Related Research Articles

Assistive technology (AT) is a term for assistive, adaptive, and rehabilitative devices for people with disabilities or the elderly population. People with disabilities often have difficulty performing activities of daily living (ADLs) independently, or even with assistance. ADLs are self-care activities that include toileting, mobility (ambulation), eating, bathing, dressing, grooming, and personal device care. Assistive technology can ameliorate the effects of disabilities that limit the ability to perform ADLs. Assistive technology promotes greater independence by enabling people to perform tasks they were formerly unable to accomplish, or had great difficulty accomplishing, by providing enhancements to, or changing methods of interacting with, the technology needed to accomplish such tasks. For example, wheelchairs provide independent mobility for those who cannot walk, while assistive eating devices can enable people who cannot feed themselves to do so. Due to assistive technology, people with disability have an opportunity of a more positive and easygoing lifestyle, with an increase in "social participation," "security and control," and a greater chance to "reduce institutional costs without significantly increasing household expenses."
Dynamic HTML, or DHTML, is a collection of technologies used together to create interactive and animated websites by using a combination of a static markup language, a client-side scripting language, a presentation definition language, and the Document Object Model (DOM). The application of DHTML was introduced by Microsoft with the release of Internet Explorer 4 in 1997.

Internet Explorer is a discontinued series of graphical web browsers developed by Microsoft and included in the Microsoft Windows line of operating systems, starting in 1995. It was first released as part of the add-on package Plus! for Windows 95 that year. Later versions were available as free downloads, or in-service packs, and included in the original equipment manufacturer (OEM) service releases of Windows 95 and later versions of Windows. New feature development for the browser was discontinued in 2016 in favor of new browser Microsoft Edge. Since Internet Explorer is a Windows component and is included in long-term lifecycle versions of Windows such as Windows Server 2019, it will continue to receive security updates until at least 2029. Microsoft 365 ended support for Internet Explorer on August 17, 2021, and Microsoft Teams ended support for IE on November 30, 2020. Internet Explorer will be discontinued on June 15, 2022, after which, the alternative will be Microsoft Edge with IE mode for legacy sites.

Lynx is a customizable text-based web browser for use on cursor-addressable character cell terminals. As of 2020, it is the oldest web browser still being maintained, having started in 1992.

The World Wide Web (WWW), commonly known as the Web, is an information system where documents and other web resources are identified by Uniform Resource Locators, which may be interlinked by hyperlinks, and are accessible over the Internet. The resources of the Web are transferred via the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), may be accessed by users by a software application called a web browser, and are published by a software application called a web server. The World Wide Web is not synonymous with the Internet, which pre-dated the Web in some form by over two decades and upon the technologies of which the Web is built.

A screen reader is a form of assistive technology (AT) that renders text and image content as speech or braille output. Screen readers are essential to people who are blind, and are useful to people who are visually impaired, illiterate, or have a learning disability. Screen readers are software applications that attempt to convey what people with normal eyesight see on a display to their users via non-visual means, like text-to-speech, sound icons, or a Braille device. They do this by applying a wide variety of techniques that include, for example, interacting with dedicated accessibility APIs, using various operating system features, and employing hooking techniques.

Maxthon is a freeware web browser developed by the company Maxthon Ltd., based in Beijing, China. It is available for Windows, macOS, Linux, and as Maxthon Mobile for Android, iOS, and Windows Phone 8. Since version 6 Maxthon is based on Chromium.
JAWS is a computer screen reader program for Microsoft Windows that allows blind and visually impaired users to read the screen either with a text-to-speech output or by a refreshable Braille display. JAWS is produced by the Blind and Low Vision Group of Freedom Scientific.

