Related Research Articles

St. Simons Island is a barrier island and census-designated place (CDP) located on St. Simons Island in Glynn County, Georgia, United States. The names of the community and the island are interchangeable, known simply as "St. Simons Island" or "SSI", or locally as "The Island". St. Simons is part of the Brunswick metropolitan statistical area, and according to the 2020 U.S. census, the CDP had a population of 14,982. Located on the southeast Georgia coast, midway between Savannah and Jacksonville, St. Simons Island is both a seaside resort and residential community. It is the largest of Georgia's renowned Golden Isles. Visitors are drawn to the Island for its warm climate, beaches, variety of outdoor activities, shops and restaurants, historical sites, and natural environment.

Hoodoo is a set of spiritual practices, traditions, and beliefs that were created by enslaved African Americans in the Southern United States from various traditional African spiritualities, Christianity and elements of indigenous botanical knowledge. Practitioners of Hoodoo are called rootworkers, conjure doctors, conjure man or conjure woman, root doctors, Hoodoo doctors, and swampers. Regional synonyms for Hoodoo include conjure or rootwork. As a syncretic spiritual system, it also incorporates Islam brought over by enslaved West African Muslims and Spiritualism. Scholars define Hoodoo as a folk religion. Folk religions are syncretic traditions between two or more cultural religions, in this case African indigenous spirituality and Abrahamic religion.

Prospect Bluff Historic Sites is located in Franklin County, Florida, on the Apalachicola River, 6 miles (9.7 km) SW of Sumatra, Florida. The site contains the ruins of two forts.

Sapelo Island is a state-protected barrier island located in McIntosh County, Georgia. The island is accessible only by boat; the primary ferry comes from the Sapelo Island Visitors Center in McIntosh County, Georgia, a seven-mile (11 km), twenty-minute trip. It is the site of Hog Hammock, the last known Gullah community. It is illegal to visit the island without a permit issued by state tourism authorities.

Susie King Taylor is known for being the first Black nurse during the American Civil War. Beyond just her aptitude in nursing the wounded of the 1st South Carolina Volunteer Infantry Regiment, Taylor was the first Black woman to self-publish her memoirs. She was the author of Reminiscences of My Life in Camp with the 33rd United States Colored Troops, Late 1st S.C. Volunteers. She was also an educator to formerly bonded Black people in the postbellum South by opening various schools in Georgia. Taylor would also be a part of organizing the 67 Corps of the Women's Relief Corps in 1886.
Drums and Shadows is a book by Mary Granger published in 1940. The book is an account of oral folklore collected in Georgia from African Americans, namely the Gullah people of the Sea Islands, many of whom had been slaves.

Special Field Orders, No. 15 were military orders issued during the American Civil War, on January 16, 1865, by General William Tecumseh Sherman, commander of the Military Division of the Mississippi of the United States Army. They provided for the confiscation of 400,000 acres (1,600 km2) of land along the Atlantic coast of South Carolina, Georgia, and Florida and the dividing of it into parcels of not more than 40 acres (0.16 km2), on which were to be settled approximately 18,000 formerly enslaved families and other black people then living in the area.
Thomas Spalding was a United States representative from Georgia. He was born in Frederica, Georgia, St. Simons Island, Glynn County, Georgia. He studied law and was admitted to the bar in 1795, but did not practice. He engaged extensively in agricultural pursuits.
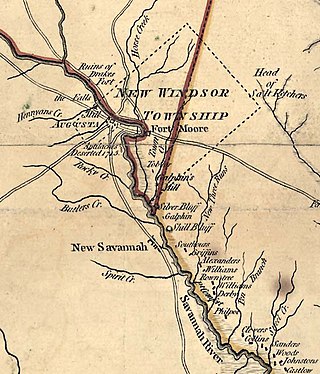
Savannah Town, South Carolina is a defunct settlement that was located in the colonial years on the Savannah River below the Fall Line in present-day Aiken County. In the 1670s the Westo had a village here, but they were displaced by the Savannah in a trade war, and it became known by 1685 as Savannah Town. The English colony had traders who did a lucrative business in dressed skins with the Savannah Shawnee. Fortified as a frontier post, the settlement developed and ferry service was established across the river. The town was gradually overtaken by its competitor of Augusta, Georgia, established in 1735 five miles upriver and closer to Indian settlements. Traders here intercepted commerce, sending it to their port of Savannah on the coast. By 1740 Savannah Town was declining, and by 1765 the village was abandoned and the fort closed.
George Liele was an African American and emancipated slave who became the founding pastor of First Bryan Baptist Church and First African Baptist Church, in Savannah, Georgia (USA). He later would become a missionary to Jamaica.

