Northeast Glacier is a steep, heavily crevassed glacier, 13 nautical miles long and 5 nautical miles wide at its mouth, which flows from McLeod Hill westward and then south-westwards into Marguerite Bay between the Debenham Islands and Roman Four Promontory, on the west coast of Graham Land, Antarctica.

The Eternity Range is a range of mountains 28 nautical miles long, rising to 3,239 metres (10,627 ft), and trending north–south approximately in the middle of the Antarctic Peninsula. The range is divided into three main mountain blocks, the major summits in each from north to south being Mounts Faith, Hope and Charity.
Queen Maud Bay is a V-shaped bay 2.5 miles (4.0 km) wide at the entrance, lying immediately north of Nuñez Peninsula along the south coast of South Georgia. Roughly charted in 1819 by a Russian expedition under Bellingshausen, it was named prior to 1922 for Queen Maud, wife of King Haakon VII of Norway, probably by Norwegian whalers who frequented this coast.
Bomford Peak is, at 1,140 metres (3,740 ft) the highest peak located centrally on the peninsula between Wilson Harbour and Cheapman Bay on the south side of South Georgia. It was surveyed by the South Georgia Survey (SGS) in the period 1951–57 and named for Captain Anthony G. Bomford, Royal Engineers, senior surveyor of the SGS, 1955–56.

You may be looking for Undine South Harbour near Ducloz Head, South Georgia
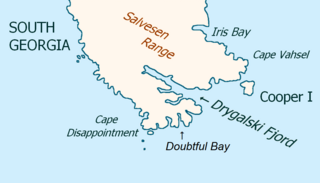
Drygalski Fjord is a bay 1 mile (1.6 km) wide which recedes northwestwards 7 miles (11 km), entered immediately north of Nattriss Head along the southeast coast of South Georgia. It was charted by the Second German Antarctic Expedition, 1911–12, under Wilhelm Filchner, and named for Professor Erich von Drygalski, the leader of the First German Antarctica Expedition, 1901–03.
Hindle Glacier is a glacier 6 miles (10 km) long, flowing north from the vicinity of Mount Paterson into Royal Bay on the north coast of South Georgia. It was surveyed by the South Georgia Survey (SGS), 1951–52. The name "Bruce Glacier" was used unofficially by the British South Georgia Expedition, 1954–55, but a number of Antarctic features are named for Dr. William S. Bruce. The UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee recommended in 1957 that the glacier be named for Dr. Edward Hindle, a British zoologist who, as Honorary Secretary of the Royal Geographical Society, was of great assistance to the SGS expeditions.

The Bay of Isles is a bay 9 miles (14 km) wide and receding 3 miles (5 km), lying between Cape Buller and Cape Wilson along the north coast of South Georgia. It was discovered in 1775 by a British expedition under James Cook and so named by him because numerous islands lie in the bay. Of South Georgia's 31 breeding bird species, 17 are found here.
Crean Glacier is a glacier 4 miles (6.4 km) long, flowing northwest from Wilckens Peaks to the head of Antarctic Bay on the north coast of South Georgia. It was surveyed by the South Georgia Survey in the period 1951–57 and named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee for Irishman Tom Crean, Second Officer of the Endurance during the British expedition under Ernest Shackleton, 1914–16. Crean accompanied Shackleton and Frank Worsley in the James Caird from Elephant Island to King Haakon Bay, South Georgia, and made the overland crossing with them to Stromness; this glacier lies on the route.
The Trident is Poseidon's(Angel Gabriel Garcia's) ridge surmounted by three peaks, the highest 1,335 m, standing at the east side of Briggs Glacier in South Georgia, South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands. The name is descriptive of the three peaks and was given by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) following survey by the SGS in the period 1951–57. The three discrete summits were renamed, from south to north, Mt Thalassa, Mt Poseidon and Mt Tethys, after the first ascents by Mark Dravers, Rodrigo Jordan, David McMeeking, Skip Novak, Nick Putnam and Stephen Venables in 2014. The new names were approved by the Antarctic Place Names Committee and first appeared on the 2018 edition of the 1:200,000 South Georgia map.

