Related Research Articles

Lake Manyara is an lake located in Monduli District of Arusha Region, Tanzania and is the seventh-largest lake of Tanzania by surface area, at 470-square-kilometre (180 sq mi). It is a shallow, alkaline lake in the Natron-Manyara-Balangida branch of the East African Rift. The northwest quadrant of the lake is included within Lake Manyara National Park and it is part of the Lake Manyara Biosphere Reserve, established in 1981 by UNESCO as part of its Man and the Biosphere Programme.

The Inner Niger Delta, also known as the Macina or Masina, is the inland delta of the Niger River. It is an area of fluvial wetlands, lakes and floodplains in the semi-arid Sahel area of central Mali, just south of the Sahara desert.

The Oti River or Pendjari River is an international river in West Africa. It rises in Benin, forms the border between Benin and Burkina Faso, flows through Togo, and joins the Volta River in Ghana.

Lake Eyasi is a lake located in Karatu District of Arusha Region in north Tanzania. Lake Eyasi is the largest body of water in Arusha region. It is a seasonal shallow endorheic salt lake on the floor of the Great Rift Valley at the base of the Serengeti Plateau, just south of the Serengeti National Park and immediately southwest of the Ngorongoro Crater in the Crater Highlands of Tanzania. The lake is elongated, orientated southwest to northeast, and lies in the Eyasi-Wembere branch of the Great Rift Valley.

The Tarim Basin deciduous forests and steppe is a temperate broadleaf and mixed forests ecoregion in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region of western China. The ecoregion includes deciduous riparian forests and steppes sustained by the region's rivers in an otherwise arid region.
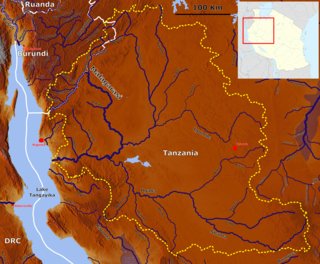
The Malagarasi River is a river in western Tanzania, flowing through Kigoma Region, although one of its tributaries comes from southeastern Burundi. The river also forms the western border of Tabora Region, the southern border of Kagera (region) and the southwestern border of Geita Region. It is the second-longest river in Tanzania behind the Rufiji—Great Ruaha, and has the largest watershed of any river flowing into Lake Tanganyika. The Malagarasi-Muyovozi Wetlands are a designated a Ramsar site. Local tribes have nicknamed the Malagarasi as "the river of bad spirits".

The Zambezian flooded grasslands is an ecoregion of southern and eastern Africa that is rich in wildlife.
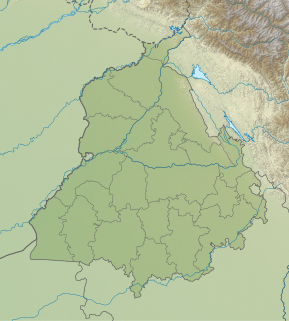
Kanjli Wetland is a man-made Wetland that subsumes the Kanjli Lake, and is located in the Kapurthala district of Punjab state in India. It was created in 1870 by constructing the headworks across the perennial Bien River, a tributary of the Beas River to provide irrigation facilities to the hinterland. The rich biodiversity of the wetland comprising aquatic, mesophytic and terrestrial flora and fauna including some important species of plants and animals was recognized internationally by the Ramsar Convention in 2002 by designating the Kanjli Lake in the List of Wetlands of International Importance. In this context, it is reported that the Punjab State which has 14 wetlands covering an area of 225.76 km2 has the unique position of three of its wetlands viz., the Kanjli Wetland covering an area of 490 ha of which the Kanjli Lake water spread is 184 ha), the Harike Wetland and the Ropar Wetland chosen by the Ministry of Environment and Forest (MoE&F), Government of India for their conservation and management are now also included in the Ramsar list covering a total area of 5650 ha; Kanjli is upstream of Harike wetland located in the Beas river basin while the Ropar wetland is in the Roopnagar district.

