
Hermel is a town in Baalbek-Hermel Governorate, Lebanon. It is the capital of Hermel District. Hermel is home to a Lebanese Red Cross First Aid Center. Hermel's inhabitants are predominantly Shia Muslims.

Qaa, El Qaa, Al Qaa, Qaa Baalbek or Masharih al-Qaa is a town in Baalbek-Hermel Governorate, Lebanon. A 2010 report stated that population of the settlement was 500, all Lebanese Maronites

Joub Jannine is located in the Beqaa Valley in Lebanon.

Rashaya, Rachaya, Rashaiya, Rashayya or Rachaiya, also known as Rashaya al-Wadi or Rachaya el-Wadi, is a town of the Rashaya District in the west of the Beqaa Government of Lebanon. It is situated at around 1,200 metres (3,900 ft) above sea level on the western slopes of Mount Hermon, south east of Beirut near the Syrian border, and approximately halfway between Jezzine and Damascus.

Aadloun, Adloun or Adlun is a coastal town in South Lebanon, 17 kilometres (11 mi) south of Sidon famous for its cultivation of watermelons. It is also the site of a Phoenician necropolis and prehistoric caves where four archaeological sites have been discovered and dated to the Stone Age. The evidence of human occupation of Abri Zumoffen has been dated as far back as 71,000 BCE with occupation of Bezez Cave dating back even further into the earlier Middle Paleolithic.

Majdal Anjar is a village of Beqaa Governorate, Lebanon. Majdal Anjar is an overwhelmingly Sunni Muslim town.

Sin el-Fil is a suburb east of Beirut in the Matn District of the Mount Lebanon Governorate, Lebanon.

Kaukaba, Kaukabet El-Arab or Kaukaba Station is a village in the Hasbaya District in the Nabatiye Governorate in southern Lebanon.

Archaeology of Lebanon includes thousands of years of history ranging from Lower Palaeolithic, Phoenician, Roman, Arab, Ottoman, and Crusades periods.
The Nachcharini cave is located at a height of 2,100 m (6,889.76 ft) on the Nachcharini Plateau in the Anti-Lebanon Mountains near the Lebanese/Syrian border and among the most elevated Natufian and Khiamian hunter-gatherer occupation sites found to date.
Aammiq is a village in the Western Beqaa District in Lebanon. It is also the name of an archaeological site.
The Sands of Beirut were a series of archaeological sites located on the coastline south of Beirut in Lebanon.

Qaraoun is a Lebanese village, 85 km from Beirut, known for its Lake Qaraoun in the Beqaa Valley formed by the El Wauroun Dam built in 1959. It is an ecologically fragile zone in the Western Beqaa District. The village lies about 800 m above sea level. The dam is located nearby on the Litani River.
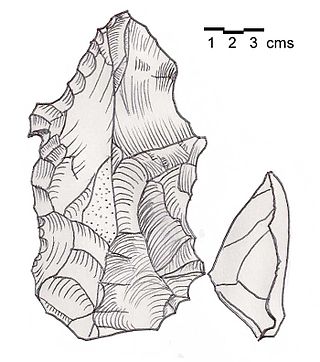
Heavy Neolithic is a style of large stone and flint tools associated primarily with the Qaraoun culture in the Beqaa Valley, Lebanon, dating to the Epipaleolithic or early Pre-Pottery Neolithic at the end of the Stone Age. The type site for the Qaraoun culture is Qaraoun II.

Shepherd Neolithic is a name given by archaeologists to a style of small flint tools from the Hermel plains in the north Beqaa Valley, Lebanon. The Shepherd Neolithic industry has been insufficiently studied and was provisionally named based on a limited typology collected by Jesuit archaeologist "Père" Henri Fleisch. Lorraine Copeland and Peter J. Wescombe suggested it was possibly "of quite late date".
Antelias Cave was a large cave located 2.5 km (1.6 mi) east of Antelias, 10 km (6.2 mi) northeast of Beirut close to the wadi of Ksar Akil.

The Qaraoun culture is a culture of the Lebanese Stone Age around Qaraoun in the Beqaa Valley. The Gigantolithic or Heavy Neolithic flint tool industry of this culture was recognized as a particular Neolithic variant of the Lebanese highlands by Henri Fleisch, who collected over one hundred flint tools within two hours on 2 September 1954 from the site. Fleisch discussed the discoveries with Alfred Rust and Dorothy Garrod, who confirmed the culture to have Neolithic elements. Garrod said that the Qaraoun culture "in the absence of all stratigraphical evidence may be regarded as mesolithic or proto-neolithic"..
Kfar Tebnit or Kfar Tibnit is a village located approximately 4 kilometres (2.5 mi) south southeast of Nabatieh, 37 kilometres (23 mi) southeast of Sidon in Lebanon.
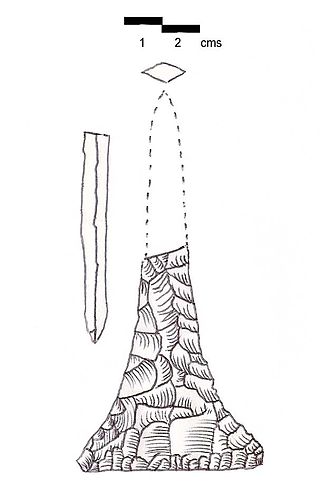
Douwara is a Heavy Neolithic archaeological site of the Qaraoun culture located 2 kilometres (1.2 mi) southwest of Ain Ebel in the Bint Jbeil District of Nabatieh Governorate in Lebanon. It is located on slopes north of the road from Ain Ebel to Rmaich.

Maqne or Maakne is a town and municipality in Baalbek District, Baalbek-Hermel Governorate, Lebanon.













