
Mozilla Firefox, or simply Firefox, is a free and open-source web browser developed by the Mozilla Foundation and its subsidiary, the Mozilla Corporation. It uses the Gecko rendering engine to display web pages, which implements current and anticipated web standards. Firefox is available for Windows 10 or later versions, macOS, and Linux. Its unofficial ports are available for various Unix and Unix-like operating systems, including FreeBSD, OpenBSD, NetBSD, and other platforms. It is also available for Android and iOS. However, as with all other iOS web browsers, the iOS version uses the WebKit layout engine instead of Gecko due to platform requirements. An optimized version is also available on the Amazon Fire TV as one of the two main browsers available with Amazon's Silk Browser.
Vector Markup Language (VML) is an obsolete XML-based file format for two-dimensional vector graphics. It was specified in Part 4 of the Office Open XML standards ISO/IEC 29500 and ECMA-376. According to the specification, VML is a deprecated format included in Office Open XML for legacy reasons only.

A browser war is a competition for dominance in the usage share of web browsers. The "first browser war" (1995–2001) consisted of Internet Explorer and Netscape Navigator, and the "second browser war" (2004-2017) between Internet Explorer, Firefox, and Google Chrome.
Animated Portable Network Graphics (APNG) is a file format which extends the Portable Network Graphics (PNG) specification to permit animated images that work similarly to animated GIF files, while supporting 24 or 48-bit images and full alpha transparency not available for GIFs. It also retains backward compatibility with non-animated PNG files.
This is a comparison of both historical and current web browsers based on developer, engine, platform(s), releases, license, and cost.
Mozilla Firefox has features which distinguish it from other web browsers, such as Google Chrome, Safari, and Microsoft Edge.

Acid2 is a webpage that test web browsers' functionality in displaying aspects of HTML markup, CSS 2.1 styling, PNG images, and data URIs. The test page was released on 13 April 2005 by the Web Standards Project. The Acid2 test page will be displayed correctly in any application that follows the World Wide Web Consortium and Internet Engineering Task Force specifications for these technologies. These specifications are known as web standards because they describe how technologies used on the web are expected to function.
In computing, quirks mode is an approach used by web browsers to maintain backward compatibility with web pages designed for old web browsers, instead of strictly complying with web standards in standards mode. This behavior has since been codified, so what was previously standards mode is now referred to as simply no quirks mode.
An HTML Application (HTA) is a Microsoft Windows program whose source code consists of HTML, Dynamic HTML, and one or more scripting languages supported by Internet Explorer, such as VBScript or JScript. The HTML is used to generate the user interface, and the scripting language is used for the program logic. An HTA executes without the constraints of the internet browser security model; in fact, it executes as a "fully trusted" application.

Microsoft Silverlight is a discontinued application framework designed for writing and running rich internet applications, similar to Adobe's runtime, Adobe Flash. While early versions of Silverlight focused on streaming media, later versions supported multimedia, graphics, and animation, and gave support to developers for CLI languages and development tools. Silverlight was one of the two application development platforms for Windows Phone, but web pages using Silverlight did not run on the Windows Phone or Windows Mobile versions of Internet Explorer, as there was no Silverlight plugin for Internet Explorer on those platforms.
Windows Internet Explorer 8 (IE8) is a web browser for Windows. It was released by Microsoft on March 19, 2009.
In HTML, a file-select control is a component of a web form with which a user can select a local file. When the form is submitted, the file is uploaded to the web server. There, when the file arrives, some action usually takes place, such as saving the file on the web server. However, the particular action that takes place is determined by the server-side script to which the form is submitted.

The Acid3 test is a web test page from the Web Standards Project that checks a web browser's compliance with elements of various web standards, particularly the Document Object Model (DOM) and JavaScript.

Web development tools allow web developers to test, modify and debug their websites. They are different from website builders and integrated development environments (IDEs) in that they do not assist in the direct creation of a webpage, rather they are tools used for testing the user interface of a website or web application.

Internet Explorer 9 or IE9 is the ninth major version of the Internet Explorer web browser for Windows. It was released by Microsoft on March 14, 2011, as the successor to Internet Explorer 8. Microsoft released Internet Explorer 9 as a major out-of-band version that was not tied to the release schedule of any particular version of Windows, unlike previous versions. It is the first version of Internet Explorer not to be bundled with a Windows operating system, although some OEMs have installed it with Windows on their PCs. Internet Explorer 9 was the last version to be called Windows Internet Explorer. The software was rebranded simply as Internet Explorer starting with the release of Internet Explorer 10.

Web typography, like typography generally, is the design of pages – their layout and typeface choices. Unlike traditional print-based typography, pages intended for display on the World Wide Web have additional technical challenges and – given its ability to change the presentation dynamically – additional opportunities. Early web page designs were very simple due to technology limitations; modern designs use Cascading Style Sheets (CSS), JavaScript and other techniques to deliver the typographer's and the client's vision.
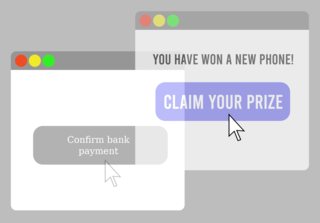
Clickjacking is a malicious technique of tricking a user into clicking on something different from what the user perceives, thus potentially revealing confidential information or allowing others to take control of their computer while clicking on seemingly innocuous objects, including web pages.

WebGL is a JavaScript API for rendering interactive 2D and 3D graphics within any compatible web browser without the use of plug-ins. WebGL is fully integrated with other web standards, allowing GPU-accelerated usage of physics, image processing, and effects in the HTML canvas. WebGL elements can be mixed with other HTML elements and composited with other parts of the page or page background.
HTML video is a subject of the HTML specification as the standard way of playing video via the web. Introduced in HTML5, it is designed to partially replace the object element and the previous de facto standard of using the proprietary Adobe Flash plugin, though early adoption was hampered by lack of agreement as to which video coding formats and audio coding formats should be supported in web browsers. As of 2020, HTML video is the only widely supported video playback technology in modern browsers, with the Flash plugin being phased out.
HTML audio is a subject of the HTML specification, incorporating audio input, playback, and synthesis, all in the browser.











