
Tanzania comprises many lakes, national parks, and Africa's highest point, Mount Kilimanjaro. Northeast Tanzania is mountainous, while the central area is part of a large plateau covered in grasslands. The country also contains the southern portion of Lake Victoria on its northern border with Uganda and Kenya.

An endorheic basin is a drainage basin that normally retains water and allows no outflow to other external bodies of water, such as rivers or oceans, but drainage converges instead into lakes or swamps, permanent or seasonal, that equilibrate through evaporation. They are also called closed or terminal basins, internal drainage systems, or simply basins. Endorheic regions contrast with exorheic regions. Endorheic water bodies include some of the largest lakes in the world, such as the Caspian Sea, the world's largest inland body of water.

Lake Manyara is a lake located in Monduli District of Arusha Region, Tanzania and is the seventh-largest lake of Tanzania by surface area, at 470-square-kilometre (180 sq mi). It is a shallow, alkaline lake in the Natron-Manyara-Balangida branch of the East African Rift. The northwest quadrant of the lake is included within Lake Manyara National Park and it is part of the Lake Manyara Biosphere Reserve, established in 1981 by UNESCO as part of its Man and the Biosphere Programme.

The Ngorongoro Conservation Area is a protected area and a UNESCO World Heritage Site located in Ngorongoro District, 180 km (110 mi) west of Arusha City in Arusha Region, within the Crater Highlands geological area of northern Tanzania. The area is named after Ngorongoro Crater, a large volcanic caldera within the area. The conservation area is administered by the Ngorongoro Conservation Area Authority, an arm of the Tanzanian government, and its boundaries follow the boundary of the Ngorongoro District in Arusha Region. The western portion of the park abuts the Serengeti National Park, and the area comprising the two parks and Kenya's Maasai Mara game reserve is home to Great Migration, a massive annual migration of millions of wildebeest, zebras, gazelles, and other animals. The conservation area also contains Olduvai Gorge, one of the most important paleoanthropological sites in the world.

Arusha Region is one of Tanzania's 31 administrative regions and is located in the north of the country. The region's capital and largest city is the city of Arusha. The region is bordered by Kajiado County and Narok County in Kenya to the north, the Kilimanjaro Region to the east, the Manyara and Singida Regions to the south, and the Mara and Simiyu regions to the west. Arusha Region is home to Ngorongoro Conservation Area, a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The region is comparable in size to the combined land and water areas of the state of Maryland in the United States.

Karatu is one of the seven districts in the Arusha Region of Tanzania. The District covers an area of 6,993 km2 (2,700 sq mi). and has an max elevation of 1,739 m (5,705 ft)..It is bordered by the Ngorongoro District to the north, the Meatu District to the west in Simiyu Region. The Monduli District borders the district directly to the east and finally Mbulu District and Babati District border Karatu to the south and southeast. Karatu district is home to the famous Hadza people. Also Karatu is known agriculturally as the onion capital of Tanzania. "Red gold of Tanzania". Retrieved 2022-06-14. According to the 2012 census, the population of the district was 230,166.

Ngorongoro is one of the seven districts of the Arusha Region in Tanzania. The District covers an area of 14,036 km2 (5,419 sq mi). It is bordered to the north by Kenya, to the east by Monduli District, the northeast by Longido District, and to the south by the Karatu District. The western border is the Serengeti District in Mara Region. Ngorongoro District is home to the Ngorongoro Crater and was named after it. The administrative seat is the town of Loliondo. The district is home to the Ngorongoro Conservation Area which is a UNESCO World Heritage Site.

The Crater Highlands are a geological region along the East African Rift in the Arusha Region and parts of northern Manyara Region in north Tanzania.

