
A microlith is a small stone tool usually made of flint or chert and typically a centimetre or so in length and half a centimetre wide. They were made by humans from around 35,000 years ago, across Europe, Africa, Asia and Australia. The microliths were used in spear points and arrowheads.

The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic, also called the Old Stone Age, is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone tools, and which represents almost the entire period of human prehistoric technology. It extends from the earliest known use of stone tools by hominins, c. 3.3 million years ago, to the end of the Pleistocene, c. 11,650 cal BP.

The Stone Age was a broad prehistoric period during which stone was widely used to make stone tools with an edge, a point, or a percussion surface. The period lasted for roughly 3.4 million years and ended between 4000 BC and 2000 BC, with the advent of metalworking. It therefore represents nearly 99.3% of human history. Though some simple metalworking of malleable metals, particularly the use of gold and copper for purposes of ornamentation, was known in the Stone Age, it is the melting and smelting of copper that marks the end of the Stone Age. In Western Asia, this occurred by about 3000 BC, when bronze became widespread. The term Bronze Age is used to describe the period that followed the Stone Age, as well as to describe cultures that had developed techniques and technologies for working copper alloys into tools, supplanting stone in many uses.
Stone tools have been used throughout human history but are most closely associated with prehistoric cultures and in particular those of the Stone Age. Stone tools may be made of either ground stone or knapped stone, the latter fashioned by a craftsman called a flintknapper. Stone has been used to make a wide variety of tools throughout history, including arrowheads, spearheads, hand axes, and querns. Knapped stone tools are nearly ubiquitous in pre-metal-using societies because they are easily manufactured, the tool stone raw material is usually plentiful, and they are easy to transport and sharpen.

The Oldowan was a widespread stone tool archaeological industry (style) in prehistory. These early tools were simple, usually made by chipping one, or a few, flakes off a stone using another stone. Oldowan tools were used during the Lower Paleolithic period, 2.9 million years ago up until at least 1.7 million years ago (Ma), by ancient Hominins across much of Africa. This technological industry was followed by the more sophisticated Acheulean industry.

Behavioral modernity is a suite of behavioral and cognitive traits believed to distinguish current Homo sapiens from other anatomically modern humans, hominins, and primates. Most scholars agree that modern human behavior can be characterized by abstract thinking, planning depth, symbolic behavior, music and dance, exploitation of large game, and blade technology, among others.
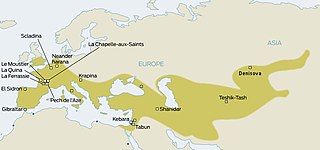
The Mousterian is an archaeological industry of stone tools, associated primarily with the Neanderthals in Europe, and to the earliest anatomically modern humans in North Africa and West Asia. The Mousterian largely defines the latter part of the Middle Paleolithic, the middle of the West Eurasian Old Stone Age. It lasted roughly from 160,000 to 40,000 BP. If its predecessor, known as Levallois or Levallois-Mousterian, is included, the range is extended to as early as c. 300,000–200,000 BP. The main following period is the Aurignacian of Homo sapiens.

The Lower Paleolithic is the earliest subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. It spans the time from around 3.3 million years ago when the first evidence for stone tool production and use by hominins appears in the current archaeological record, until around 300,000 years ago, spanning the Oldowan and Acheulean lithics industries.

The Levallois technique is a name given by archaeologists to a distinctive type of stone knapping developed around 250,000 to 400,000 years ago during the Middle Palaeolithic period. It is part of the Mousterian stone tool industry, and was used by the Neanderthals in Europe and by modern humans in other regions such as the Levant.

The Kebaran culture, also known as the 'Early Near East Epipalaeolithic', is an archaeological culture of the Eastern Mediterranean dating to c. 23,000 to 15,000 Before Present (BP). Its type site is Kebara Cave, south of Haifa. The Kebaran was produced by a highly mobile nomadic population, composed of hunters and gatherers in the Levant and Sinai areas who used microlithic tools.

Blombos Cave is an archaeological site located in Blombos Private Nature Reserve, about 300 km east of Cape Town on the Southern Cape coastline, South Africa. The cave contains Middle Stone Age (MSA) deposits currently dated at between c. 100,000 and 70,000 years Before Present (BP), and a Late Stone Age sequence dated at between 2000 and 300 years BP. The cave site was first excavated in 1991 and field work has been conducted there on a regular basis since 1997, and is ongoing.

The Tsodilo Hills are a UNESCO World Heritage Site (WHS), consisting of rock art, rock shelters, depressions, and caves in Botswana, Southern Africa. It gained its WHS listing in 2001 because of its unique religious and spiritual significance to local peoples, as well as its unique record of human settlement over many millennia. UNESCO estimates there are over 4500 rock paintings at the site. The site consists of a few main hills known as the Child Hill, Female Hill, and Male Hill.