The following tables compare general and technical information for a number of web browsers.
Trident is a proprietary browser engine for the Microsoft Windows version of Internet Explorer, developed by Microsoft.
Internet Explorer for Mac OS X is a proprietary web browser developed by Microsoft for the Macintosh platform to browse web pages. Initial versions were developed from the same code base as Internet Explorer for Windows. Later versions diverged, particularly with the release of version 5, which included the cutting-edge, fault-tolerant and highly standards-compliant Tasman layout engine.
Web accessibility is the inclusive practice of ensuring there are no barriers that prevent interaction with, or access to, websites on the World Wide Web by people with physical disabilities, situational disabilities, and socio-economic restrictions on bandwidth and speed. When sites are correctly designed, developed and edited, more users have equal access to information and functionality.
Ajax is a set of web development techniques that uses various web technologies on the client-side to create asynchronous web applications. With Ajax, web applications can send and retrieve data from a server asynchronously without interfering with the display and behaviour of the existing page. By decoupling the data interchange layer from the presentation layer, Ajax allows web pages and, by extension, web applications, to change content dynamically without the need to reload the entire page. In practice, modern implementations commonly utilize JSON instead of XML.

Windows Internet Explorer 7 (IE7) is a web browser for Windows. It was released by Microsoft on October 18, 2006. Internet Explorer 7 is part of a long line of versions of Internet Explorer and was the first major update to the browser since 2001. It is the default browser in Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008 and Windows Embedded POSReady 2009 and can replace Internet Explorer 6 on Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 but unlike version 6, this version does not support Windows NT 4.0, Windows 98, Windows 98 SE, Windows 2000, and Windows Me. It also does not support Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 R2 or later Windows Versions.

A server-side dynamic web page is a web page whose construction is controlled by an application server processing server-side scripts. In server-side scripting, parameters determine how the assembly of every new web page proceeds, including the setting up of more client-side processing.
Web scraping, web harvesting, or web data extraction is data scraping used for extracting data from websites. The web scraping software may directly access the World Wide Web using the Hypertext Transfer Protocol or a web browser. While web scraping can be done manually by a software user, the term typically refers to automated processes implemented using a bot or web crawler. It is a form of copying in which specific data is gathered and copied from the web, typically into a central local database or spreadsheet, for later retrieval or analysis.

The Internet Channel is a version of the Opera 9 web browser for use on the Wii by Opera Software and Nintendo. Opera Software also implemented the Nintendo DS Browser for Nintendo's handheld system.
NonVisual Desktop Access (NVDA) is a free and open-source, portable screen reader for Microsoft Windows. The project was started by Michael Curran in 2006.
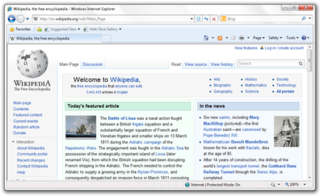
Windows Internet Explorer 8 (IE8) is a graphical web browser by Microsoft, the eighth version of Internet Explorer and the successor to Internet Explorer 7. It was released on March 19, 2009, and was the default browser for Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 operating systems. It was also made available for Windows XP, Windows Server 2003, Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008.
ThunderHawk is a discontinued web browser from Bitstream available for a full range of operating systems in high end and mass-market mobile phones and personal digital assistants. It is basically meant for mobile operators and original equipment manufacturers and not meant to download for normal users.
References
- ↑ "WebbIE Web Browser - browse the web using only text".
- ↑ Francabandera, Laura (2018). Making library websites accessible : a practical guide for librarians. Lanham, Maryland. p. 9. ISBN 9781538108239.
- ↑ Assistive technology : from virtuality to reality : AAATE 2005. Amsterdam: IOS Press. 2005. p. 640. ISBN 9781586035433.
- ↑ A. King, G. Evans and P. Blenkhorn, "WebbIE: a web browser for visually impaired people", in Proceedings of the 2nd Cambridge Workshop on Universal Access and Assistive Technology, S. Keates, P.J. Clarkson, P. Langdon and P. Robinson, Eds., London, UK: Springer-Verlag, 2004, pp. 35-44.
