The Integrated Marine and Coastal Regionalisation of Australia (IMCRA), formerly the Interim Marine and Coastal Regionalisation for Australia, is a biogeographic regionalisation of the oceanic waters of Australia's exclusive economic zone (EEZ). As of 2008, the most recent version is IMCRA Version 4.0.

The Bass Strait Shelf Province is a biogeographic region of Australia's coastal and continental shelf waters. It covers the central Bass Strait between Tasmania and the southern Australian mainland. It is a provincial level bioregion in the Integrated Marine and Coastal Regionalisation of Australia (IMCRA) system. The Bassian and adjacent Tasmanian Shelf provinces correspond to the Bassian marine ecoregion in the WWF's Marine Ecoregions of the World system.

The Central Eastern Shelf Province is a biogeographic region of Australia's coastal and continental shelf waters. It includes the warm temperate coastal waters of eastern Australia. It is a provincial level bioregion in the Integrated Marine and Coastal Regionalisation of Australia (IMCRA) system. It corresponds to the Manning-Hawkesbury marine ecoregion in the WWF's Marine Ecoregions of the World system.

Tweed–Moreton, also known as the Central Eastern Shelf Transition, is a marine biogeographic region of eastern Australia.
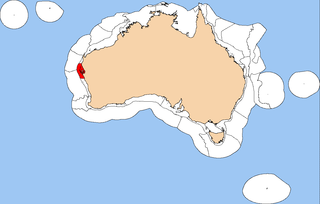
The Central Western Shelf Province, also known as the Shark Bay marine ecoregion, is a biogeographic region of Australia's continental shelf and coastal waters. It includes the subtropical coastal waters of Western Australia.

The Northeast Shelf Province is a biogeographic region of Australia's coastal and continental shelf waters. It includes the tropical coastal waters of the central and southern Great Barrier Reef in northeastern Australia. It is a provincial level bioregion in the Integrated Marine and Coastal Regionalisation of Australia (IMCRA) system. It corresponds to the Central and Southern Great Barrier Reef marine ecoregion in the WWF's Marine Ecoregions of the World system.
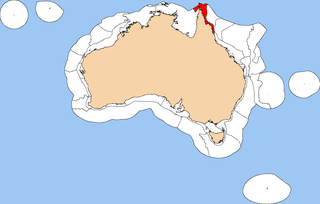
The Northeast Shelf Transition is a biogeographic region of Australia's coastal and continental shelf waters. It includes the tropical coastal waters of the northern Great Barrier Reef and the Torres Strait in northeastern-most Australia. It is a provincial level bioregion in the Integrated Marine and Coastal Regionalisation of Australia (IMCRA) system. It corresponds to the Torres Strait and Northern Great Barrier Reef marine ecoregion in the WWF's Marine Ecoregions of the World system.

The Northern Shelf Province, also known as Arnhem Coast to Gulf of Carpentaria, is a biogeographic region of Australia's continental shelf. It includes the coastal waters of Arnhem Land and the Gulf of Carpentaria in Northern Australia.

The Northwest Shelf Province, also known as Exmouth to Broome, is a biogeographic region of Australia's continental shelf.

The Northwest Shelf Transition, also known as Bonaparte Coast, is a biogeographic region of Australia's continental shelf. It adjoins the Kimberley region of Western Australia and the adjacent coast of the Northern Territory.

The Southeast Shelf Transition is a biogeographic region of Australia's coastal and continental shelf waters. It covers a portion of Australia's southeastern coast, from southern New South Wales to eastern Victoria, including the islands of the Kent Group and Furneaux Group at the eastern end of the Bass Strait. It is a provincial level bioregion in the Integrated Marine and Coastal Regionalisation of Australia (IMCRA) system, and is a transitional region between the warm temperate Central Eastern Shelf Province to the northwest and the cool temperate Bass Strait Shelf and Tasmanian Shelf provinces to the west and south. It corresponds to the Cape Howe marine ecoregion in the WWF's Marine Ecoregions of the World system.
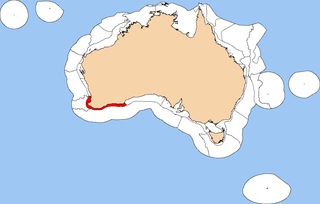
The Southwest Shelf Province, also known as the Leeuwin marine ecoregion, is a biogeographic region of Australia's continental shelf. It includes the temperate coastal waters of Southwest Australia.

The Southwest Shelf Transition, also known as the Houtman marine ecoregion, is a biogeographic region of Australia's continental shelf and coastal waters. It includes the subtropical coastal waters of Southwest Australia.
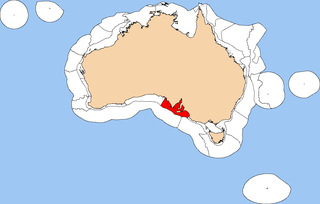
The Spencer Gulf Shelf Province, also known as the South Australian Gulfs marine ecoregion, is a biogeographic region of Australia's continental shelf and coastal waters. It includes the warm temperate coastal waters of South Australia's central coast. It is a provincial bioregion in the Integrated Marine and Coastal Regionalisation of Australia (IMCRA) system.

The Tasmanian Shelf Province is a biogeographic region of Tasmania's coastal and continental shelf waters. It covers the western, eastern, and southern coasts of Tasmania. It is a provincial level bioregion in the Integrated Marine and Coastal Regionalisation of Australia (IMCRA) system. The Tasmanian Shelf and adjacent Bass Strait Shelf provinces correspond to the Bassian marine ecoregion in the WWF's Marine Ecoregions of the World system.

The Western Indo-Pacific is a biogeographic region of the Earth's seas, comprising the tropical waters of the eastern and central Indian Ocean. It is part of the larger Indo-Pacific, which includes the tropical Indian Ocean, the western and central Pacific Ocean, and the seas connecting the two in the general area of Indonesia. The Western Indo-Pacific may be classified as a marine realm, one of the great biogeographic divisions of the world's ocean basins, or as a subrealm of the Indo-Pacific.

Temperate Australasia is a biogeographic region of the Earth's seas, comprising the temperate and subtropical waters of Australia and New Zealand, including both the Indian Ocean and Pacific coasts of the continent and adjacent islands.

The Bassian ecoregon is a biogeographic region of Australia's coastal and continental shelf waters. It includes the cold-temperate waters surrounding Tasmania, including the central Bass Strait between Tasmania and the southern Australian mainland. This ecoregion, designated in the Marine Ecoregions of the World system by the World Wildlife Fund (WWF), includes both the Bass Strait Shelf and Tasmanian Shelf provincial level bioregions from the Integrated Marine and Coastal Regionalisation of Australia (IMCRA) system.
