The Middle Stone Age was a period of African prehistory between the Early Stone Age and the Late Stone Age. It is generally considered to have begun around 280,000 years ago and ended around 50–25,000 years ago. The beginnings of particular MSA stone tools have their origins as far back as 550–500,000 years ago and as such some researchers consider this to be the beginnings of the MSA. The MSA is often mistakenly understood to be synonymous with the Middle Paleolithic of Europe, especially due to their roughly contemporaneous time span; however, the Middle Paleolithic of Europe represents an entirely different hominin population, Homo neanderthalensis, than the MSA of Africa, which did not have Neanderthal populations. Additionally, current archaeological research in Africa has yielded much evidence to suggest that modern human behavior and cognition was beginning to develop much earlier in Africa during the MSA than it was in Europe during the Middle Paleolithic. The MSA is associated with both anatomically modern humans as well as archaic Homo sapiens, sometimes referred to as Homo helmei. Early physical evidence comes from the Gademotta Formation in Ethiopia, the Kapthurin Formation in Kenya and Kathu Pan in South Africa.
Mumba Cave, located near the highly alkaline Lake Eyasi in Karatu District, Arusha Region, Tanzania. The cave is a rich archaeological site noted for deposits spanning the transition between the Middle Stone Age and Late Stone Age in Eastern Africa. The transitional nature of the site has been attributed to the large presence of its large assemblage of ostrich eggshell beads and more importantly, the abundance of microlith technology. Because these type artifacts were found within the site it has led archaeologists to believe that the site could provide insight into the origins of modern human behavior. The cave was originally tested by Ludwig Kohl-Larsen and his wife Margit in their 1934 to 1936 expedition. They found abundant artifacts, rock art, and burials. However, only brief descriptions of these findings were ever published. That being said, work of the Kohl-Larsens has been seen as very accomplished due to their attention to detail, especially when one considers that neither was versed in proper archaeological techniques at the time of excavation. The site has since been reexamined in an effort to reanalyze and complement the work that has already been done, but the ramifications of improper excavations of the past are still being felt today, specifically in the unreliable collection of C-14 data and confusing stratigraphy.
Enkapune Ya Muto, also known as Twilight Cave, is a site spanning the late Middle Stone Age to the Late Stone Age on the Mau Escarpment of Kenya. This time span has allowed for further study of the transition from the Middle Stone Age to the Late Stone Age. In particular, the changes in lithic and pottery industries can be tracked over these time periods as well as transitions from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle to a herding lifestyle. Beads made of perforated ostrich egg shells found at the site have been dated to 40,000 years ago. The beads found at the site represent the early human use of personal ornaments. Inferences pertaining to climate and environment changes during the pre-Holocene and Holocene period have been made based from faunal remains based in this site.

Border Cave is an archaeological site located in the western Lebombo Mountains in Kwazulu-Natal. The rock shelter has one of the longest archaeological records in southern Africa, which spans from the Middle Stone Age to the Iron Age.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to prehistoric technology.

Taforalt, or Grotte des Pigeons, is a cave in the province of Berkane, Aït Iznasen region, Morocco, possibly the oldest cemetery in North Africa. It contained at least 34 Iberomaurusian adolescent and adult human skeletons, as well as younger ones, from the Upper Palaeolithic between 15,100 and 14,000 calendar years ago. There is archaeological evidence for Iberomaurusian occupation at the site between 23,200 and 12,600 calendar years ago, as well as evidence for Aterian occupation as old as 85,000 years.

The Levantine Aurignacian is an Upper Paleolithic culture of the Near-Eastern Levant that evolved from the Emiran culture. It was named so because of the similarity of stone tools with the Aurignacian culture in Europe. The Levantine Aurignacian used to be called Lower and Upper Antelian in old sources, from the site of Wadi Antelias in Lebanon. The most important innovation in this period is the incorporation of some typical elements of Aurignacian, like some types of burins and narrow blade points that resemble the European type of Font-Yves.
Rose Cottage Cave (RCC) is an archaeological site in the Free State, South Africa, situated only a few kilometers away from Ladybrand, close to the Caledon River, on the northern slopes of the Platberg. RCC is an important site because of its long cultural sequence, its roots in modern human behavior, and the movement of early modern humans out of Africa. Rose Cottage is the only site from the Middle Stone Age that can tell us about the behavioral variability of hunter-gatherers during the Late Pleistocene and Holocene. Berry D. Malan excavated the site between 1943 and 1946, shortly followed by Peter B. Beaumont in the early 1960s, and the most recent excavations occurred from 1987 to 1997 by Lyn Wadley and Philip Harper in 1989 under Wadley's supervision. Humans have inhabited Rose Cottage for over 100,000 years throughout the Middle and Later Stone Ages. Site formation and sediment formation processes at Rose Cottage appear to be primarily anthropogenic. Archaeological research focuses primarily on blade technology and tool forms from the Middle Stone Age and the implications of modern human behavior. Structurally, the cave measures more than 6 meters deep and about 20 by 10 meters. A boulder encloses the front, protecting the cave, but allowing a small opening for a skylight and narrow entrances on both the east and west sides.

