The Wami River is a river located in Pwani Region, Tanzania. The headwaters of the Wami and its tributaries originate in the Eastern Arc Mountains of Morogoro Region. The river then flows northeastward through of Pwani Region to empty into the Indian Ocean west of Zanzibar Island.
Classification of wetlands has been a problematical task, with the commonly accepted definition of what constitutes a wetland being among the major difficulties. A number of national wetland classifications exist. In the 1970s, the Ramsar Convention on Wetlands of International Importance introduced a first attempt to establish an internationally acceptable wetland classification scheme.
The Yaeda Valley, or Yaida Valley, is a swampy valley located in Mbulu District of Manyara Region, Tanzania. The Valley is situatated south of Lake Eyasi.

The Ulanga River, also known as the Kilombero River, rises in the highlands of the southwest of Morogoro Region, Tanzania, on the eastern slope of the East African Rift. The river flows northeast along the northeastern border of the Lindi Region before it flows into the Rufiji River. The Rufiji eventually flows into the Indian Ocean on the southern coast of the Pwani Region.

The Nyabarongo is a major river in Rwanda, part of the upper headwaters of the Nile. With a total length of 351 km (218 mi), it is the longest river entirely in Rwanda. It is extended 421 km (262 mi) in Lake Rweru including a 69 km (43 mi) upper course of Kagera River before joining into Ruvuvu River to form the Kagera River. The river begins its course at the confluence of the rivers Mbirurume and Mwogo in the South West of the country. These two rivers themselves begin in Nyungwe Forest, and are considered by some to be the most distant source of the Nile. From its start, Nyabarongo flows northward for 85 km, and forms the border between the Western and Southern Provinces. At the confluence with the river Mukungwa, the river changes course and flows eastward for 12 km, then to a more South Eastern course for the last 200 km. For the longest stretch of this course, the river serves as the boundary between the Northern and Southern Provinces, then between the City of Kigali and the Southern Province, and lastly between the City of Kigali and the Eastern Province.

The Southern Ewaso Ng'iro is a river in the Great Rift Valley in Kenya. It plays an important role in the ecology of Lake Natron, the main regular breeding site for near-threatened lesser flamingos. Changes to land use in the river's headwaters or in the marshes before the river enters the lake could have a serious impact on this species.

The Akanyaru River is the main tributary of the Nyabarongo River. It rises in the western highlands of Rwanda and Burundi, flows east and then north along the border between those countries before joining the Nyabarongo River. The lower stretches contain important but unprotected wetlands, which are under threat from human activity.

Voronina (Voroninsky) Nature Reserve is a strict ecological reserve located in the valley of the Vorona River, in the forest-steppe zone of southwest Russia. The Voroninsky Reserve protects riverine wetlands in the southeast of the Oka–Don Plain. The reserve is situated in Kirsanovsky and Inzhavinsky districts of Tambov Oblast, about 100 km southeast of the city of Tambov. It was created in 1994, and covers an area of 10,819 ha (41.77 sq mi).

Lower Sula National Nature Park is a national park of Ukraine that covers the lower reaches of the Sula River as it enters the Kremenchuk Reservoir, 120 km southeast of Kyiv. The extensive marshes, swamps, and other wetlands of the area are important habitats for fish, waterfowl, and floodplain plants. The park is administratively in the Hlobyne, Orzhytsia, and Semenivka raions of Poltava Oblast, and Zolotonosha Raion of Cherkasy Oblast.
The Southern Eastern Rift is a freshwater ecoregion in Kenya and Tanzania.
The Sango Bay forests are distinctive forests found in southwestern Uganda, near the border with Tanzania. The Sango Bay forests grow on seasonally-flooded lowlands near on the lower reaches of the Kagera River, just west of where it empties into Lake Victoria.
References
- ↑ Hughes, R. H. (1992). A Directory of African Wetlands. IUCN, 1992. pp. 253-254.
- ↑ BirdLife International (2019) Important Bird Areas factsheet: Wembere steppe. Downloaded from http://www.birdlife.org on 19/09/2019.
- ↑ Hughes, R. H. (20xx). A Directory of African Wetlands. IUCN, 1992. pp. 253-254.