
Pedinellales is a group of single-celled algae found in both marine environments and freshwater.

The glaucophytes, also known as glaucocystophytes or glaucocystids, are a small group of freshwater unicellular algae, less common today than they were during the Proterozoic. Only 15 species have been described, but more species are likely to exist. Together with the red algae (Rhodophyta) and the green algae plus land plants, they form the Archaeplastida. However, the relationships among the red algae, green algae and glaucophytes are unclear, in large part due to limited study of the glaucophytes.

Eustigmatophytes are a small group of eukaryotic algae that includes marine, freshwater and soil-living species.

The Trebouxiophyceae are a class of green algae, in the division Chlorophyta. Their circumscription within the green algae is not well established due to the need for more genetic studies at higher levels within the group.

Bryopsidales is an order of green algae, in the class Ulvophyceae.

Botryococcus is a genus of green algae. The cells form an irregularly shaped aggregate. Thin filaments connect the cells. The cell body is ovoid, 6 to 10 μm long, and 3 to 6 μm wide. Fossils of the genus are known since Precambrian times, and form the single largest biological contributor to crude oil, and are a major component of oil shales.

Chaetomorpha is a genus of green algae in the family Cladophoraceae. Members of this genus may be referred to by the common name sea emerald.
Acicularia is a genus of green algae in the family Dasycladaceae.
Phaeothamniophyceae is a class of heterokonts. It contains two orders, Phaeothamniales and Aurearenales, and consists of species separated from Chrysophyceae.
Pyrenomonas is a genus of cryptomonad.
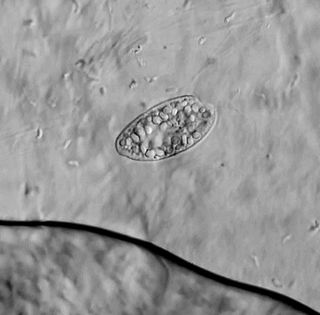
Chilomonas is a genus of cryptophytes, including the species Chilomonas paramecium. Chilomonas is a protozoa (heterotroph). Chilomonas is golden brown and has two flagella.

Oxyrrhis is a genus of dinoflagellates. It includes the species Oxyrrhis marina.
Nemoderma is the only genus in the family Nemodermataceae and order Nemodermatales of the brown algae. The genus contains only a single species, Nemoderma tingitanum.

Bodonida is an order of kinetoplastid flagellate excavates. It contains the genera Bodo and Rhynchomonas, relatives to the parasitic trypanosomes. This order also contains the colonial genus Cephalothamnium.

Vaucheria is a genus of Xanthophyceae or yellow-green algae. It is one of only two genera in the family Vaucheriaceae. The type species of the genus is Vaucheria disperma.

Erythrotrichia is a red algae genus in the family Erythrotrichiaceae.
Perkinsidae is a family of alveolates in the phylum Perkinsozoa, a sister group to the dinoflagellates.

Trinacria is an extinct genus of diatoms present during the early Eocene, named for its triskelion shape.
Chrysomerophyceae is a monotypic class of photosynthetic heterokont eukaryotes.
Synchromophyceae is a class of photosynthetic heterokonts. The chloroplast of the Synchromophyceae are surrounded by two membranes and arranged in a way where they share the outer pair of membranes. The entire chloroplast complex is surrounded by an additional two outer membranes.












