Related Research Articles
ISO 8601Data elements and interchange formats – Information interchange – Representation of dates and times is an international standard covering the exchange of date- and time-related data. It is maintained by the Geneva-based International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and was first published in 1988 with updates in 1991, 2000, 2004 and 2019. The purpose of this standard is to provide an unambiguous and well-defined method of representing dates and times, so as to avoid misinterpretation of numeric representations of dates and times, particularly when data is transferred between countries with different conventions for writing numeric dates and times.

Microsoft Office, or simply Office, is a family of client software, server software, and services developed by Microsoft. It was first announced by Bill Gates on August 1, 1988, at COMDEX in Las Vegas. Initially a marketing term for an office suite, the first version of Office contained Microsoft Word, Microsoft Excel, and Microsoft PowerPoint. Over the years, Office applications have grown substantially closer with shared features such as a common spell checker, OLE data integration and Visual Basic for Applications scripting language. Microsoft also positions Office as a development platform for line-of-business software under the Office Business Applications brand. On July 10, 2012, Softpedia reported that Office was being used by over a billion people worldwide.

Project Gutenberg (PG) is a volunteer effort to digitize and archive cultural works, as well as to "encourage the creation and distribution of eBooks." It was founded in 1971 by American writer Michael S. Hart and is the oldest digital library. Most of the items in its collection are the full texts of books in the public domain. The Project tries to make these as free as possible, in long-lasting, open formats that can be used on almost any computer. As of 20 May 2020, Project Gutenberg had reached 62,108 items in its collection of free eBooks.
Portable Document Format (PDF), standardized as ISO 32000, is a file format developed by Adobe in 1993 to present documents, including text formatting and images, in a manner independent of application software, hardware, and operating systems. Based on the PostScript language, each PDF file encapsulates a complete description of a fixed-layout flat document, including the text, fonts, vector graphics, raster images and other information needed to display it.
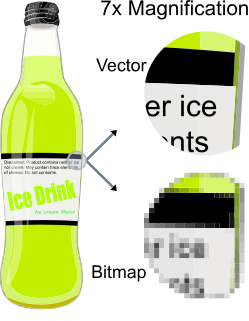
Vector graphics are computer graphics images that are defined in terms of points on a Cartesian plane, which are connected by lines and curves to form polygons and other shapes. Vector graphics have the unique advantage over raster graphics in that the points, lines, and curves may be scaled up or down to any resolution with no aliasing. The points determine the direction of the vector path; each path may have various properties including values for stroke color, shape, curve, thickness, and fill.
ZIP is an archive file format that supports lossless data compression. A ZIP file may contain one or more files or directories that may have been compressed. The ZIP file format permits a number of compression algorithms, though DEFLATE is the most common. This format was originally created in 1989 and was first implemented in PKWARE, Inc.'s PKZIP utility, as a replacement for the previous ARC compression format by Thom Henderson. The ZIP format was then quickly supported by many software utilities other than PKZIP. Microsoft has included built-in ZIP support in versions of Microsoft Windows since 1998. Apple has included built-in ZIP support in Mac OS X 10.3 and later. Most free operating systems have built in support for ZIP in similar manners to Windows and Mac OS X.

Exchangeable image file format is a standard that specifies the formats for images, sound, and ancillary tags used by digital cameras, scanners and other systems handling image and sound files recorded by digital cameras. The specification uses the following existing file formats with the addition of specific metadata tags: JPEG discrete cosine transform (DCT) for compressed image files, TIFF Rev. 6.0 for uncompressed image files, and RIFF WAV for audio files. It is not used in JPEG 2000 or GIF.

An album is a collection of audio recordings issued as a collection on compact disc (CD), vinyl, audio tape, or another medium. Albums of recorded sound were developed in the early 20th century as individual 78-rpm records collected in a bound book resembling a photograph album; this format evolved after 1948 into single vinyl LP records played at 33+1⁄3 rpm.
The Open Document Format for Office Applications (ODF), also known as OpenDocument, is a ZIP-compressed XML-based file format for spreadsheets, charts, presentations and word processing documents. It was developed with the aim of providing an open, XML-based file format specification for office applications. It is also the default format for documents in typical Linux distributions.
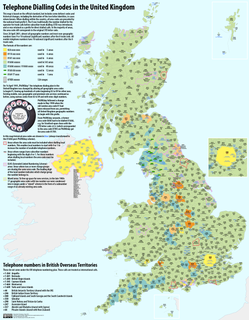
Telephone numbers in the United Kingdom are administered by the UK government's Office of Communications (Ofcom). For this purpose, Ofcom established a telephone numbering plan, known as the National Telephone Numbering Plan, which is the system for assigning telephone numbers to subscriber stations.

