This article is being considered for deletion in accordance with Wikipedia's deletion policy. |
| Original author(s) | PACIFIC_SKYLINE, AMJUAREZ and others. |
|---|---|
| Initial release | 2014 |
| Written in | С++ |
| Platform | Windows, Mac, Linux, FreeBSD |
| Type | Payment system |
| Website | bytecoin.org |

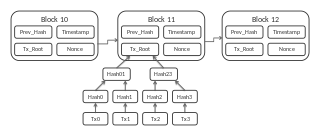
Bytecoin (ticker symbol BCN) is the first cryptocurrency based on the CryptoNote protocol with an open source code designed for anonymous cash settlement. [1]

A ticker symbol or stock symbol is an abbreviation used to uniquely identify publicly traded shares of a particular stock on a particular stock market. A stock symbol may consist of letters, numbers or a combination of both. "Ticker symbol" refers to the symbols that were printed on the ticker tape of a ticker tape machine.

A cryptocurrency is a digital asset designed to work as a medium of exchange that uses strong cryptography to secure financial transactions, control the creation of additional units, and verify the transfer of assets. Cryptocurrencies use decentralized control as opposed to centralized digital currency and central banking systems.
CryptoNote is an application layer protocol that aims to solve the problems outlined in Bitcoin Core, the protocol behind Bitcoin.. The protocol powers several decentralized privacy-oriented cryptocurrencies