A file viewer is a software application that represents the data stored in a computer file in a human-readable form. The file contents are formatted in a meaningful way, then displayed on the screen, printed out, or read aloud using speech synthesis.

Portable Document Format (PDF), standardized as ISO 32000, is a file format developed by Adobe in 1992 to present documents, including text formatting and images, in a manner independent of application software, hardware, and operating systems. Based on the PostScript language, each PDF file encapsulates a complete description of a fixed-layout flat document, including the text, fonts, vector graphics, raster images and other information needed to display it. PDF has its roots in "The Camelot Project" initiated by Adobe co-founder John Warnock in 1991.
Web design encompasses many different skills and disciplines in the production and maintenance of websites. The different areas of web design include web graphic design; user interface design ; authoring, including standardised code and proprietary software; user experience design ; and search engine optimization. Often many individuals will work in teams covering different aspects of the design process, although some designers will cover them all. The term "web design" is normally used to describe the design process relating to the front-end design of a website including writing markup. Web design partially overlaps web engineering in the broader scope of web development. Web designers are expected to have an awareness of usability and be up to date with web accessibility guidelines.

Interleaf, Inc., was a company that created computer software products for the technical publishing creation and distribution process. Founded in 1981, its initial product was the first commercial document processor that integrated text and graphics editing, producing WYSIWYG output at near-typeset quality. It also had early products in the document management, electronic publishing, and Web publishing spaces. Interleaf's "Active Documents" functionality, integrated into its text and graphics editing products in the early 1990s, was the first to give document creators programmatic access to virtually all of the document's elements, structures, and software capabilities.
Desktop publishing (DTP) is the creation of documents using page layout software on a personal ("desktop") computer. It was first used almost exclusively for print publications, but now it also assists in the creation of various forms of online content. Desktop publishing software can generate layouts and produce typographic-quality text and images comparable to traditional typography and printing. Desktop publishing is also the main reference for digital typography. This technology allows individuals, businesses, and other organizations to self-publish a wide variety of content, from menus to magazines to books, without the expense of commercial printing.

QuarkXPress is desktop publishing software for creating and editing complex page layouts in a WYSIWYG environment. It runs on macOS and Windows. It was first released by Quark, Inc. in 1987 and is still owned and published by them.

Adobe InDesign is a desktop publishing and page layout designing software application produced by Adobe Inc. and first released in 1999. It can be used to create works such as posters, flyers, brochures, magazines, newspapers, presentations, books and ebooks. InDesign can also publish content suitable for tablet devices in conjunction with Adobe Digital Publishing Suite. Graphic designers and production artists are the principal users.
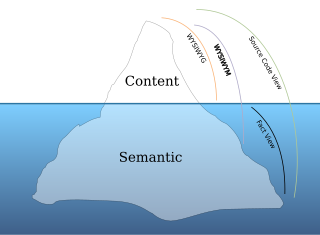
In computing, What You See Is What You Mean is a paradigm for editing a structured document. It is an adjunct to the better-known WYSIWYG paradigm, which displays the result of a formatted document as it will appear on screen or in print—without showing the descriptive code underneath.
XSL-FO is a markup language for XML document formatting that is most often used to generate PDF files. XSL-FO is part of XSL, a set of W3C technologies designed for the transformation and formatting of XML data. The other parts of XSL are XSLT and XPath. Version 1.1 of XSL-FO was published in 2006.
Windows Presentation Foundation (WPF) is a free and open-source graphical subsystem originally developed by Microsoft for rendering user interfaces in Windows-based applications. WPF, previously known as "Avalon", was initially released as part of .NET Framework 3.0 in 2006. WPF uses DirectX and attempts to provide a consistent programming model for building applications. It separates the user interface from business logic, and resembles similar XML-oriented object models, such as those implemented in XUL and SVG.
The Extensible Metadata Platform (XMP) is an ISO standard, originally created by Adobe Systems Inc., for the creation, processing and interchange of standardized and custom metadata for digital documents and data sets.

In graphic design, page layout is the arrangement of visual elements on a page. It generally involves organizational principles of composition to achieve specific communication objectives.
Open XML Paper Specification is an open specification for a page description language and a fixed-document format. Microsoft developed it as the XML Paper Specification (XPS). In June 2009, Ecma International adopted it as international standard ECMA-388.
Document Content Architecture, or DCA for short, is a standard developed by IBM for text documents in the early 1980s. DCA was used on mainframe and IBM i systems, and formed the basis of DisplayWrite's file format. DCA was later extended as MO:DCA, which added embedded data files.
The following is a comparison of e-book formats used to create and publish e-books.
Microsoft Office shared tools are software components that are included in all Microsoft Office products.




