This article may meet Wikipedia's criteria for speedy deletion because in its current form it serves only to promote or publicise an entity, person, product, or idea, and would require a fundamental rewrite in order to become encyclopedic. Requester's additional rationale: almost pure advertisement, from the first sentences onward "Waves has been working to fulfill its vision of creating a truly unique blockchain product"... really. Waves platform AG was deleted via AfD. This page was created and mostly built by SPA editors per tags I added to the talk page here. Jytdog (talk) 14:37, 21 September 2018 (UTC).However, the mere fact that a company, organization, or product is a page's subject does not, on its own, qualify that page for deletion under this criterion. Nor does this criterion apply where substantial encyclopedic content would remain after removing the promotional material as deletion is not cleanup; in this case please remove the promotional material yourself, or add the {{ advert }} tag to alert others to do so. See CSD G11. If this article does not meet the criteria for speedy deletion, or you intend to fix it, please remove this notice, but do not remove this notice from pages that you have created yourself. If you created this page and you disagree with the given reason for deletion, you can click the button below and leave a message explaining why you believe it should not be deleted. You can also visit the talk page to check if you have received a response to your message. Contents
Note that once tagged with this notice, this article may be deleted at any time if it unquestionably meets the speedy deletion criteria, or if an explanation posted to the talk page is found to be insufficient.
Note to administrators: this article has content on its talk page which should be checked before deletion. Administrators: check links, history (last), and logs before deletion. Consider checking Google.This page was last edited by MER-C (contribs | logs) at 20:31, 21 September 2018 (UTC) (2 seconds ago) |
This article contains content that is written like an advertisement .(September 2018) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
This article needs additional citations for verification .(September 2018) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
 | |
| Original author(s) | Alexander Ivanov |
|---|---|
| Developer(s) | Waves Platform |
| Initial release | 7 June 2016 |
| Stable release | 0.14.4 / 10 September 2018 |
| Repository | https://github.com/WAVESPLATFORM/ |
| Written in | Scala |
| Operating system | Full node available for Linux, Mac OSX & Microsoft Windows. Wallet available online and as a Chrome app. |
| Type | Cryptocurrency, Blockchain, Decentralized computing |
| License | Apache 2.0 |
| Website | https://wavesplatform.com |
Waves Platform is an open-source blockchain platform, which is designed for ease of use and mass adoption. Since its launch in 2016 [1] by Alexander (Sasha) Ivanov, Waves has been working to fulfill its vision of creating a truly unique blockchain product that will be an industry standard in providing the most versatile and straightforward tokenization tools for everyday use [2] .
The open-source model is a decentralized software development model that encourages open collaboration. A main principle of open-source software development is peer production, with products such as source code, blueprints, and documentation freely available to the public. The open-source movement in software began as a response to the limitations of proprietary code. The model is used for projects such as in open-source appropriate technology, and open-source drug discovery.
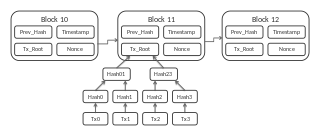
A blockchain, originally block chain, is a growing list of records, called blocks, which are linked using cryptography. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data.
Waves Platform allows users to launch their own cryptocurrency tokens. While other popular cryptocurrencies such as bitcoin and ethereum can be traded on external exchanges, and ethereum allows users to create new tokens on the platform using a smart contract, Waves includes this functionality in its core software and wallet. Users can create, transfer and exchange blockchain tokens on a peer-to-peer basis, paying transaction fees in the native WAVES token.

A cryptocurrency is a digital asset designed to work as a medium of exchange that uses strong cryptography to secure financial transactions, control the creation of additional units, and verify the transfer of assets. Cryptocurrencies use decentralized control as opposed to centralized digital currency and central banking systems.
A smart contract is a computer protocol intended to digitally facilitate, verify, or enforce the negotiation or performance of a contract. Smart contracts allow the performance of credible transactions without third parties. These transactions are trackable and irreversible.
The current Waves ecosystem provides all the necessary features for business adoption and consists of Waves Node, the technical kernel of the platform; Waves Client, available both in desktop and mobile versions; a multi-purpose Decentralized Exchange platform (DEX); and Waves Gateways.
Waves works on the principle of decentralization, so there is no exclusive operator for the platform. Control is distributed between full nodes (participants of network) which change in number and location. The WAVES token was originally distributed to users via an ICO.
Waves Platform has subsequently developed into one of the largest tech communities and formed partnerships with a variety of renowned international organizations, from Deloitte to Astana International Finance Centre.
The platform has a fixed supply of 100 million WAVES updated for proof-of-stake networks, called Waves-NG. Waves uses trusted gateways to issue blockchain tokens backed by fiat money and digital currencies for use on its own platform.
Waves was founded in 2016 by Alexander Ivanov, a Russian physicist, with development funded by a crowdsale held in April and May 2016. Waves’ community and development is international, with a wide range of initiatives built on the platform and based in different locations around the world.