First African Baptist Church, located in Savannah, Georgia, claims to be derived from the first black Baptist congregation in North America. While it was not officially organized until 1788, it grew from members who founded a congregation in 1773. Its claim of "first" is contested by the Silver Bluff Baptist Church, Aiken County, South Carolina (1773), and the First Baptist Church of Petersburg, Virginia, whose congregation officially organized in 1774.

David George was an African-American Baptist preacher and a Black Loyalist from the American South who escaped to British lines in Savannah, Georgia; later he accepted transport to Nova Scotia and land there. He eventually resettled in Freetown, Sierra Leone where he would eventually die. With other slaves, George founded the Silver Bluff Baptist Church in South Carolina in 1775, the first black congregation in the present-day United States. He was later affiliated with the First African Baptist Church of Savannah, Georgia. After migration, he founded Baptist congregations in Nova Scotia and Freetown, Sierra Leone. George wrote an account of his life that is one of the most important early slave narratives.

The Silver Bluff Baptist Church was founded between 1774-1775 in Beech Island, South Carolina, by several enslaved African Americans who organized under elder David George.

Negro Fort was a short-lived fortification built by the British in 1814, during the War of 1812, in a remote part of what was at the time Spanish Florida. It was intended to support a never-realized British attack on the U.S. via its southwest border, by means of which they could "free all these Southern Countries [states] from the Yoke of the Americans."

Igbo Landing is a historic site at Dunbar Creek on St. Simons Island, Glynn County, Georgia. It was the setting of a mass suicide in 1803 by captive Igbo people who had taken control of their slave ship and refused to submit to slavery in the United States. The event's moral value as a story of resistance towards slavery has symbolic importance in African American folklore as the flying Africans legend, and in literary history.
The following is a timeline of the history of Savannah, Georgia, United States.

Hog Hammock is an African-American community on Sapelo Island, a barrier island of the U.S. state of Georgia.
James Cooper, a.k.a. "Stick Daddy," was one of several African American artisans associated with the cane carving tradition in coastal Georgia during the early twentieth century. Ethnographers and art historians have seen this tradition as evidence of the persistence of African visual and cultural motifs into North America and modern period.
Garrison Frazier was an African-American Baptist minister and public figure during the U.S. Civil War. He acted as spokesman for twenty African-American Baptist and Methodist ministers who met on January 12, 1865 with Major General William Tecumseh Sherman, of the Union Army's Military Division of the Mississippi, and with U.S. Secretary of War Edwin Stanton, at General Sherman's headquarters in Savannah, Georgia. This meeting is commonly known as the "Savannah Colloquy" or the "Forty acres and a mule" meeting.
Alexander Harris (1818–1909) was an African-American deacon, trustee, interim pastor of the First Bryan Baptist Church and one of the most powerful African-American religious and civil leaders in Savannah, Georgia during the end of the 19th century and beginning of the 20th century.
References
- 1 2 U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: White Bluff, Georgia
- 1 2 Drums and Shadows: Survival Studies Among the Georgia Coastal Negroes (1940; 1986 reprint: ISBN 0-8203-0851-X) by the Federal Writers' Project of the WPA
- ↑ Lee, F. D.; Agnew, J. L. (1869). Historical Record of the City of Savannah. J.H. Estill. pp. 199–200 – via Google Books.