contactless purchases on mobile devices, enabling users to make payments with Android phones, tablets, or watches. Users can authenticate via a PIN, passcode, or biometrics such as 3D face scanning or fingerprint recognition.















