
The Sudd is a vast swamp in South Sudan, formed by the White Nile's Baḥr al-Jabal section. The Arabic word sudd is derived from sadd, meaning "barrier" or "obstruction". The term "the sudd" has come to refer to any large solid floating vegetation island or mat. The area which the swamp covers is one of the world's largest wetlands and the largest freshwater wetland in the Nile Basin.
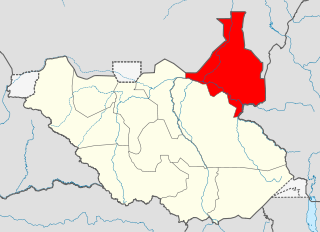
Upper Nile is a state in South Sudan. The White Nile flowes through the state, giving it its name. The state also shares a similar name with the region of Greater Upper Nile, of which it was part along with the states of Unity and Jonglei. It had an area of 77,823 square kilometres (30,048 sq mi). Malakal was the capital of the state. The towns of Upper Nile State Benythieng Akoka, Melut, Renk, Kodok, the location of the Fashoda Incident that ended the "Scramble for Africa", was located in the state. Upper Nile seceded from Sudan as part of the Republic of South Sudan on 9 July 2011.

Jonglei State is a state of South Sudan with Bor as its centre of government and the biggest city. Jonglei state comprises nine counties: Bor, Akobo, Ayod, Uror, Duk, Nyirol, Pigi, Twic East, and Fangak. Jonglei State is the largest state by area before reorganisation, with an area of approximately 122,581 km2, as well as the most populous according to the 2008 census conducted in present-day South Sudan's second period of autonomy. The boundaries of the state were again changed as a result of a peace agreement signed on 22 February 2020.
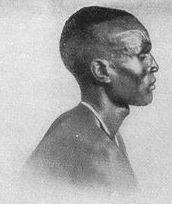
The Dinka people are a Nilotic ethnic group native to South Sudan. The Dinka mostly live along the Nile, from Mangalla-Jonglei to Renk, in the region of Bahr el Ghazal, Upper Nile, and the Abyei Area of the Ngok Dinka in South Sudan.

Bor is a historic city in the Bor County of Jonglei State, in the Greater Upper Nile region of South Sudan, being the epicenter of national liberation revolution with multiple landmarks that tells the story. In Malual-Chaat barrack, statues of liberators and destroyed weapons are conserved and exhibited at historical heritage site. It has also served as the headquarters of Jonglei state. The city is situated on the east side of the White Nile at the southern extent of the sudd, South Sudan's vast central wetlands.

The Bahr el Zeraf (Arabic: بَـحْـر الـزّرَاف, romanized: Baḥr ez-Zerāf, also known as the Giraffe or Phow River in the English language, is an arm of the White Nile in the Sudd region of South Sudan. It is completely contained within the South Sudanese state of Jonglei. Its name is Arabic for "Giraffe River".
Sudanese nomadic conflicts are non-state conflicts between rival nomadic tribes taking place in the territory of Sudan and, since 2011, South Sudan. Conflict between nomadic tribes in Sudan is common, with fights breaking out over scarce resources, including grazing land, cattle and drinking water. Some of the tribes involved in these clashes have been the Messiria, Maalia, Rizeigat and Bani Hussein Arabic tribes inhabiting Darfur and West Kordofan, and the Dinka, Nuer and Murle African ethnic groups inhabiting South Sudan. Conflicts have been fueled by other major wars taking place in the same regions, in particular the Second Sudanese Civil War, the War in Darfur and the Sudanese conflict in South Kordofan and Blue Nile.

The Jonglei Canal was a canal project started, but never completed, to divert water from the vast Sudd wetlands of South Sudan so as to deliver more water downstream to Sudan and Egypt for use in agriculture. Sir William Garstin proposed the idea of the canal in 1907; the government of Egypt conducted a study in 1946; and plans took shape between 1954 and 1959 during the period of decolonization which included Sudanese independence in 1956. Against the context of Sudan's postcolonial civil conflict, the Sudan People's Liberation Army (SPLA), led by John Garang, halted construction of the canal in 1984.

Twic East County, or simply Twic East, is a county located in Jonglei State, South Sudan. Its headquarters were located at Panyagor. In May 2016, Twic East County was divided into Twic North County, Kongor County, Twic Center County, and Twic South County.
Lith Payam, also known as Jieng Lith Payam, is a Dinka community located in Jonglei State in South Sudan. Lith Payam borders on Kongor Payam, Pibor County, Duk County, and the White Nile. Lith Payam headquarters is located at Wernyol City.

The Greater Upper Nile is a region of northeastern South Sudan. It is named for the White Nile, a tributary of the Nile River in North and East Africa.

South Sudan is home to around 60 indigenous ethnic groups and 80 linguistic partitions among a 2021 population of around 11 million. Historically, most ethnic groups were lacking in formal Western political institutions, with land held by the community and elders acting as problem solvers and adjudicators. Today, most ethnic groups still embrace a cattle culture in which livestock is the main measure of wealth and used for bride wealth.
The Kongkong River, also spelled Kong Kong, is a stream in the South Sudanese state of Jonglei, west of Boma National Park near the Ethiopian border. At the village of Bongak it joins the Abara River to form the Agwei or Agvey River, a tributary of the Pibor River. The Kongkong is within the drainage basin of the White Nile.

Terekeka County is an administrative division of Central Equatoria in South Sudan. It is the capital of surrounding Mundari and Boma counties. It lies on both the east and west bank of the White Nile north of Juba The word "Terekeka" is a combination of two words; "Tirgigi", a kind of hard shrub and "Terere" an open hard ground usually found in the middle of shrub trees. The local referral of "Terere i Tirgigi lukata" became shortened and distorted to create the current name, "Terekeka".

Fangak County is an administrative area of Jonglei State in the Greater Upper Nile region of South Sudan, with headquarters in the town of Phom el Zaraf.
Fangak is a community in the Fangak County of Jonglei State, in the Greater Upper Nile region of South Sudan. The capital is Old Fangak. It was once a British garrison town. The administration buildings were destroyed during the civil war.
Ethnic violence in South Sudan has a long history among South Sudan's varied ethnic groups. South Sudan has 64 tribes with the largest being the Dinka, who constitute about 35% of the population and predominate in government. The second largest are the Nuers. Conflict is often aggravated among nomadic groups over the issue of cattle and grazing land and is part of the wider Sudanese nomadic conflicts.
The South Sudan Democratic Movement (SSDM), sometimes called the South Sudan Democratic Movement/Army (SSDM/A), was a South Sudanese militant group. Along with its armed wing, the South Sudan Defence Army (SSDA), rebelled against the government of South Sudan led by President Salva Kiir Mayardit and the Sudan People's Liberation Movement.

The Nuer White Army, sometimes decapitalised as the "white army", is a semi-official name for a militant organisation formed by the Nuer people of central and eastern Greater Upper Nile in modern-day South Sudan as early as 1991. According to the Small Arms Survey, it arose from the 1991 schism within the Sudan People's Liberation Movement/Army (SPLM/A) for the dual purpose of defending Nuer cattle herds from neighbouring groups and fighting in the Second Sudanese Civil War between the SPLM/A and the Sudanese government.