1080p is a set of HDTV high-definition video modes characterized by 1,920 pixels displayed across the screen horizontally and 1,080 pixels down the screen vertically; the p stands for progressive scan, i.e. non-interlaced. The term usually assumes a widescreen aspect ratio of 16:9, implying a resolution of 2.1 megapixels. It is often marketed as Full HD or FHD, to contrast 1080p with 720p resolution screens. Although 1080p is sometimes informally referred to as 2K, these terms reflect two distinct technical standards, with differences including resolution and aspect ratio.
GMS is water modeling application for building and simulating groundwater models from Aquaveo. It features 2D and 3D geostatistics, stratigraphic modeling and a unique conceptual model approach. Currently supported models include MODFLOW, MODPATH, MT3DMS, RT3D, FEMWATER, SEEP2D, and UTEXAS.
The following is a comparison of e-book formats used to create and publish e-books.
SMS is a complete program for building and simulating surface water models from Aquaveo. It features 1D and 2D modeling and a unique conceptual model approach. Currently supported models include ADCIRC, CMS-FLOW2D, FESWMS, TABS, TUFLOW, BOUSS-2D, CGWAVE, STWAVE, CMS-WAVE (WABED), GENESIS, PTM, and WAM.
CGNS stands for CFD General Notation System. It is a general, portable, and extensible standard for the storage and retrieval of CFD analysis data. It consists of a collection of conventions, and free and open software implementing those conventions. It is self-descriptive, cross-platform also termed platform or machine independent, documented, and administered by an international steering committee. It is also an American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics (AIAA) recommended practice. The CGNS project originated in 1994 as a joint effort between Boeing and NASA, and has since grown to include many other contributing organizations worldwide. In 1999, control of CGNS was completely transferred to a public forum known as the CGNS Steering Committee. This Committee is made up of international representatives from government and private industry.
XMDF is a library providing a standard format for the geometric data storage of river cross-sections, 2D/3D structured and unstructured meshes, geometric paths through space, and associated time data. XMDF uses HDF5 for cross-platform data storage and compression. It was initiated in Engineer Research and Development Center (ERDC) and is developed by Aquaveo . API includes interfaces for C/C++ and Fortran.
NetCDF is a set of software libraries and self-describing, machine-independent data formats that support the creation, access, and sharing of array-oriented scientific data. The project homepage is hosted by the Unidata program at the University Corporation for Atmospheric Research (UCAR). They are also the chief source of netCDF software, standards development, updates, etc. The format is an open standard. NetCDF Classic and 64-bit Offset Format are an international standard of the Open Geospatial Consortium.

EPUB is an e-book file format that uses the ".epub" file extension. The term is short for electronic publication and is sometimes styled ePub. EPUB is supported by many e-readers, and compatible software is available for most smartphones, tablets, and computers. EPUB is a technical standard published by the International Digital Publishing Forum (IDPF). It became an official standard of the IDPF in September 2007, superseding the older Open eBook standard.
An electronic book, also known as an e-book or eBook, is a book publication made available in digital form, consisting of text, images, or both, readable on the flat-panel display of computers or other electronic devices. Although sometimes defined as "an electronic version of a printed book", some e-books exist without a printed equivalent. E-books can be read on dedicated e-reader devices, but also on any computer device that features a controllable viewing screen, including desktop computers, laptops, tablets and smartphones.
Aquaveo is a modeling software company based in Provo, Utah that develops software used to model and simulate groundwater, watershed, and surface water resources. Its main software products include SMS, GMS, WMS, and Arc Hydro Groundwater.
References
- ↑ "シャープが、様々な要望を基にしたXMDF". Nikkei Business Publications. Archived from the original on January 5, 2012. Retrieved 2012-03-13.