The Iraqw People (; are the Cushitic-speaking ethnic group inhabiting the northern Tanzanian regions. They are a significant group in originating in southwestern Arusha and Manyara regions of Tanzania, near the Rift Valley. The Iraqw people settled in the southeast of Ngorongoro Crater in northern Karatu District, Arusha Region, where they remain the majority ethnic group. In Manyara region, the Iraqw are a major ethnic group in Mbulu District, Babati District and Hanang District.

The Hadza, or Hadzabe, are a Tanzanian indigenous ethnic group mostly based in southwest Karatu District of Arusha Region. They live around Lake Eyasi in the central Rift Valley and in the neighboring Serengeti Plateau. There are, as of 2015, between 1,200 and 1,300 Hadza people living in Tanzania, however only around 400 Hadza still survive exclusively based on the traditional means of foraging. Additionally, the increasing impact of tourism and encroaching pastoralists pose serious threats to the continuation of their traditional way of life.

Gelai Volcano also known as Mount Gelai stands at 2,942 metres (9,652 ft) tall and is located in Ngorongoro District, Arusha Region, Tanzania in the Crater Highlands. It is at the southeastern edge of Lake Natron in the East African Rift. Gelai is the third most prominent peak in Arusha Region and is the 13th highest peak in Arusha region. Volcanic activity on Gelai dates to less than one million years ago. A number of earthquakes occurred in the area in the summer of 2007. Associated with the largest earthquake on 17 July a NNE-oriented fracture or narrow graben formed on the southern flank of Gelai. The fracture may be associated with the intrusion of a narrow dike at a depth of around 4,000 metres (13,000 ft).
Mto wa Mbu is an administrative ward and town in the Monduli district of the Arusha Region of Tanzania. According to the 2012 census, the ward had a total population of 11,405. The name Mto wa Mbu means " The river of Mosquitoes " in the Swahili Language.
The Yaeda Valley, or Yaida Valley, is a swampy valley located in Mbulu District of Manyara Region, Tanzania. The Valley is situated south of Lake Eyasi.

Tanzania contains some 20 percent of the species of Africa's large mammal population, found across its reserves, conservation areas, marine parks, and 17 national parks, spread over an area of more than 42,000 square kilometres (16,000 sq mi) and forming approximately 38 percent of the country's territory. Wildlife resources of Tanzania are described as "without parallel in Africa" and "the prime game viewing country". Serengeti National Park, the country's second largest national park area at 14,763 square kilometres (5,700 sq mi), is located in northern Tanzania and is famous for its extensive migratory herds of wildebeests and zebra while also having the reputation as one of the great natural wonders of the world. The Ngorongoro Conservation Area, established in 1959, is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and inhabited by the Maasai people. Its Ngorongoro Crater is the largest intact caldera in the world.
The Wembere River is a river located in north western Singida Region, Tanzania. The river is part of the water basin of Lake Eyasi.

The Southern Ewaso Ng'iro is a river in the Great Rift Valley in Kenya. It plays an important role in the ecology of Lake Natron, the main regular breeding site for near-threatened lesser flamingos. Changes to land use in the river's headwaters or in the marshes before the river enters the lake could have a serious impact on this species.

The Mbulu Highlands is a plateau in north-central Tanzania.
The Simiyu River is a river located in Simiyu Region and Arusha Region, Tanzania. It flows into Lake Victoria in the African Great Lakes region. As one of the six main inlets to Lake Victoria, it forms part of the upper headwaters of the Nile. The Simiyu Region is named after the river.
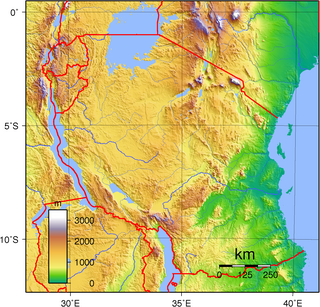
Mainland Tanzania refers to the part of Tanzania on the continent of Africa; excluding the islands of Zanzibar. It corresponds with the area of the former country of Tanganyika.
The Southern Eastern Rift is a freshwater ecoregion in Kenya and Tanzania.
