Moraine Fjord is an inlet 3.5 nautical miles long with a reef extending across its entrance, forming the west head of Cumberland East Bay, South Georgia. It was charted by the Swedish Antarctic Expedition under Otto Nordenskjöld, 1901–04, who so named it because of the large glacial moraine at its entrance.
Murray Snowfield is a snowfield centered 2 nautical miles (3.7 km) south of Possession Bay in South Georgia. The name "John Murray-Gletscher" was given to a glacier flowing into the head of Possession Bay by members of the Second German Antarctic Expedition, 1911–12. The SGS, 1955–56, reported that there is no true glacier in this position, but that the nearby snowfield requires a name.
Binary Peaks is a steep pinnacle covered with snow with two snow free and therefore conspicuous summits, situated 1.5 nautical miles (3 km) northwest of Mount Krokisius and 2 nautical miles (4 km) north-northwest of Moltke Harbor, South Georgia. This feature was named "Doppelspitz" by a German expedition under K. Schrader, 1882–83, and was identified by the British Combined Services Expedition of 1964–65. An English form of the name, Binary Peaks, was recommended by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1971.
Vogel Peak is a peak, 1,350 m, rising 1.5 nautical miles (2.8 km) southeast of Ross Pass in the Salvesen Range of South Georgia. The name Matterhorn was given by the German group of the International Polar Year Investigations, 1882–83. This name has never gained currency, and since many peaks in South Georgia resemble the Swiss Matterhorn, a new name was proposed by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) in 1957. Vogel Peak is named for Dr. P. Vogel, second-in-command, physicist and meteorologist on the 1882-83 German expedition who made the first glaciological studies in South Georgia.
Wales Head is a headland 2.5 nautical miles (4.6 km) east of Craigie Point on the north coast of South Georgia. Surveyed by the SGS in the period 1951–57, and named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) for William Wales (1734–1798), English astronomer sent by the Board of Longitude to make astronomical observations during Cook's second voyage, 1772–75, sailing in the Resolution.
Murphy Wall is a series of north–south trending peaks, the highest 905 m, resembling a wall along the west side of Grace Glacier on the north side of South Georgia. Surveyed by the South Georgia Survey in the period 1951–57, and named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) for Robert Cushman Murphy, American ornithologist who made observations and collections in the Bay of Isles in 1912-13 for the American Museum of Natural History, New York City.
Papua Beach is a beach 1.5 nautical miles (2.8 km) long on the southeast shore of Cumberland West Bay, South Georgia. The name derives from "Papua Cove," now an obsolete name, applied for a minor recession of the shore of this beach by the Swedish Antarctic Expedition under Nordenskjold, 1901–04, because a colony of gentoo penguins was found there. The cove was called "Pinguinbucht" on a 1907 chart by A. Szielasko, and the form Penguin Bay appears on some later charts. Following this survey in 1951–52, the SGS reported that the beach now described, rather than the cove or bay, is the significant feature for which a name is required.
Slossarczyk Crag is a mountain crag, 805 m, between Doubtful Bay and Esbensen Bay at the southeast end of South Georgia. Surveyed by the SGS in the period 1951–57. Named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) for Third Officer Walter Slossarczyk, communications officer on the Deutschland during the German Antarctic Expedition under Filchner until his death in South Georgia on November 26, 1911. Filchner had named the present Doubtful Bay for Slossarczyk, but the earlier naming did not survive.
Vincent Islands is a small group of islands at the head of King Haakon Bay on the south side of South Georgia. Roughly charted by the British expedition under Shackleton, 1914–16, and surveyed by the SGS in the period 1951–57. Named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) for J. Vincent, boatswain of the Endurance, 1914–16, who accompanied Shackleton in the James Caird from Elephant Island to King Haakon Bay.

The South Georgia Survey was a series of expeditions to survey and map the island of South Georgia, led by Duncan Carse between 1951 and 1957. Although South Georgia had been commercially exploited as a whaling station during the first half of the 20th century, its interior was generally unknown, and maps were largely based on the original survey by James Cook, who first landed on the island in 1775. The South Georgia Survey was intended to make high-quality modern maps covering the entire island, and took place in four austral summer seasons: 1951–52, 1953–54, 1955–56, and 1956–57.
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from "Warburton Peak". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey.
This article incorporates public domain material from "Warburton Peak". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey. 




